Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2022; 11(5): 310-320
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.310
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.310
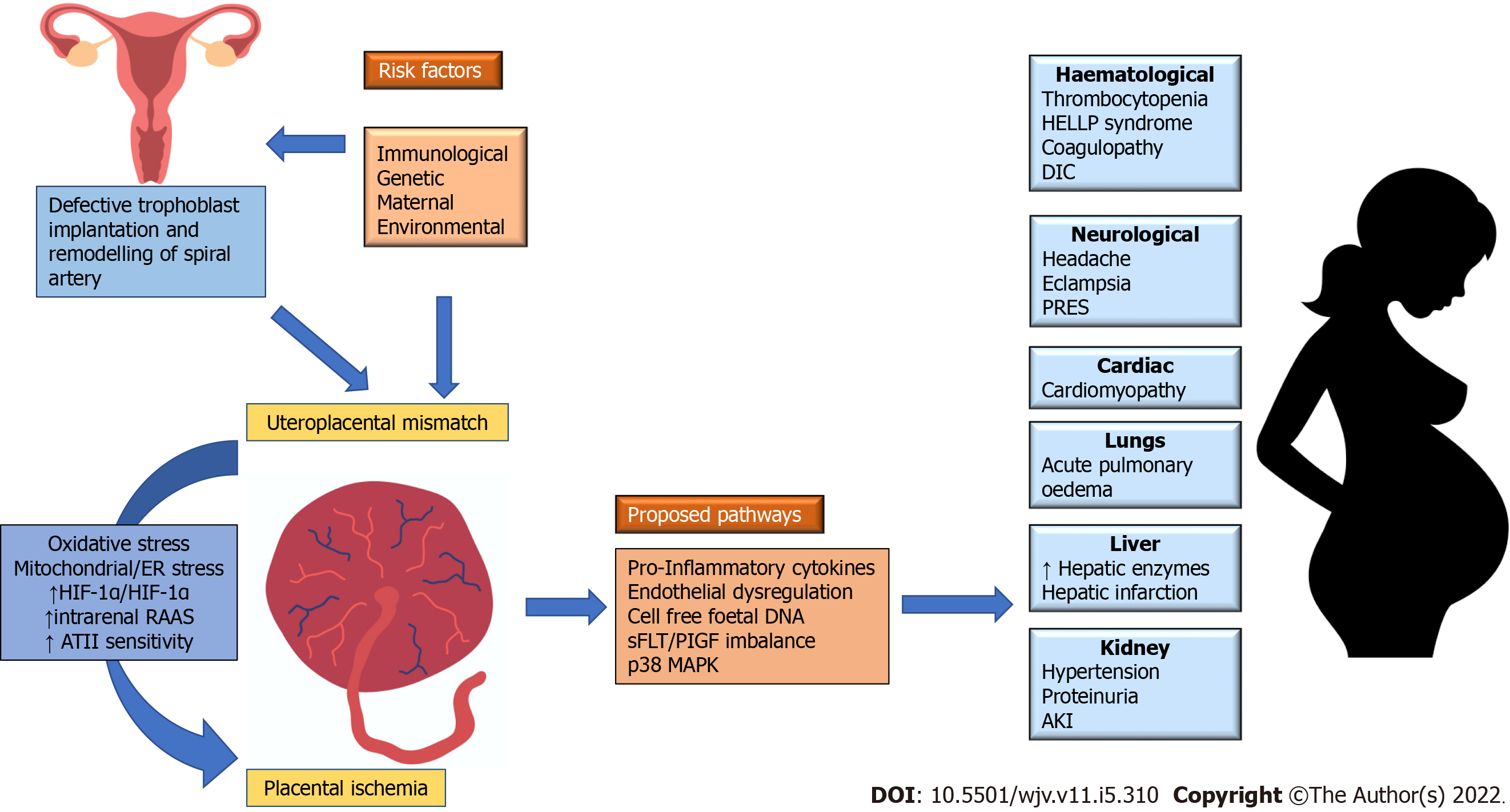
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet syndrome.
Placenta ischemia is central mechanism which is suspected to play a central role in hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet (HELLP) syndrome. Abnormal trophoblast implantation and remodelling of uterine arteries along with genetic, environmental, nutritional, or maternal risk factors cause uteroplacental perfusion mismatch. Various pathways proposed for systemic manifestations of HELLP syndrome include, releases of inflammatory cytokines, endothelial dysfunction, release of cell-free fetal DNA, imbalance of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase to placental growth factor ratio (sFLT/PIGF ratio). HELLP: Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet; ATII: Angiotensin II; HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha; RAAS: Renin angiotensin aldosterone system; sFlt/PlGF: Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase and platelet growth factor ratio; ↑: Increased.
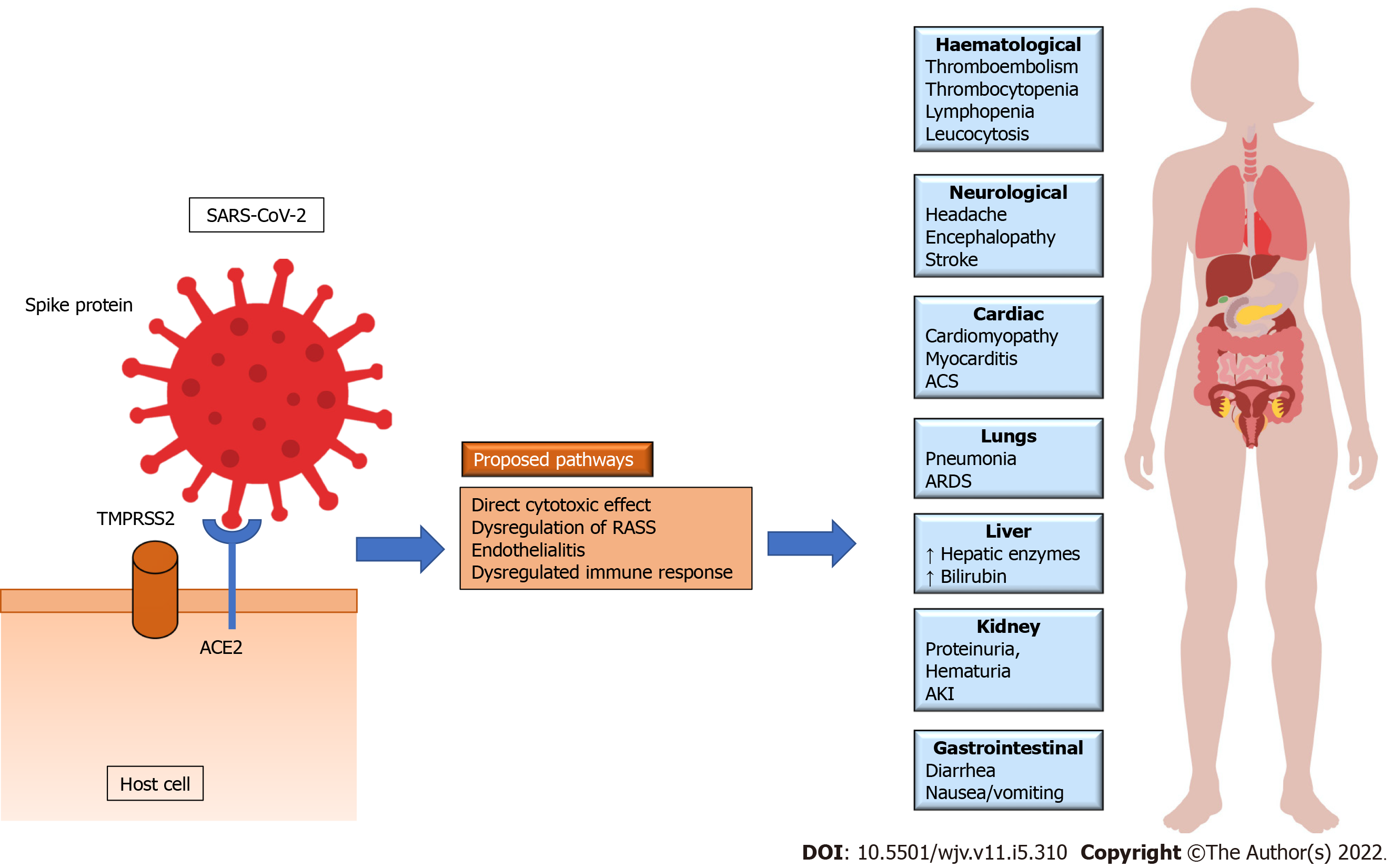
Figure 2 Pathogenesis of coronavirus disease 2019.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 entry into the host cell is mediated through its binding with angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor and transmembrane serine protease 2 enzyme. The pathogenetic pathways include direct cytotoxicity, endothelialitis, (endothelial damage), dysregulated host-immune response and renin-angiotensin aldosterone system. Respiratory system is the primary target organ, but other systems are involved either with direct invasion or in response of systemic dysregulated immune response. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane serine protease 2; RAAS: Renin angiotensin aldosterone system; ACS: Acute coronary syndrome; AKI: Acute kidney injury.
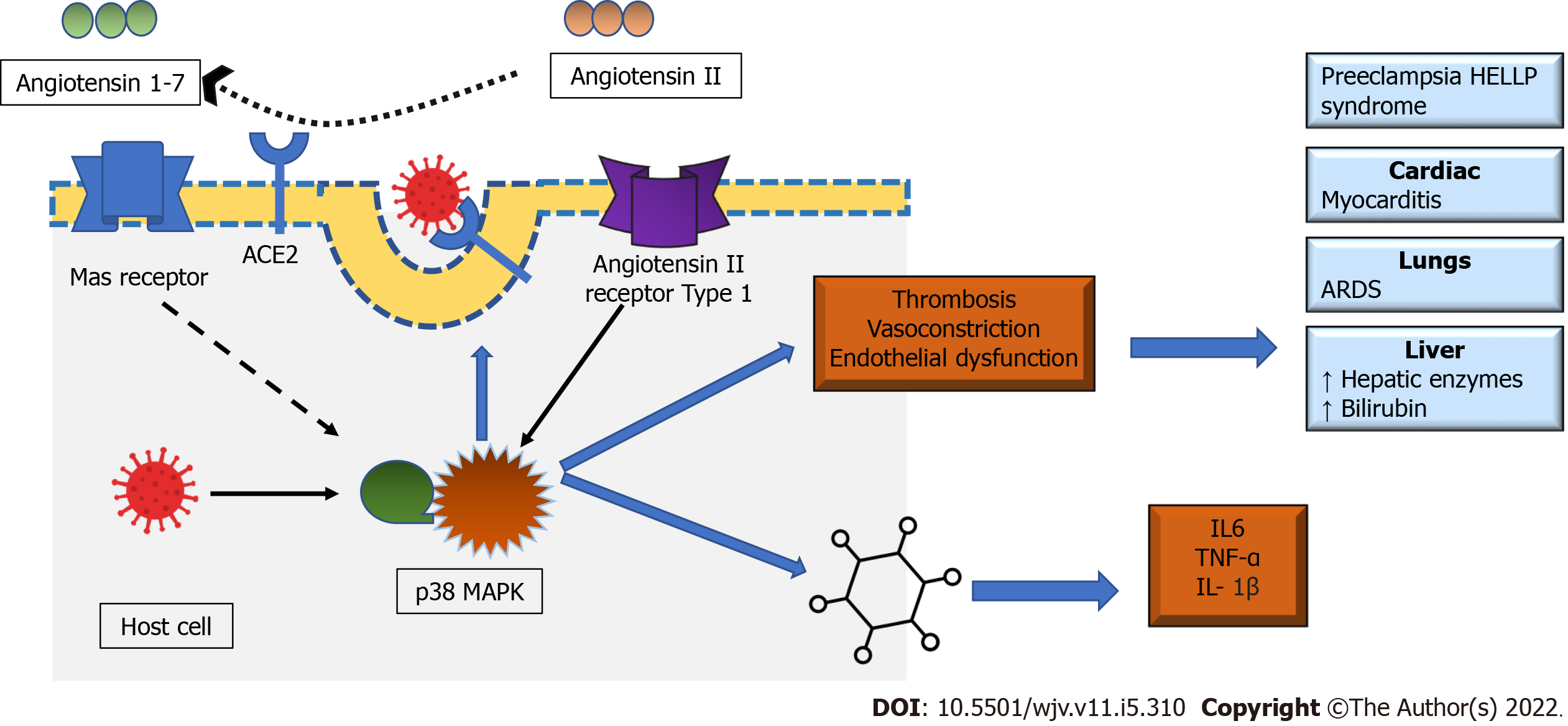
Figure 3 Pathophysiological linkage between coronavirus disease 2019 and Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets syndrome.
The binding of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) allows its entry to host cells and, subsequently, downregulation. ACE2 also converts angiotensin II (ATII) to angiotensin 1-7. The downregulation of ACE2 increases the concentration of AT II, which causes activation of the p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. p38 MAPK stimulates the production of inflammatory cytokines, platelet aggregation and thrombosis. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and ATII are also involved in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia and hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP) syndrome. Serum levels of p38 MAPK are elevated in the HELLP syndrome. ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; HELLP: Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count;ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Solid black arrow- stimulation (positive feedback), Dashed black arrow- inhibition (negative feedback), blue arrow: Effects of p38 MAPK overexpression.
- Citation: Nasa P, Juneja D, Jain R, Nasa R. COVID-19 and hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and thrombocytopenia syndrome in pregnant women - association or causation? World J Virol 2022; 11(5): 310-320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i5/310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.310