Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 1, 2004; 10(13): 1928-1933
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1928
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1928
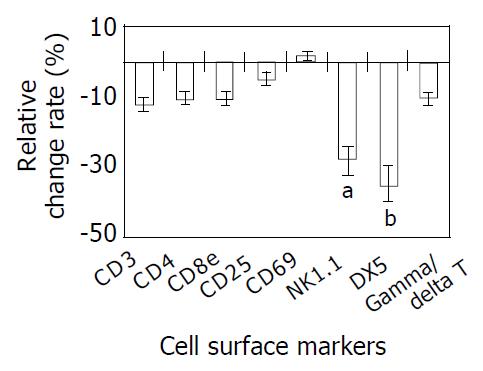
Figure 1 Effects of enzymatic digestion on surface molecules of hepatic lymphocytes.
aP < 0.05, NK1.1 vs other groups except DX5; bP < 0.01, DX5 vs other groups except NK1.1.
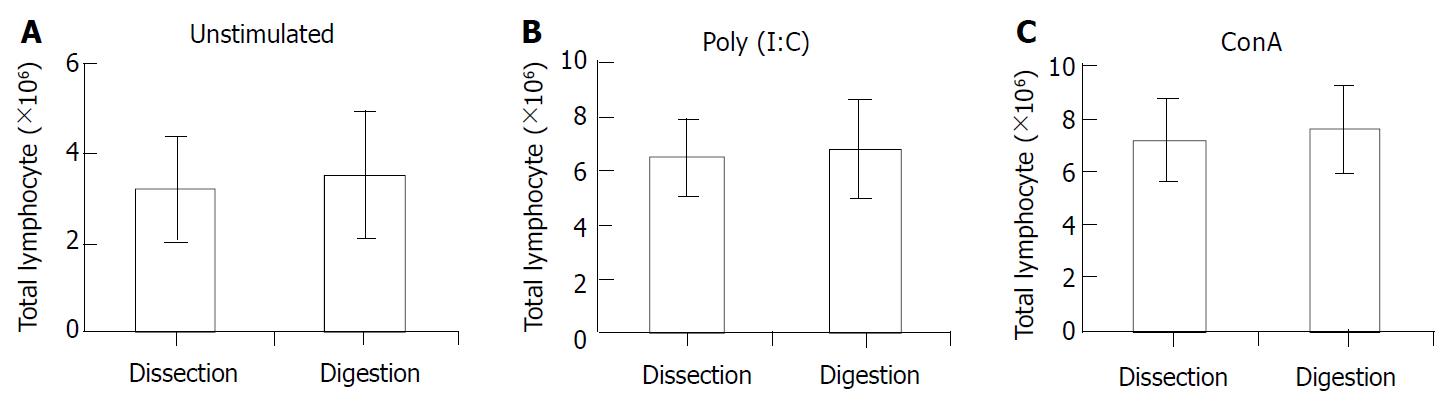
Figure 2 Cell yields between the two isolating methods.
Hepatic lymphocytes were isolated using mechanical dissection method and the enzymatic digestion method, respectively, from normal C57BL/6 mice (A), Poly (I:C)-treated C57BL/6 mice (B) or ConA-treated C57BL/6 mice(C).
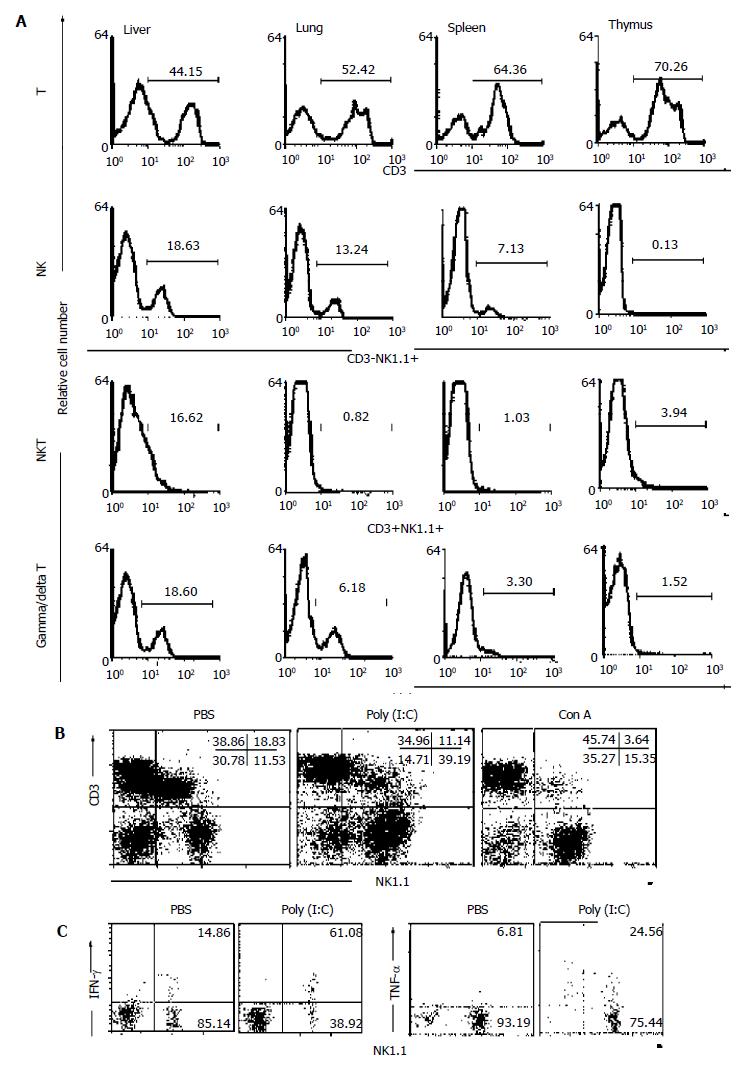
Figure 3 Hepatic lymphocytes isolated with mechanical dissection were suitable for phenotypic analysis of NK1.
1+ cells. A: Lymphocytes from liver, lung, spleen and thymus of normal C57BL/6 mice were labeled with two-color immunofluorescence; B, C: C57BL/6 mice were injected with PBS, Poly (I:C) or ConA, respectively. Hepatic lymphocytes were isolated and labeled for phenotype (CD3 and NK1.1) and intracellular cytokine (IFN-γ and TNF-α) detection.
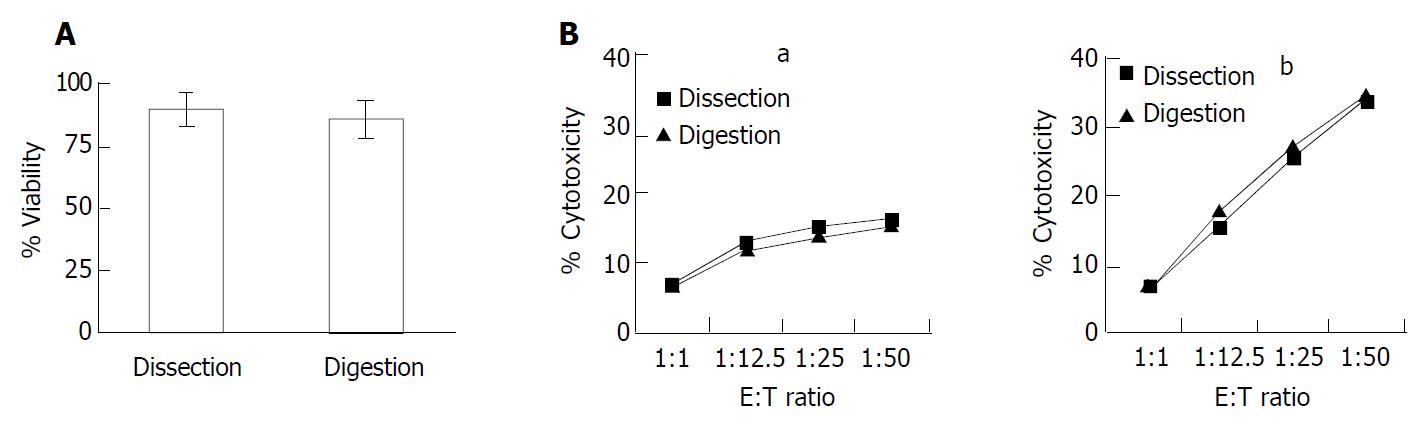
Figure 4 Hepatic lymphocytes isolated with mechanical dissection were suitable for the functional analysis of NK1.
1+ cells. A: Viability of hepatic lymphocytes isolated with two methods; B: Cytotoxicity analysis of hepatic lymphocytes. Hepatic lymphocytes were isolated by two different methods, respectively, from control B6 mice (a) or Poly (I:C)-treated B6 mice (b). Their cytotoxicity against YAC-1 cells was tested at the (E/T) ratios.
- Citation: Dong ZJ, Wei HM, Sun R, Gao B, Tian ZG. Isolation of murine hepatic lymphocytes using mechanical dissection for phenotypic and functional analysis of NK1.1+ cells. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(13): 1928-1933
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i13/1928.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1928