Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Nephrol. Oct 27, 2019; 8(6): 95-108
Published online Oct 27, 2019. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v8.i6.95
Published online Oct 27, 2019. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v8.i6.95
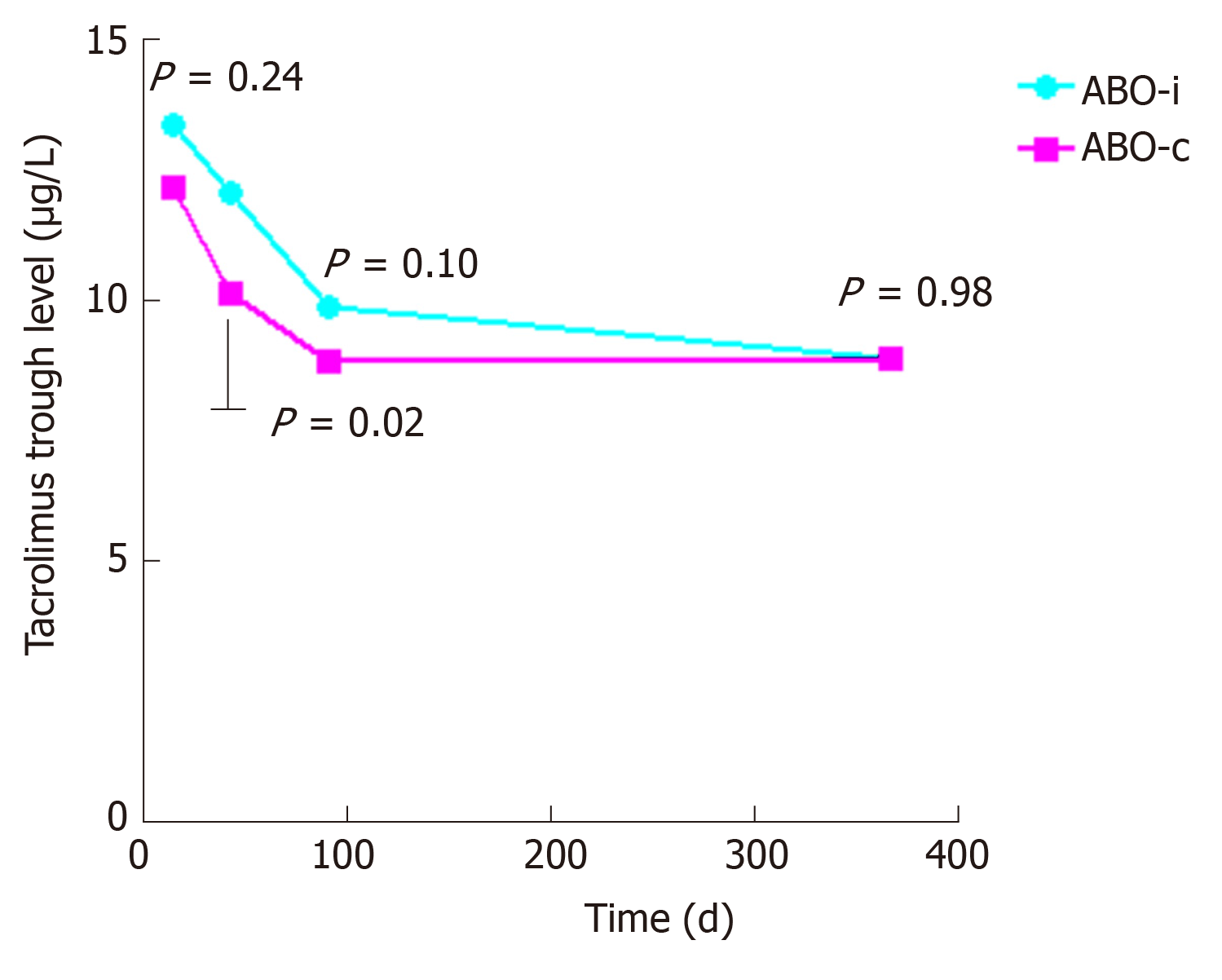
Figure 1 Tacrolimus trough levels.
Tacrolimus trough levels at 2 wk, 6 wk, 3 mo, and 1 year after transplantation.
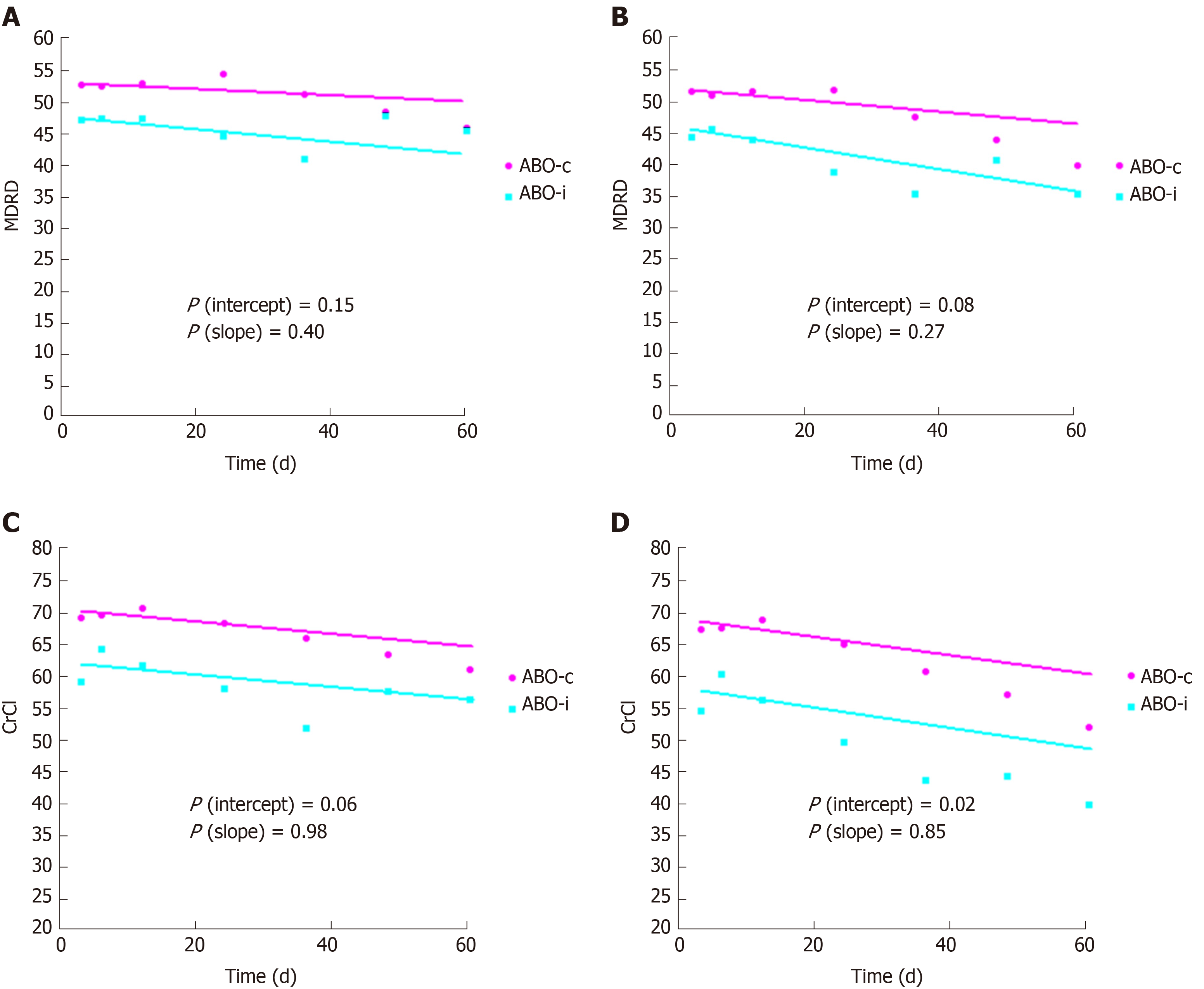
Figure 2 Kidney function.
A: Estimated glomerular filtration rate (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease) without imputation in case of graft loss; B: Estimated glomerular filtration rate (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease) with imputation of 10 mL/min/1.73 m2 in case of graft loss; C: Creatinine clearance without imputation in case of graft loss; D: Creatinine clearance with imputation of 10 mL/min/1.73 m2 in case of graft loss. Curves were estimated using linear mixed models. The dots indicate point estimates at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48 and 60 months. CrCl: Creatinine clearance; MDRD: Modification of Diet in Renal Disease.
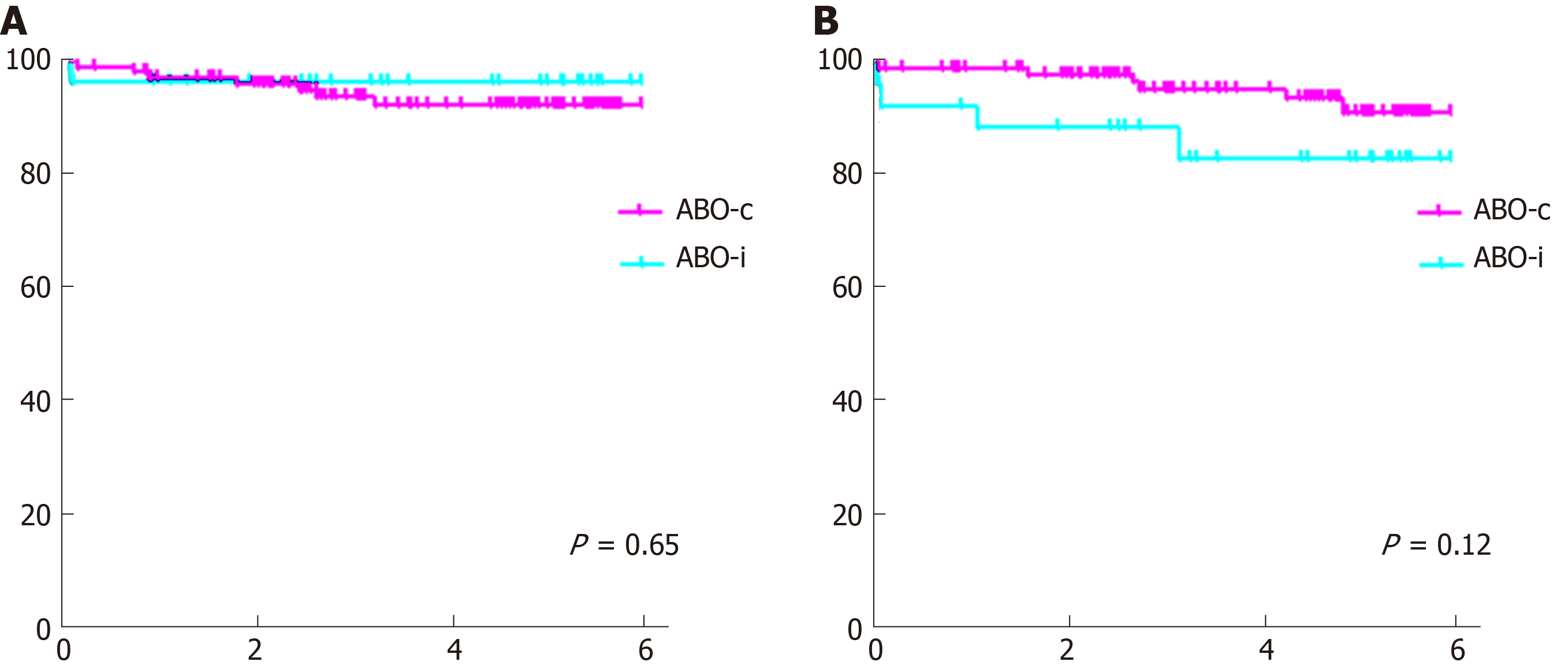
Figure 3 Patient and graft survival.
A: Patient survival; B: Death-censored graft survival.
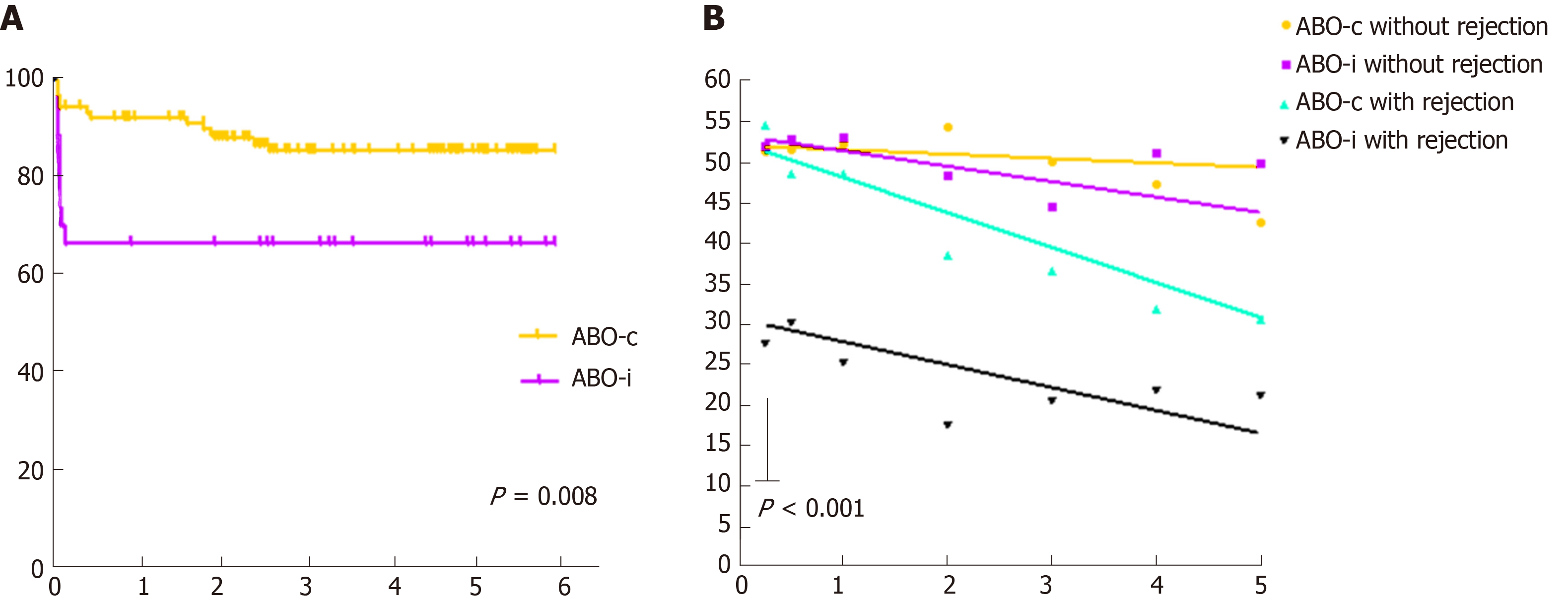
Figure 4 Rejection-free survival and kidney function split by occurrence of rejection.
A: Rejection-free survival; B: Estimated glomerular filtration rate (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease). P value calculated for intercept of ABO-i recipients with rejection (black line) compared to all other groups.
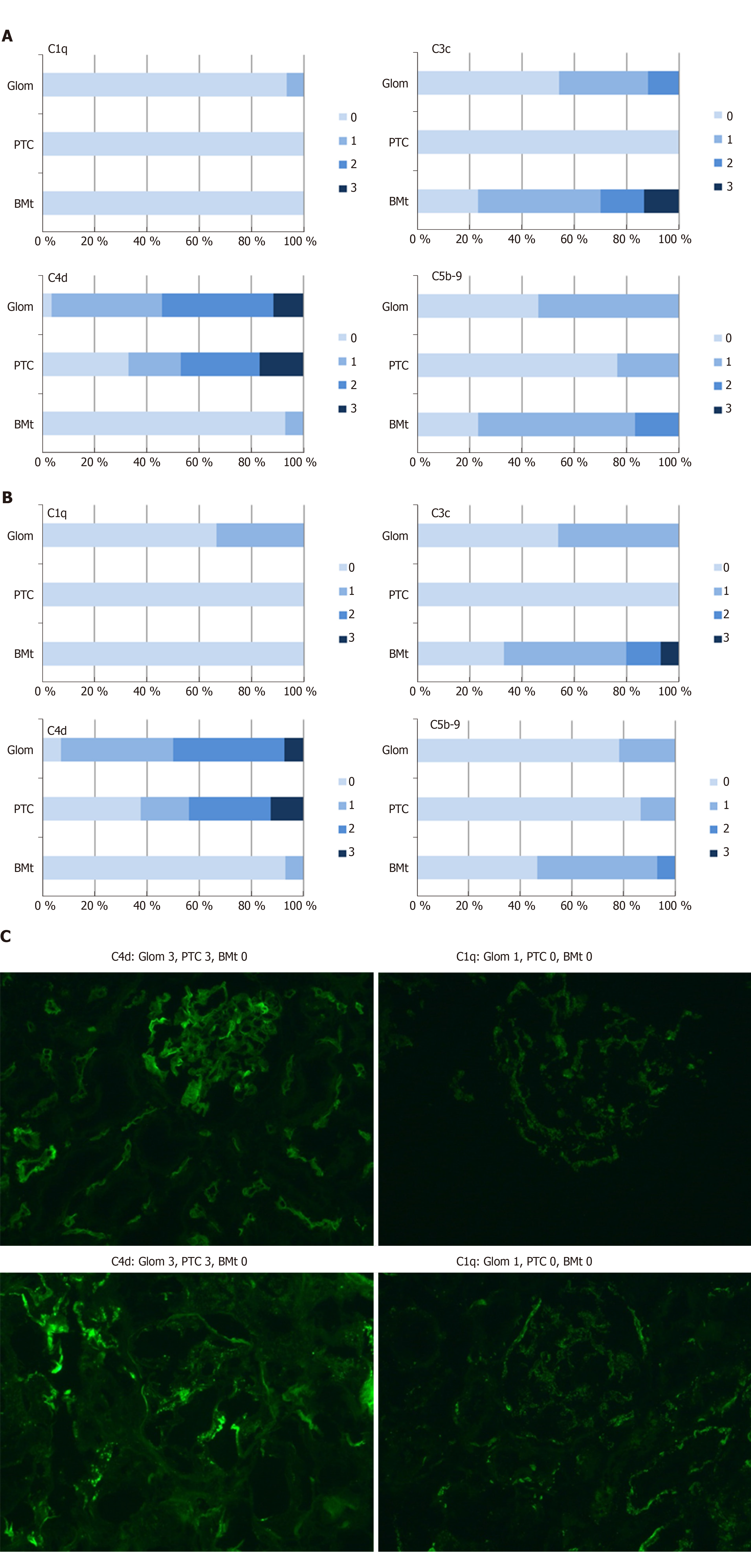
Figure 5 Complement activation in ABO-incompatible.
A: Complement activation in ABO-incompatible indication biopsies; B: Complement activation in ABO-incompatible protocol biopsies; C: Digital photographs of complement activation. Intensity of staining ranges from 0-3. Figures indicate the percentage of biopsies with each intensity score. Glom: Glomerular; PTC: Peritubular capillaries; BMt: Basal membrane of the tubuli.
- Citation: van Sandwijk MS, Klooster A, ten Berge IJ, Diepstra A, Florquin S, Hoelbeek JJ, Bemelman FJ, Sanders JS. Complement activation and long-term graft function in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. World J Nephrol 2019; 8(6): 95-108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v8/i6/95.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v8.i6.95