Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2017; 23(37): 6894-6901
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6894
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6894
Figure 1 Normal mucosa (fundic gland mucosa).
A: Endocytoscopic appearance of fundic gland mucosa. The foveolar epithelium was arranged in a circle, and the glandular lumens were round. The nuclei were weakly stained; B: Histological appearance of the corresponding normal mucosa (H&E-stained horizontal section, × 200).
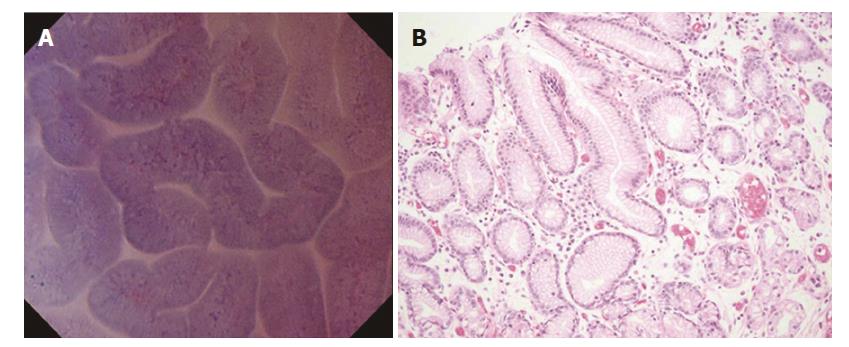
Figure 2 Normal mucosa (pyloric gland mucosa).
A: Endocytoscopic appearance of pyloric gland mucosa. The foveolar epithelium was regularly arranged in ridges, and the glandular lumens were slit-like. The nuclei were weakly stained; B: Histological appearance of the corresponding pyloric gland mucosa (H&E-stained horizontal section, × 200).
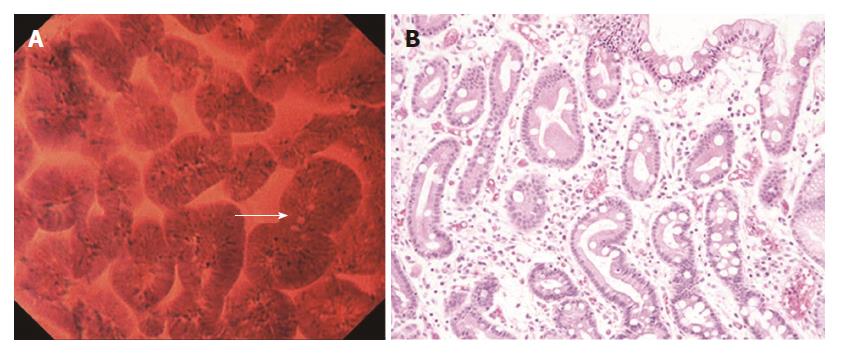
Figure 3 Intestinal metaplastic mucosa.
A: Endocytoscopic appearance of intestinal metaplastic mucosa. The foveolar epithelium exhibited a villous architecture and the gland lumens were widened. Goblet cells (arrow) were observed among the epithelial cells. The nuclei were stained more intensely than in the normal mucosa; B: Histological appearance of the corresponding intestinal metaplastic mucosa (H&E-stained horizontal section, × 200).
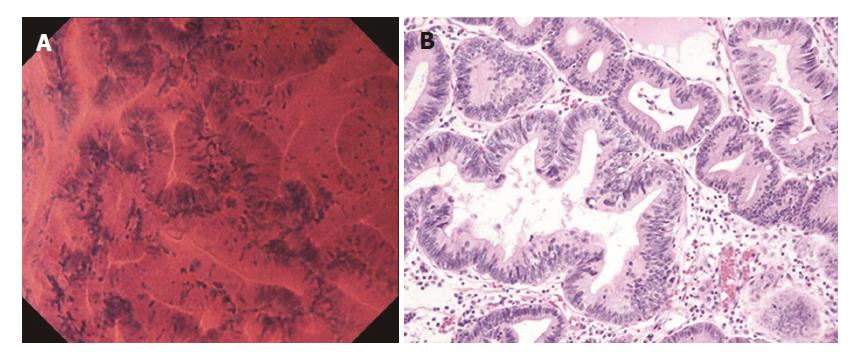
Figure 4 Well differentiated adenocarcinoma.
A: Endocytoscopic appearance of a well differentiated adenocarcinoma. The glands were branched irregularly and the width of the lumen varied. The epithelium was arranged in a disorderly fashion. The nuclei were deeply stained and pseudostratified; B: Histological appearance of the corresponding well-differentiated adenocarcinoma (H&E-stained horizontal section, × 200).
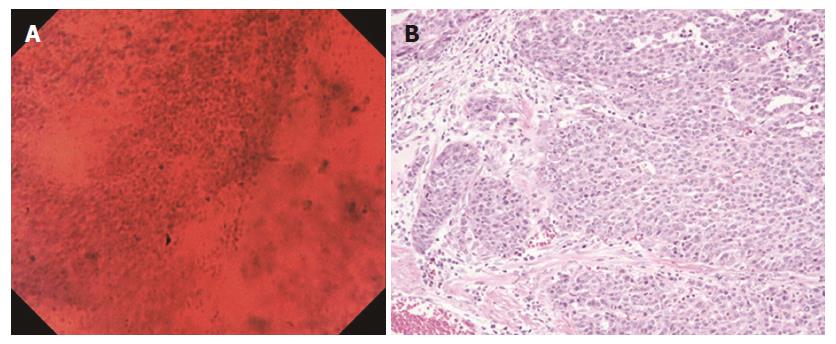
Figure 5 Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma.
A: Endocytoscopic appearance of a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. The tubular architecture was lost, and the nuclei were hyper-chromatic and anisokaryotic; B: Histological appearance of the corresponding poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (H&E-stained horizontal section, × 200).
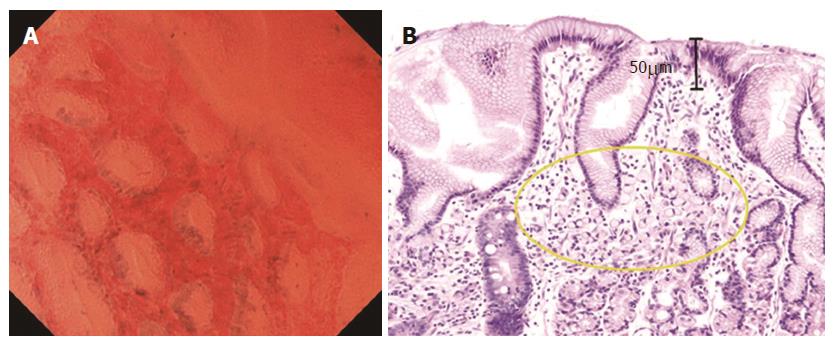
Figure 6 Signet ring cell carcinoma.
A: Endocytoscopic appearance of a signet ring cell carcinoma. Slit-like glandular lumens surrounded by regularly arranged foveolar cells were observed, a finding consistent with normal mucosa in endocytoscopy; B: Histological appearance of the corresponding signet ring cell carcinoma (H&E-stained horizontal section, × 200). Signet-ring cells were observed in the lamina propria (circle), but not exposed on the mucosal surface.
- Citation: Tsurudome I, Miyahara R, Funasaka K, Furukawa K, Matsushita M, Yamamura T, Ishikawa T, Ohno E, Nakamura M, Kawashima H, Watanabe O, Nakaguro M, Satou A, Hirooka Y, Goto H. In vivo histological diagnosis for gastric cancer using endocytoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(37): 6894-6901
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i37/6894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6894