Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2016; 22(21): 5033-5041
Published online Jun 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.5033
Published online Jun 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.5033
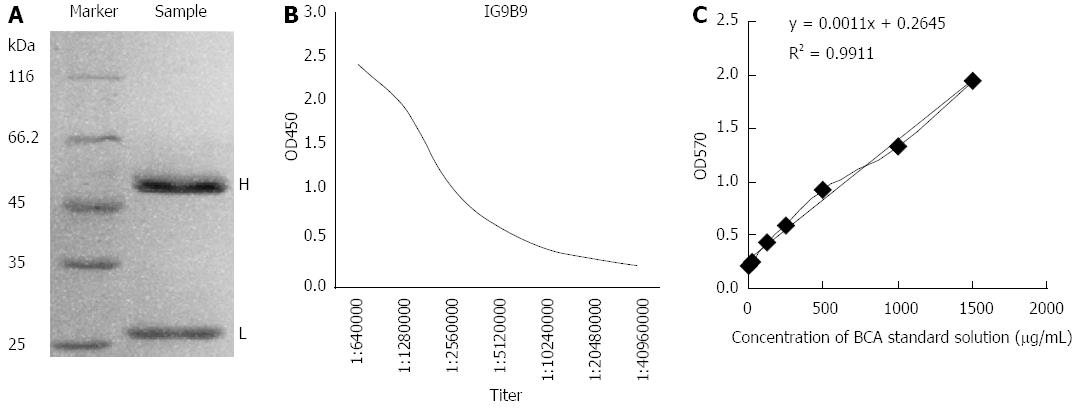
Figure 1 Characterization of anti-bFGF mAb.
A: SDS-PAGE of purified bFGF mAb (H: heavy chain; L: light chain); B: Titer of purified bFGF mAb stock solution tested by indirect ELISA; C: Concentration of purified bFGF mAb stock solution assayed by BCA standard assay kit. (Standard curve: y = 0.0011x + 0.2645; Relevancy: R2 = 0.9911). BCA: Bicinchoninic acid; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; mAB: Monoclonal antibody; SDS-PAGE: Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
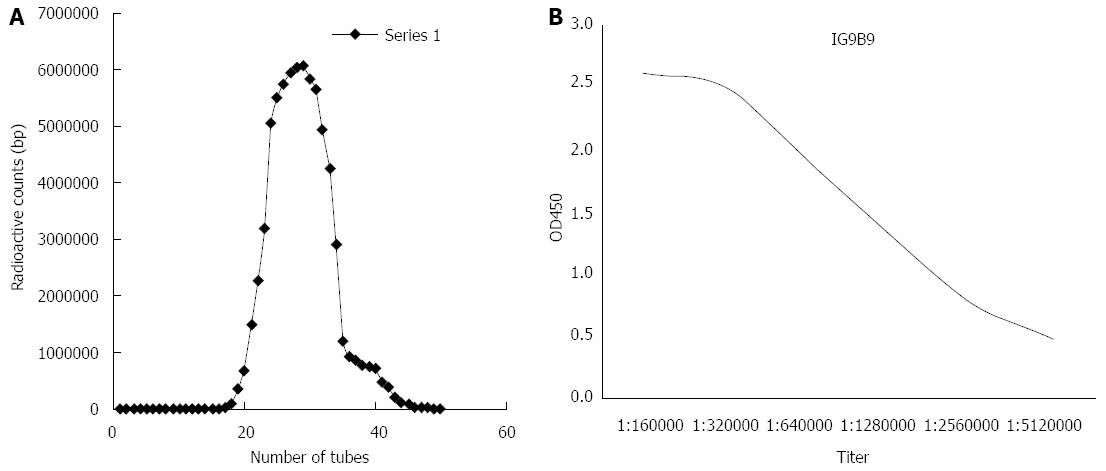
Figure 2 Radioactivity and titer of purified 125I-bFGF mAb.
A: Product peak of purified 125I-bFGF mAb tested by gamma radiation counter GC-1200; B: Titer of purified 125I-bFGF mAb stock solution assayed by indirect ELISA.
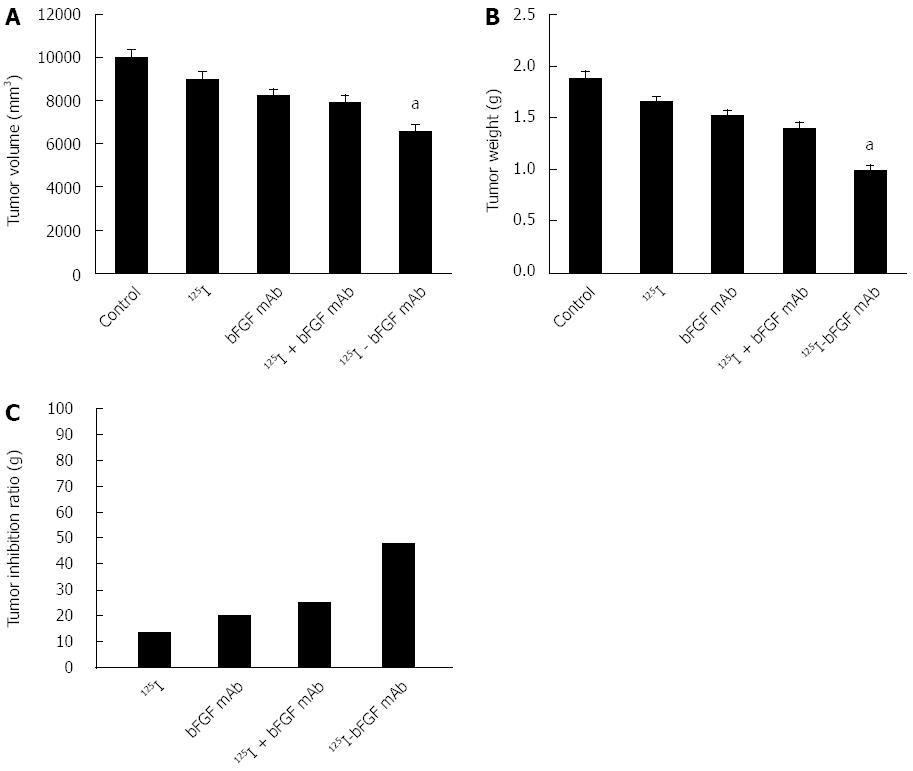
Figure 3 Therapeutic efficacy of 125I-bFGF mAb in mice with H22 hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Tumor volume of H22 HCC; B: Tumor weight of H22 HCC; C: Tumor inhibition ratios of experimental groups; aP < 0.05, 125I-bFGF mAb group vs other groups (control, 125I, bFGF mAb and 125I plus bFGF mAb). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
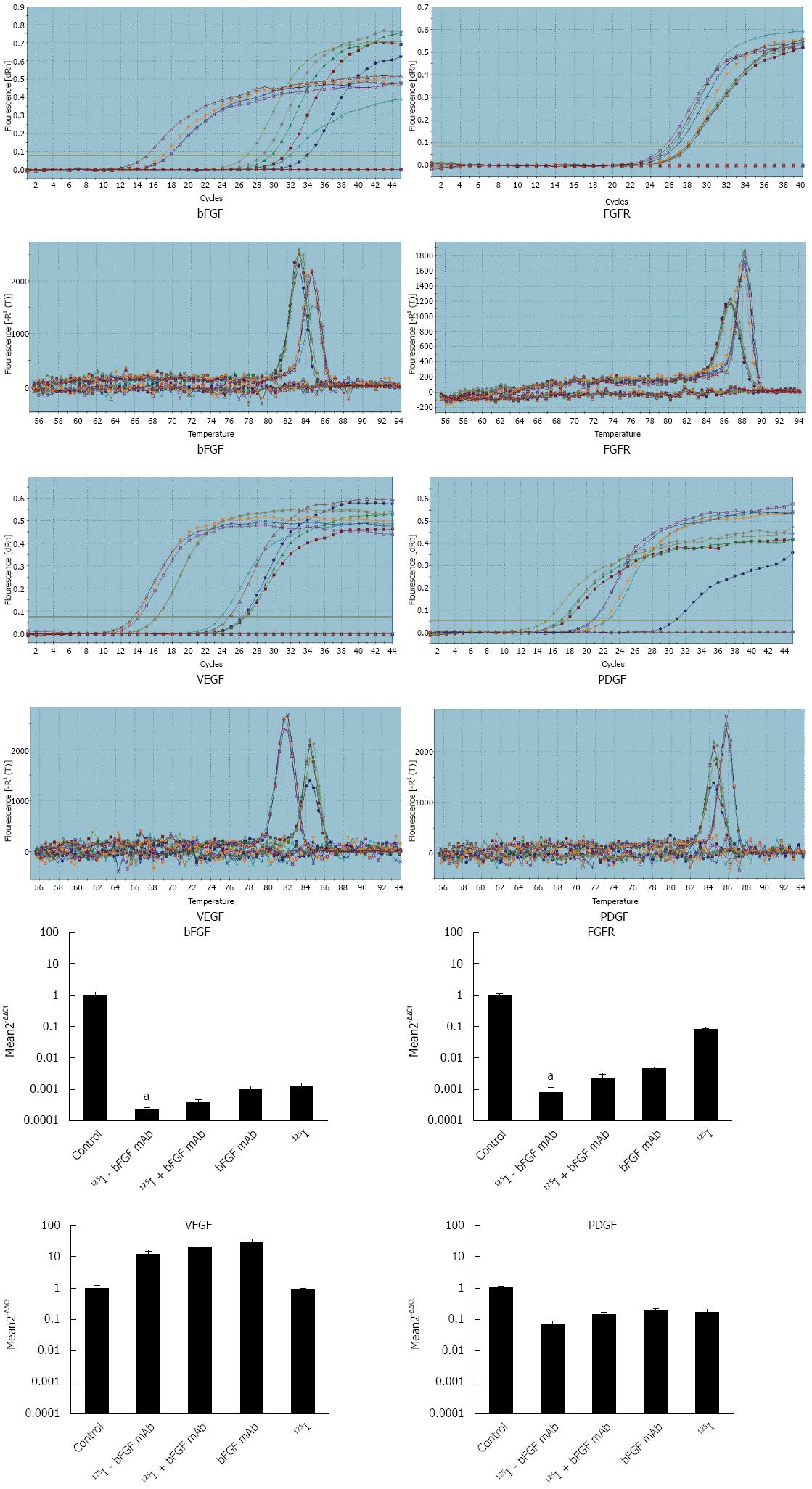
Figure 4 Quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction amplification curves, melt curves and expression of bFGF, FGFR, VEGF and PDGF mRNA.
aP < 0.05, 125I-bFGF mAb group vs other groups (control, 125I, bFGF mAb and 125I plus bFGF mAb). qRT-PCR: Quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Hu PH, Pan LH, Wong PTY, Chen WH, Yang YQ, Wang H, Xiang JJ, Xu M. 125I-labeled anti-bFGF monoclonal antibody inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(21): 5033-5041
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i21/5033.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.5033