Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2006; 12(46): 7478-7481
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7478
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7478
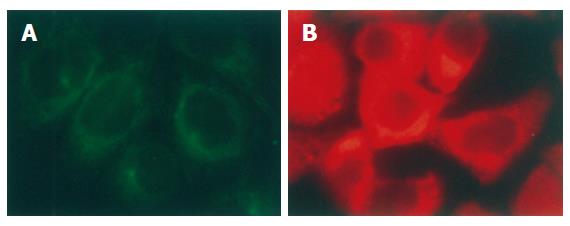
Figure 1 Distribution of α-tubulin (A) and p-VASP (B) in interphase of SGC-7901 cells (immunofluorescent staining × 200).
α-tubulin was stained with monoclonal antibody against the protein. p-VASP was stained with polyclonal antibody specifically against VASP phosphorylated at Ser157. Both α-tubulin and p-VASP were located in cytoplasm of the cells.
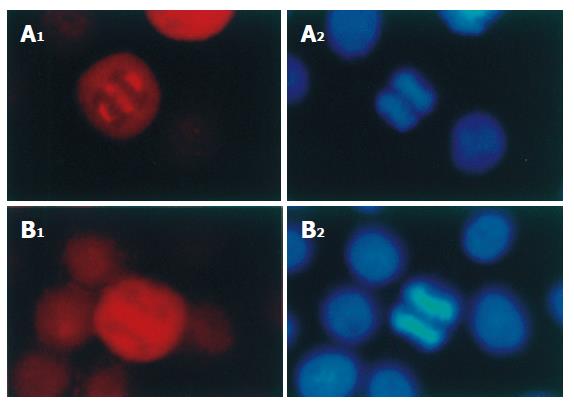
Figure 2 Distribution of p-VASP (A) and VASP (B) in mitotic SGC-7901 cells (× 200).
p-VASP and VASP in mitotic SGC-7901 cells were immunofluorescently stained with polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies respectively. The chromosomes were stained with Hoechst 33342.
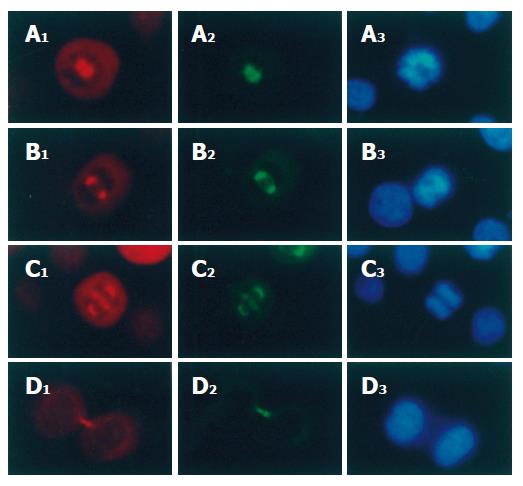
Figure 3 p-VASP co-localization with α-tubulin and chromosomes on spindles of mitotic SGC-7901 cells (× 200).
p-VASP and α-tubulin were stained with polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies respectively. A1-D1: p-VASP localization in prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase respectively; A2-D2: α-tubulin localization in the same phases; A3-D3: chromosomes of the cells were stained with Hoechst 33342.
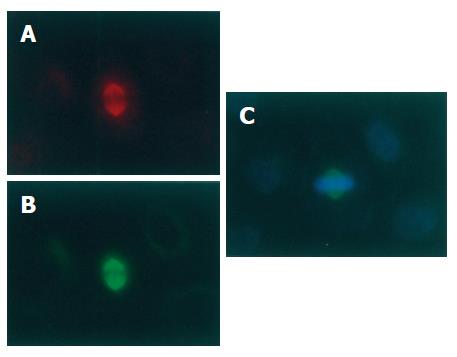
Figure 4 No effect of PKA and PKG inhibitor H89 on location of p-VASP on spindles of mitotic SGC-7901 cells (× 200).
SGC-7901 cells were treated with H89 (10 μmol/L) for 6 h and immunofluorescently stained for p-VASP (A) and α-tubulin (B). The chromosomes were stained with Hoechst 33342 (C).
- Citation: Tao Y, Chen YC, Wang Y, Zhang ZJ, Xu WR. Phosphorylated vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is localized on mitotic spindles of the gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(46): 7478-7481
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i46/7478.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7478