Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2005; 11(11): 1610-1615
Published online Mar 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i11.1610
Published online Mar 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i11.1610
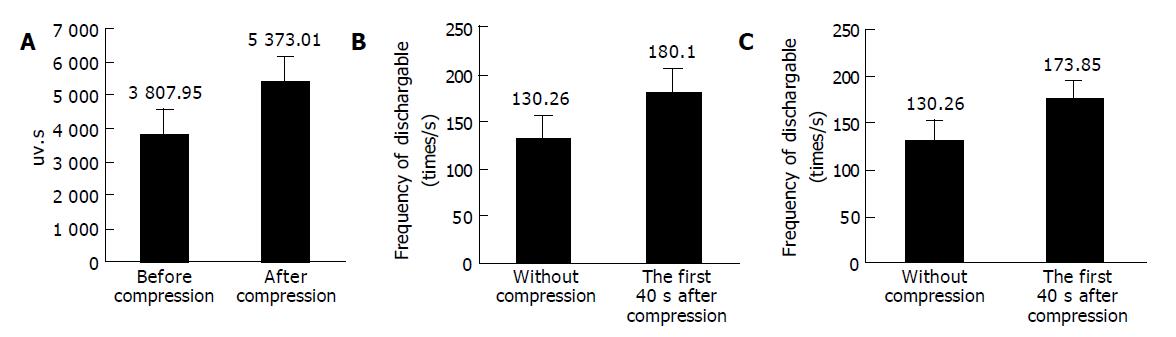
Figure 5 Comparison of electric discharge of vagus nerve.
A: The comparison of the electric discharge of vagus nerve through analyzing the absolute value of an area of wave form before and after the compression (from 4 to 40 s under the intracranial hypertension), and the neural discharge of vagus nerve had increased after intracranial hypertension, n = 20, P<0.05; B: The comparison of the electric discharge of vagus nerve before and during the first 4 s after the rabbit’s lateral ventricle compression. We analyzed the electric discharge frequency of the dischargeable wave in each time segment by setting a single liminal value line, and the neural discharge of vagus nerve had increased after intracranial hypertension; C: The comparison of the electric discharge of vagus nerve before the compression and during continuous compression (from 4 to 40 s). We analyzed the electric discharge frequency of the dischargeable wave in each time segment by setting a single liminal value line, and the neural discharge of vagus nerve had increased after intracranial hypertension.
- Citation: Jin XL, Zheng Y, Shen HM, Jing WL, Zhang ZQ, Huang JZ, Tan QL. Analysis of the mechanisms of rabbit’s brainstem hemorrhage complicated with irritable changes in the alvine mucous membrane. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(11): 1610-1615
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i11/1610.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i11.1610