Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2022; 28(14): 1430-1443
Published online Apr 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1430
Published online Apr 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1430
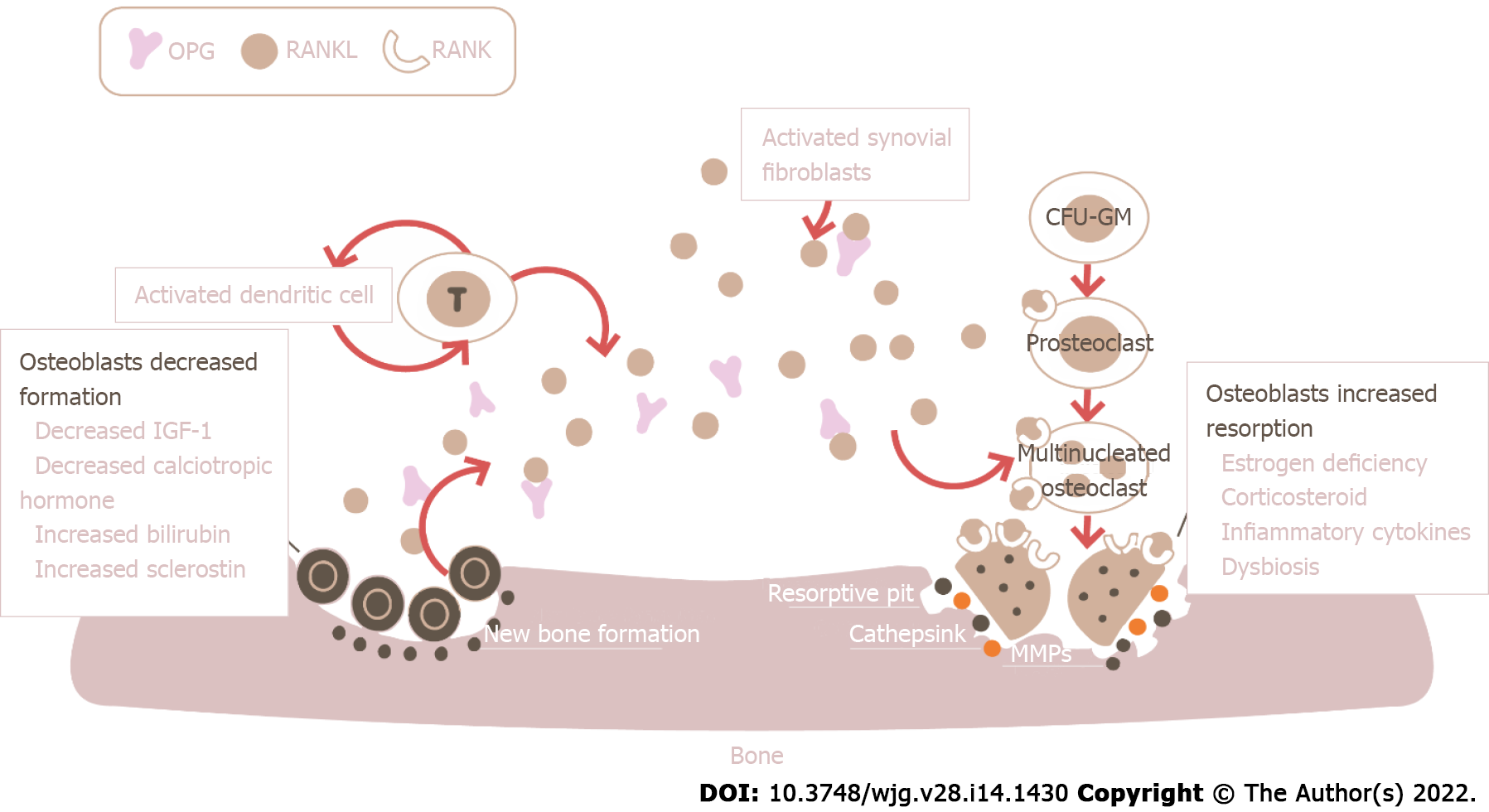
Figure 1 Possible pathophysiological mechanisms of development of osteoporosis in cholestatic diseases.
The figure describes the role of multiple factors linked to cholestatic diseases in the development of osteoporosis. Emphasis is placed on the difference between factors that cause osteoblasts dysfunction and factors that cause increased osteoclasts activity. OPG: Osteoprotegerin; RANK: Receptor activator for nuclear factor kappa B; RANKL: Receptor activator for nuclear factor kappa B ligand; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; CFU-GM: Granulocyte-macrophage-colony forming unit; MMPs: Matrix Metalloproteinases.
- Citation: Pugliese N, Arcari I, Aghemo A, Lania AG, Lleo A, Mazziotti G. Osteosarcopenia in autoimmune cholestatic liver diseases: Causes, management, and challenges . World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(14): 1430-1443
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i14/1430.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1430