Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2006; 12(4): 556-560
Published online Jan 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.556
Published online Jan 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.556
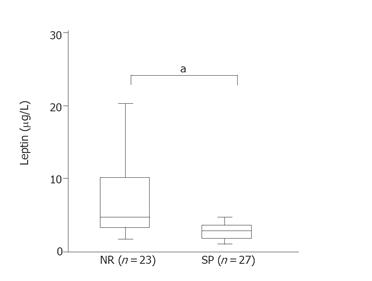
Figure 1 Effectiveness of IFN and serum leptin level in subjects with a low viremia level.
NR: Non-responder group for IFN therapy; SR: Sustained responder group. aP < 0.05, NR vs SR. Mann-Whitney U-test.
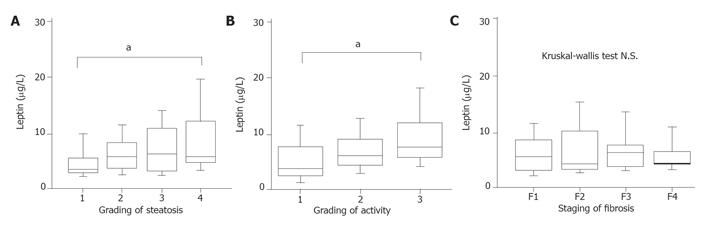
Figure 2 Histopathological parameters and serum leptin level.
A: Hepatic steatosis and serum leptin level. Steatosis was evaluated by the Adinolfi grading system in which steatosis is graded from 0 to 4 based on the percentage of hepatocytes involved. There were significant relationships between leptin level and hepatic steatosis evaluated by Kruskal-Wallis test (bP < 0.01, steatosis 1 vs 2 vs 3 vs 4); B: Necroinflammatory activity and serum leptin level. There were significant relationships between leptin level and activity grading evaluated by Kruskal-Wallis test (P < 0.05). The scoring system includes the semi-quantitative assessment of liver disease grading of histopathological inflammatory activity (1: mild, 2: moderate, 3: severe activity; aP < 0.05, activity 1 vs 2 vs 3); C: Fibrosis and serum leptin level. F1: Fibrosis is located to the portal tract; F2: fibrosis is located septally with distinct widening of portal fields; F3: fibrosis extended portally to the portal; F4: liver cirrhosis. There was no relationship between leptin level and liver fibrotic staging evaluated by Kruskal-Wallis test. NS: not significant.
- Citation: Eguchi Y, Mizuta T, Yasutake T, Hisatomi A, Iwakiri R, Ozaki I, Fujimoto K. High serum leptin is an independent risk factor for non-response patients with low viremia to antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(4): 556-560
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i4/556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.556