Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Transl Med. Apr 12, 2016; 5(1): 46-52
Published online Apr 12, 2016. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v5.i1.46
Published online Apr 12, 2016. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v5.i1.46
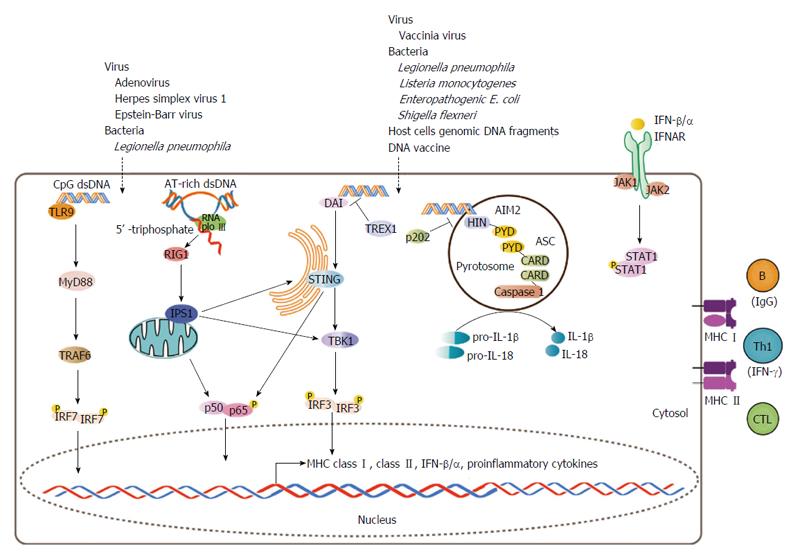
Figure 1 Cytosolic double-stranded DNA signal pathways.
TLR9-dependent and TLR9-independent signal pathways have been proposed to mediate foreign- or self-derived cytosolic dsDNA signal to induce the expression of MHC molecules, type I IFNs, and proinflammatory cytokines. At the same time, cytosolic dsDNA can trigger AIM2-mediated inflammasome formation to produce active IL-1 and IL-18. Consequently, exposure to cytosol dsDNA will increase the probability of (auto)immune response. TLR9: Toll-like receptor 9; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; TRAF6: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6; IRF7/3: Interferon regulatory factor 7/3; RNA pol III: RNA polymerase III; RIG1: Retinoic acid-inducible gene 1; IPS1: Interferon-promoter stimulator 1; DAI: DNA-dependent activator of interferon - regulatory factors; TREX1: 3-5 exonuclease (also known as DNase III); STING: Stimulator of interferon genes; TBK1: TANK-binding kinase 1; AIM2: Absent in melanoma 2; ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein complex; HIN: C-terminal HIN-200 domain; PYD: N-terminal pyrin domain; CARD: Caspase activation and recruitment domain; IFNAR: Type I interferon receptor; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; JAK1: Janus kinase 1; CTL: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes; IFN: Interferon; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; IL: Interleukin; dsDNA: Double-stranded DNA.
- Citation: Luo Y, Yoshihara A, Oda K, Ishido Y, Hiroi N, Suzuki K. Naked DNA in cells: An inducer of major histocompatibility complex molecules to evoke autoimmune responses? World J Transl Med 2016; 5(1): 46-52
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6132/full/v5/i1/46.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5528/wjtm.v5.i1.46