Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2022; 11(5): 362-374
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.362
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.362
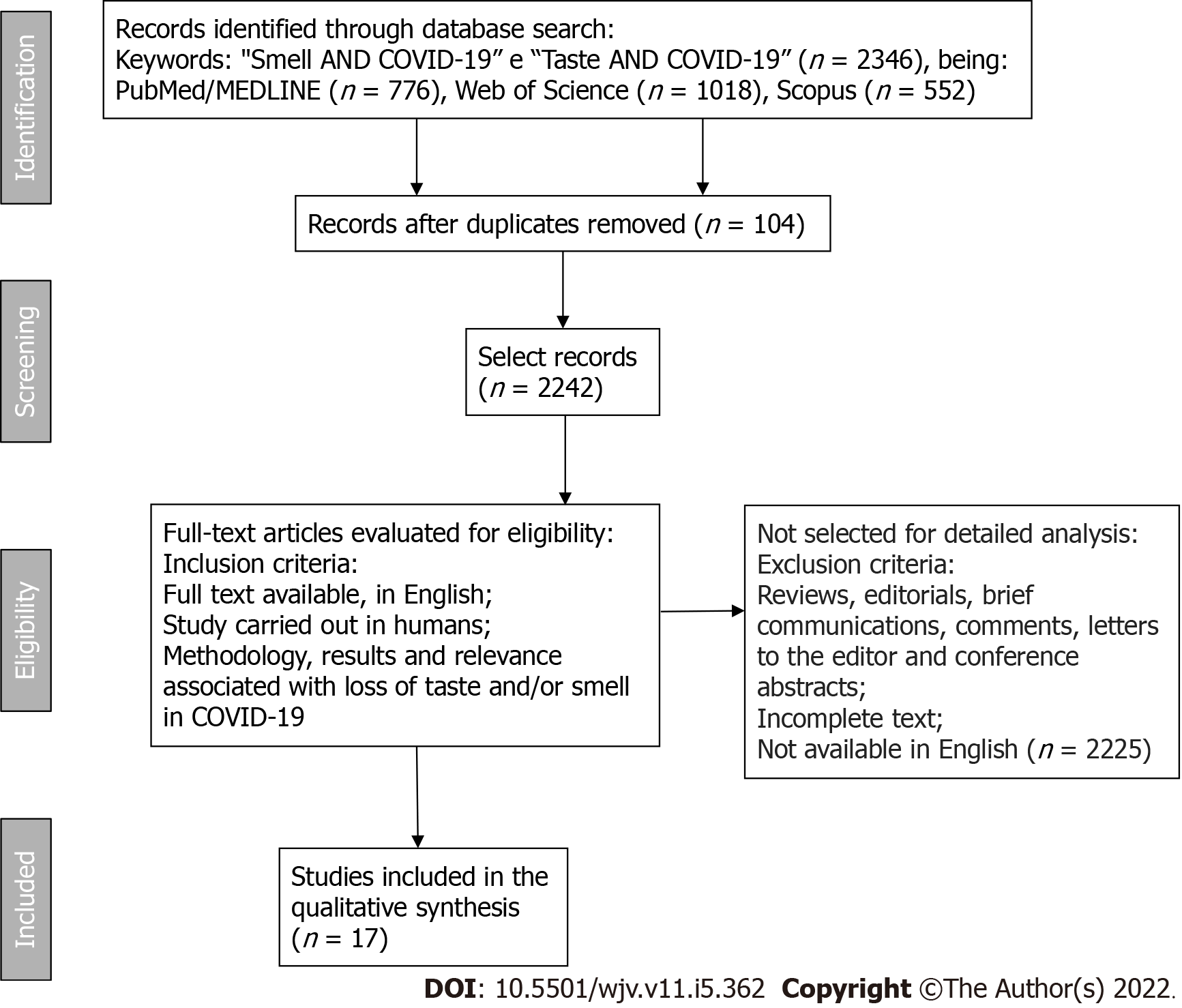
Figure 1 Flow diagram showing the selection of articles in the PubMed/MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Scopus databases.
COVID-19: The new coronavirus 2019.
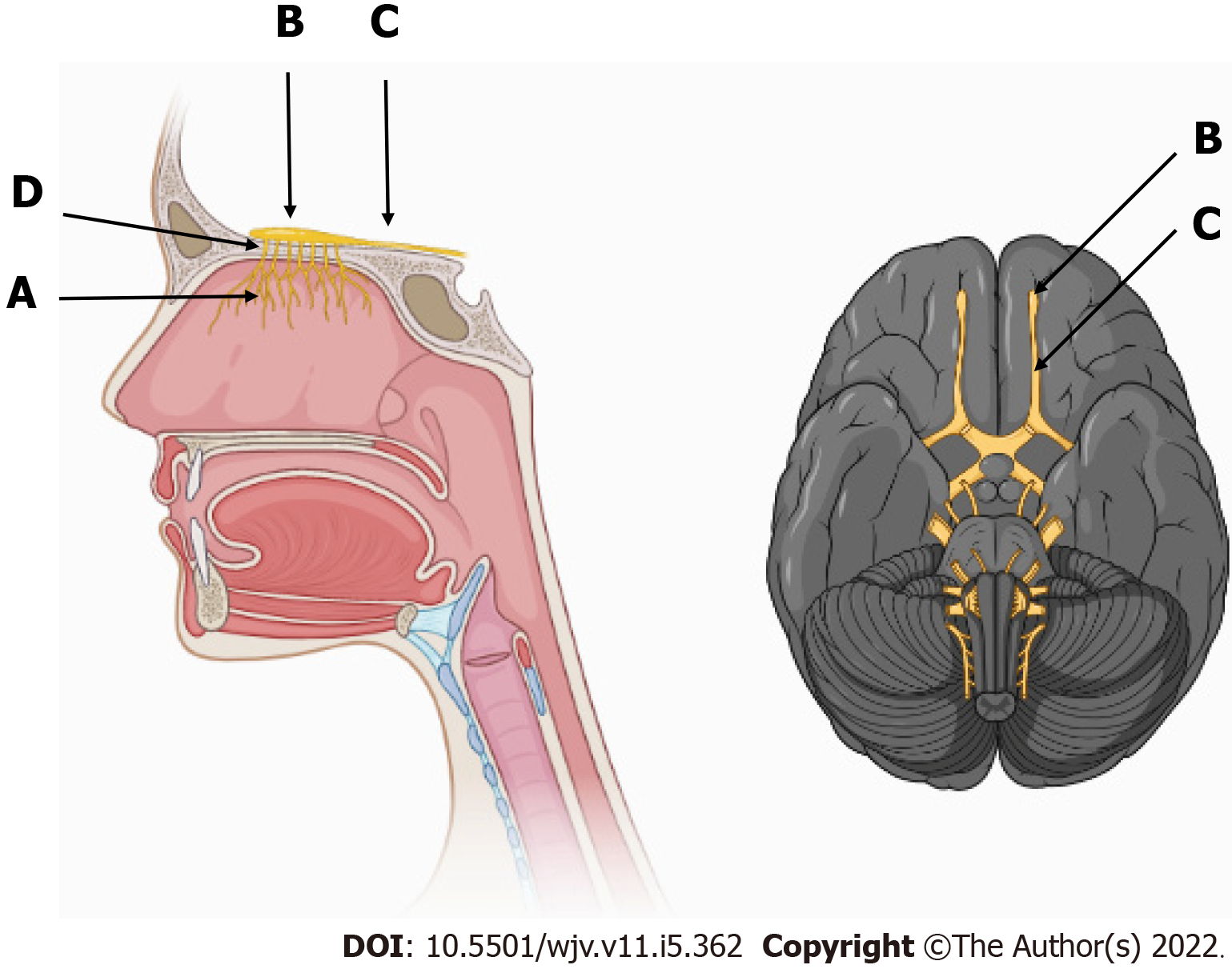
Figure 2 Olfactory pathway and its components.
A: Fillets of the olfactory nerves, the first pair of cranial nerves, inside the nasal cavity in the upper third of the nasal septum; B: Olfactory bulb; C: Olfactory tract; D: Cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone, which communicates the nasal cavity with the anterior cranial fossa.
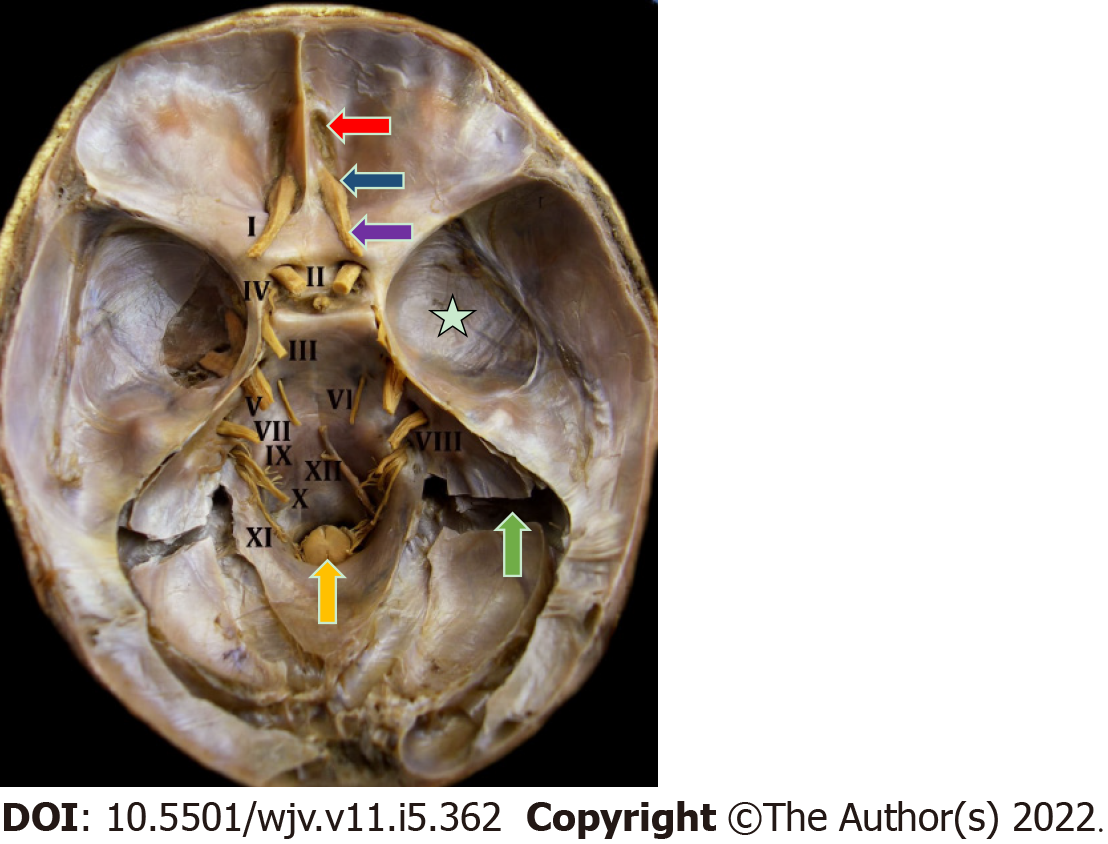
Figure 3 Endocranial view of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves in a natural anatomical piece.
I: Olfactory nerve; II: Optic nerve; III: Oculomotor nerve; IV: Trochlear nerve; V: Trigeminal nerve; VI: Abducens nerve; VII: Facial and intermediate nerve; VIII: Vestibulocochlear nerve; IX: Glossopharyngeal nerve; X: Vagus nerve; XI: Accessory nerve; XII: Hypoglossal nerve. Red arrow indicates the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone; blue arrow indicates the olfactory bulb; purple arrow indicates the olfactory tract; yellow arrow indicates the beginning of the spinal cord at the level of the foramen magnum; green arrow indicates the sigmoid sinus; white star indicates the cranial dura mater.
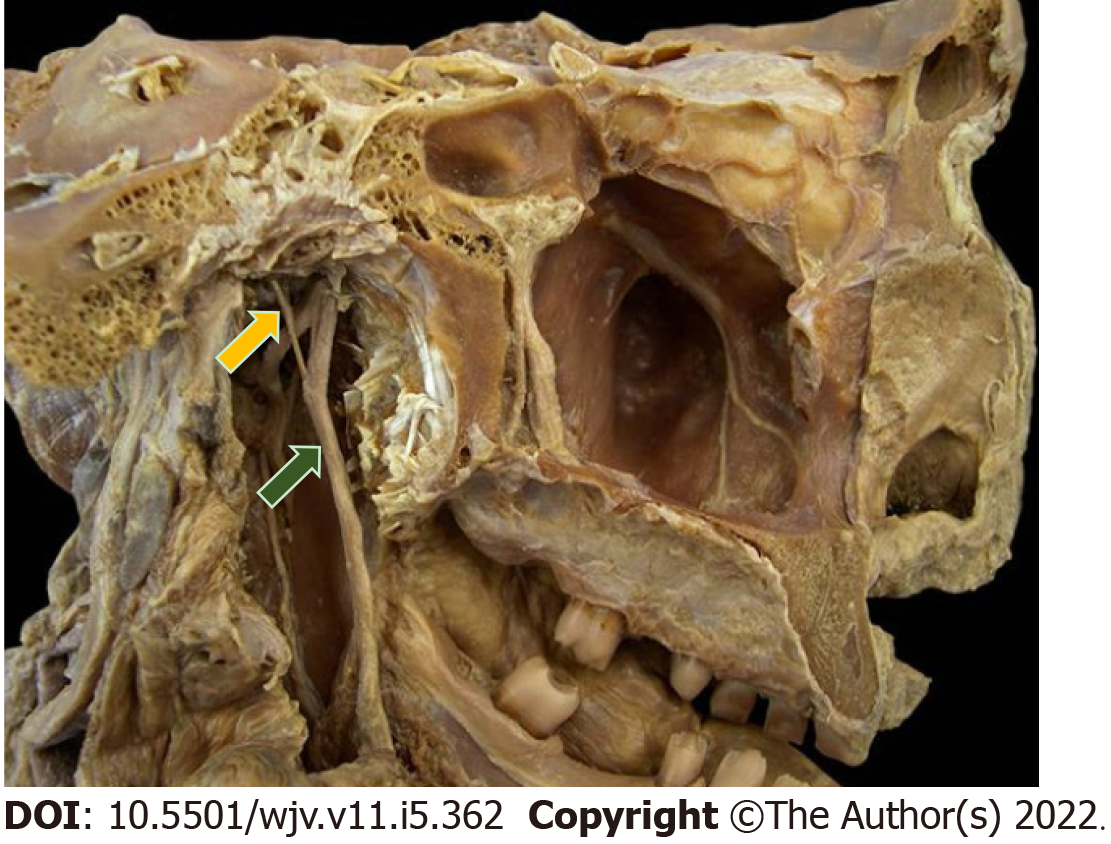
Figure 4 Natural anatomical piece in midsagittal section (medial view).
Yellow arrow represents the chorda tympani nerve, a branch of the intermediate nerve; green arrow represents the lingual nerve, a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve.
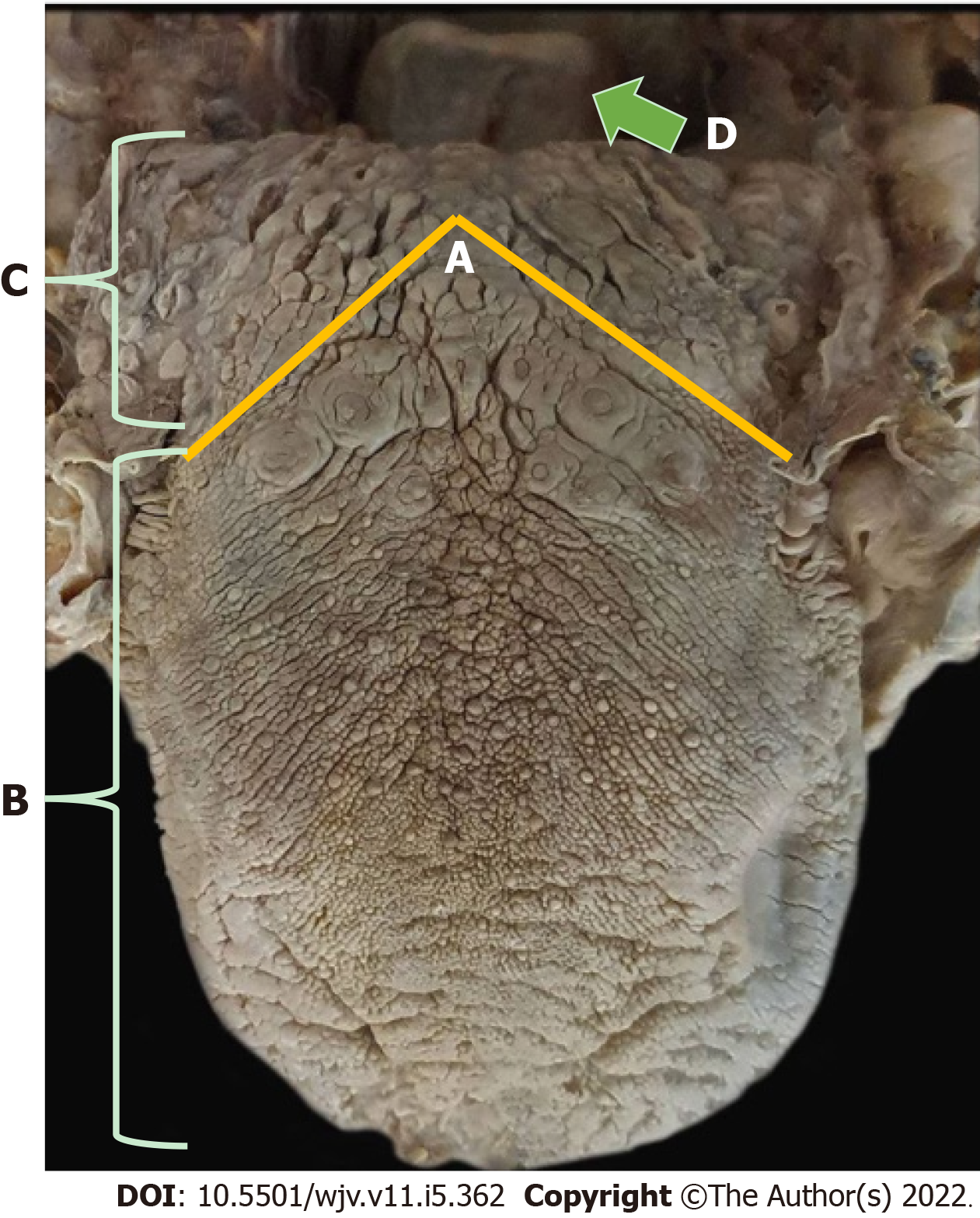
Figure 5 Dorsal region of the tongue.
A-C: Yellow line indicates the terminal sulcus, which separates the tongue into body or two anterior thirds and root or posterior third; D: Green arrow indicates the epiglottis cartilage of the larynx, where taste is made by the vagus nerve.
- Citation: Vigliar MFR, Pomini KT, Buchaim DV, Buchaim RL. Anatomophysiological relationships and clinical considerations of taste and smell loss in patients with COVID-19. World J Virol 2022; 11(5): 362-374
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i5/362.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.362