Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2006; 12(6): 885-895
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885
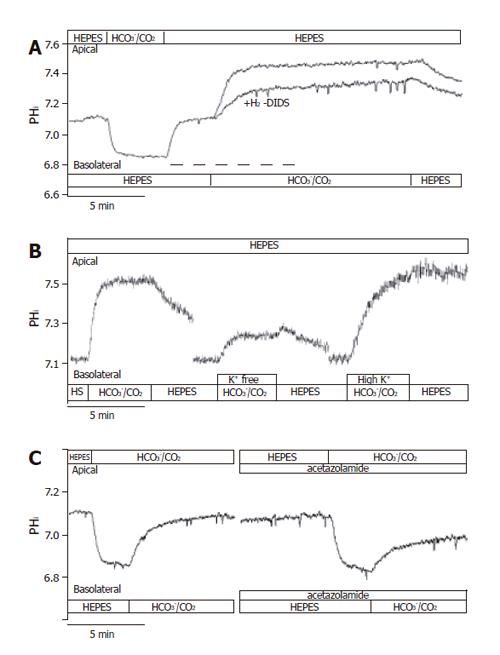
Figure 5 Basolateral HCO3– uptake – effects of H2-DIDS, acetazolamide and varying extracellular K+ concentration.
The figure shows representative pHi traces. A: The anion transport inhibitor 600 µmol/L H2-DIDS (added to the basolateral membrane of cells for 2 min before and during the administration of basolateral HCO3–/CO2, dashed line, n=6) significantly decreased the extent of alkalinization (∆pHi) and rate of J(B) (n=6); B: Varying extracellular [K+] caused significant differences in ∆pHi and J(B) (n=9–11); C: The application of the membrane-permeable carbonic anhydrase inhibitor acetazolamide (100 µmol/L, n = 6) significantly decreased the overall ∆pHi and J(B). HS: HEPES.
- Citation: Jr ZR, Fearn A, Hegyi P, Boros I, Gray MA, Argent BE. Characterization of H+ and HCO3- transporters in CFPAC-1 human pancreatic duct cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(6): 885-895
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i6/885.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885