Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2006; 12(30): 4836-4842
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4836
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4836
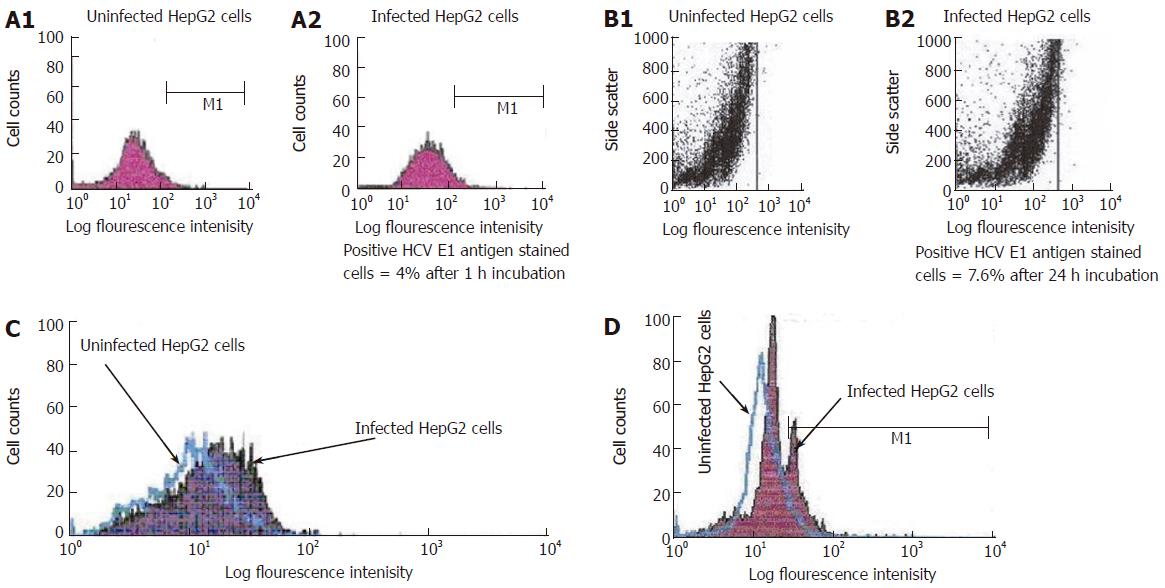
Figure 4 A: Single parameter histogram for flow cytometric analysis of surface staining of HCV E1 gene expression on the infected HepG2 cells after one hour incubation.
HepG2 cells were incubated with PBS (A1) (uninfected) or with HCV positive serum (A2) (infected) for 1 h incubation. Cells were harvested and stained with FITIC labeled HCV anti-E1 antibody as described in materials and methods; B: Dot histogram for flow cytometric analysis of surface staining of HCV E1 gene expression on the infected HepG2 cells after 24 h incubation. HepG2 cells were incubated with PBS (B1) (uninfected) or with HCV positive serum (B2) (infected) for 24 h incubation. Cells were harvested and stained with FITIC labeled HCV anti-E1 antibody; C: Overlap histogram for flow cytometric analysis of surface staining of HCV E1 gene expression on the infected HepG2 cells after one week incubation. HepG2 cells were incubated with PBS (uninfected) or with HCV positive serum (infected) for one week incubation. Cells were harvested and stained with FITIC labeled HCV anti-E1 antibody; D: Overlap histogram for flow cytometric analysis of intracellular staining of HCV core gene expression in the infected HepG2 cells after 3 d incubation. HepG2 cells were incubated with PBS (uninfected) or with HCV positive serum (infected) for 3 d incubation. Cells were harvested and stained with FITIC labeled HCV anti-core antibody Labeled cells were analyzed with flow cytometry (FACS Calibure, Becton Dickinson).
- Citation: El-Awady MK, Tabll AA, El-Abd YS, Bahgat MM, Shoeb HA, Youssef SS, Din NGBE, Redwan ERM, El-Demellawy M, Omran MH, El-Garf WT, Goueli SA. HepG2 cells support viral replication and gene expression of hepatitis C virus genotype 4 in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(30): 4836-4842
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i30/4836.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4836