Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2017; 23(15): 2660-2672
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2660
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2660
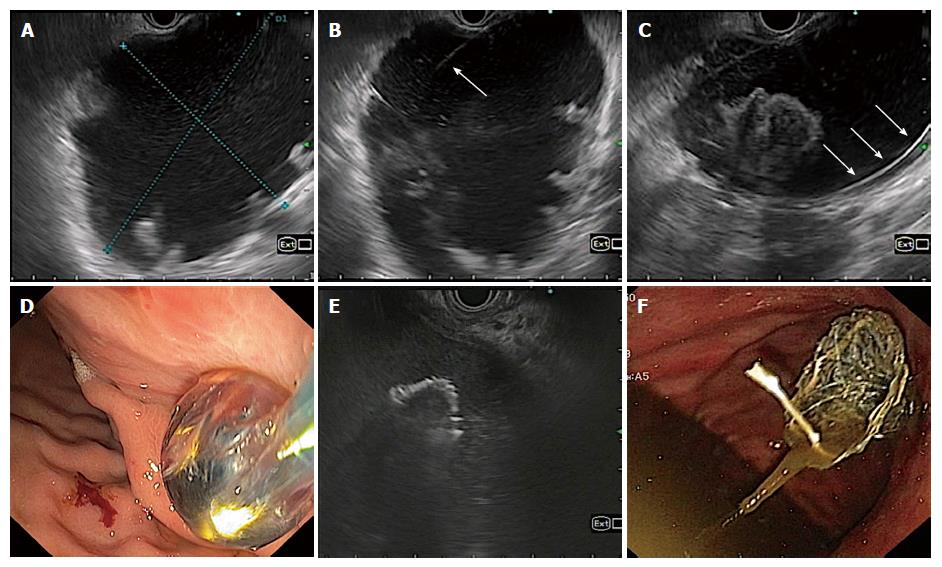
Figure 1 Technique of endoscopic ultrasonography guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collection.
A: EUS evaluation of pancreatic fluid collection; B: Puncture of pancreatic fluid collections (PFC) wall with 21 G fine needle aspiration needle; C: Coiling of guidewire inside PFC cavity; D: Enlarging the cysto-gastric tract with balloon; E: Placement of stent under EUS-guidance; F: Final position of stent after placement.
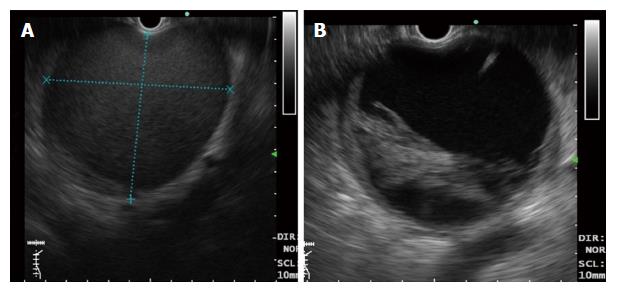
Figure 2 Differentiation of pancreatic fluid collections on endoscopic ultrasonography after 4 wk.
A: Pseudocyst - note the clear contents of a pseudocyst (without solid debris); B: Walled off necrosis- note the presence of debris inside the cyst cavity.
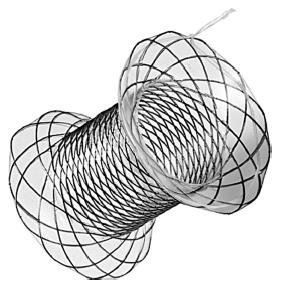
Figure 3 Specially designed bi-flanged metal stent (Nagi stent, Taewoong Medical Co, Ilsan, South Korea) for drainage of pancreatic fluid collection.
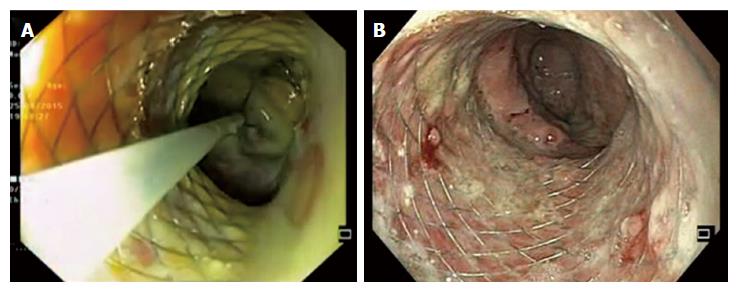
Figure 4 Direct endoscopic necrosectomy.
A: Removal of necrotic debris with a snare; B: After completion of endoscopic necrosectomy.
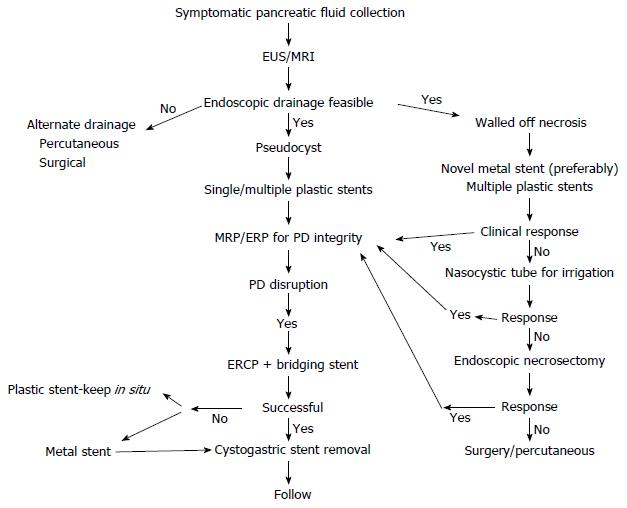
Figure 5 Algorithmic approach to the management of pancreatic fluid collections.
EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; PD: Pancreatic duct; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
- Citation: Nabi Z, Basha J, Reddy DN. Endoscopic management of pancreatic fluid collections-revisited. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(15): 2660-2672
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i15/2660.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2660