Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2012; 18(42): 6088-6095
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6088
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6088
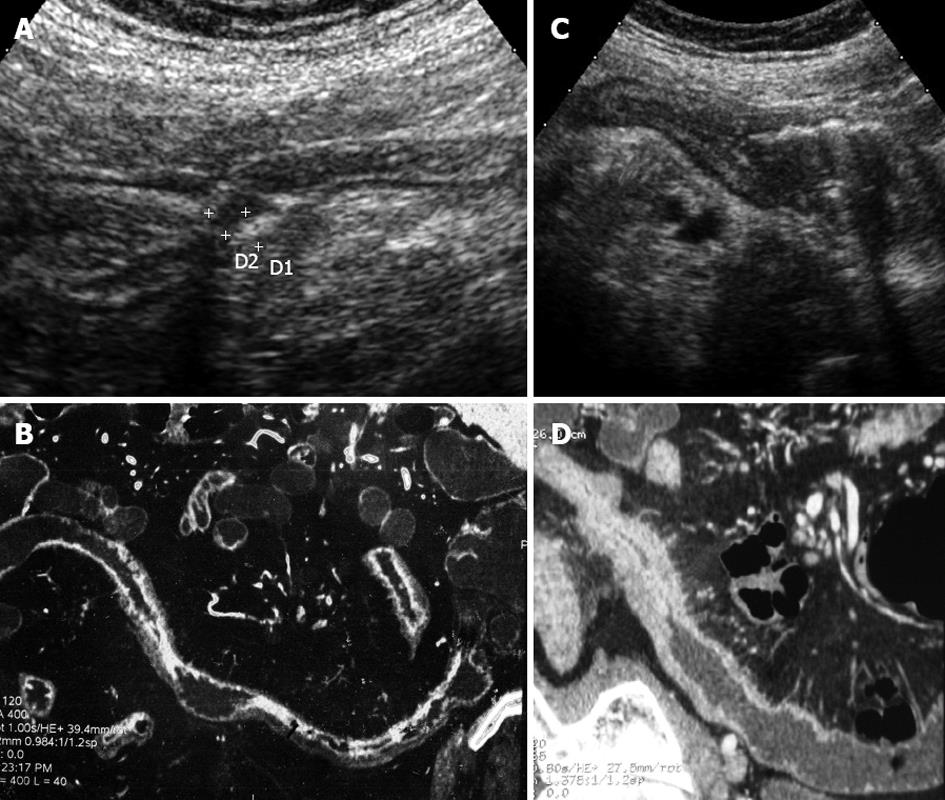
Figure 1 The figure shows images from the distal ileum from one patient with Crohn's disease of the distal and neo-terminal ileum undergoing ileo-colonic resection, as assessed by small intestine contrast ultrasonography and computed tomography-enteroclysis.
A: Small intestine contrast ultrasonography (SICUS) showed a stenosis of the terminal ileum, with a thickened bowel wall, with lumen narrowing. The lumen diameter did not change after the ingestion of polyethylen glycole; B: Computed tomography-enteroclysis (CTE) showed findings comparable with SICUS, including a marked narrowing of the distal ileum, associated with an increased bowel wall thickness; C: SICUS showed a stricture of the neo-terminal ileum presenting as a thickened bowel wall, with lumen narrowing associated with pre-stenotic dilation; D: CTE showed findings comparable with SICUS, including a marked narrowing of the distal ileum, associated with an increased bowel wall thickness, but no bowel dilation).
-
Citation: Onali S, Calabrese E, Petruzziello C, Zorzi F, Sica G, Fiori R, Ascolani M, Lolli E, Condino G, Palmieri G, Simonetti G, Pallone F, Biancone L. Small intestine contrast ultrasonography
vs computed tomography enteroclysis for assessing ileal Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(42): 6088-6095 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i42/6088.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6088