Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2005; 11(38): 5966-5972
Published online Oct 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5966
Published online Oct 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5966
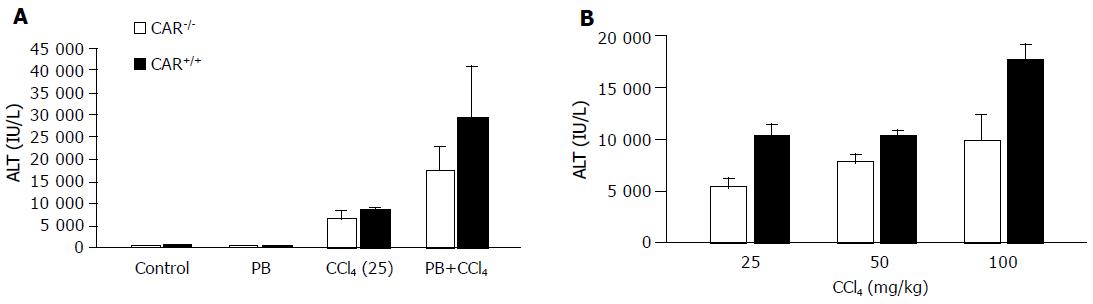
Figure 1 (A) PB pretreatment induced CCl4 toxicity.
CAR+/+ or CAR–/– mice were administered a 25-mg/kg dose of CCl4 by intraperitoneal injection with or without PB pretreatment (n=6 per treatment group). Serum was collected and ALT levels were measured after 24 h. The ALT level was slightly higher in CAR+/+ mice than in CAR–/– mice with CCl4 treatment (P<0.001). The difference in ALT levels became clearer between CAR+/+ and CAR–/– mice with pre-treatment by PB (P<0.001). (B) Dose dependency of CCl4 toxicity. CAR+/+ and CAR–/– mice were given 25-, 50-, or 100-mg/kg doses of CCl4. Blood samples were collected 24 h later, and serum ALT levels were measured (n=4). CAR–/– animals were significantly less sensitive than CAR+/+ mice to CCl4 toxicity (P<0.001). Data are mean±SD.
- Citation: Yamazaki Y, Kakizaki S, Horiguchi N, Takagi H, Mori M, Negishi M. Role of nuclear receptor CAR in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(38): 5966-5972
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i38/5966.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5966