Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Nephrol. Jul 6, 2016; 5(4): 308-320
Published online Jul 6, 2016. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v5.i4.308
Published online Jul 6, 2016. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v5.i4.308
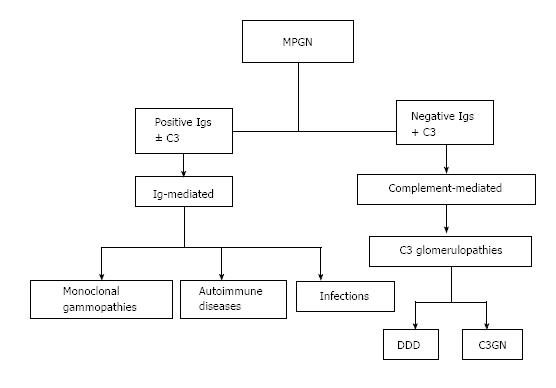
Figure 1 Proposed classification for membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis based on the presence or absence of Igs and the presence of C3 by immunofluorescence.
MPGN: Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; Igs: Immunoglobulins; DDD: Dense deposit disease.
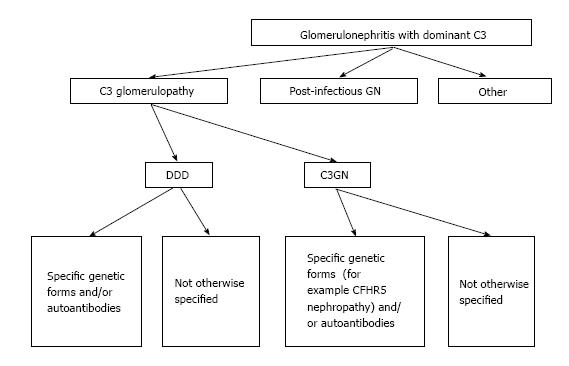
Figure 2 Approach to the classification of glomerulonephritis with dominant C3.
DDD: Dense deposit disease; CFHR5: Complement factor H related protein.
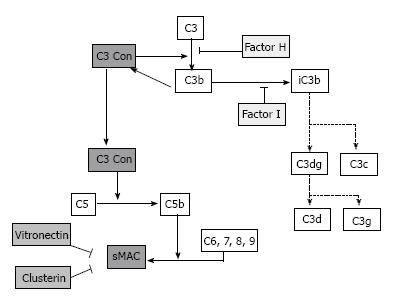
Figure 3 Pathway of complement and complement regulator factors.
C3 Con: C3 covertase; sMAC: Serum membrane attack complex; C3dg, C3c, C3d, C3g: Complement degradation products.
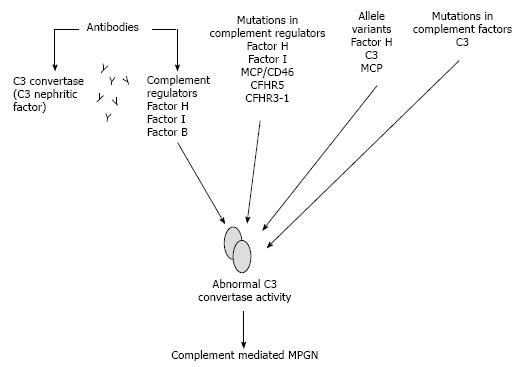
Figure 4 Acquired and genetic abnormalities associated with complement-mediated membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.
MCP: Membrane cofactor protein; CHFR: Complement factor H related proteins; MPGN: Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.
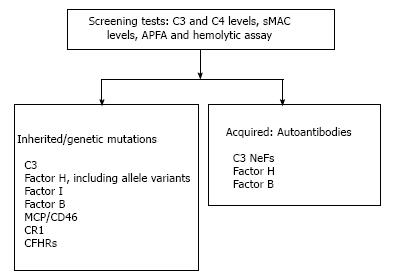
Figure 5 Proposed work-up of complement mediated membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.
APFA: Alternative pathway functional assay; CFHR: Complement factor H related proteins; CR1: Complement receptor 1; MCP: Membrane cofactor protein; sMAC: Serum membrane attack complex; MPGN: Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.
- Citation: Salvadori M, Rosso G. Reclassification of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis: Identification of a new GN: C3GN. World J Nephrol 2016; 5(4): 308-320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v5/i4/308.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v5.i4.308