Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Jul 25, 2022; 11(4): 176-185
Published online Jul 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i4.176
Published online Jul 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i4.176
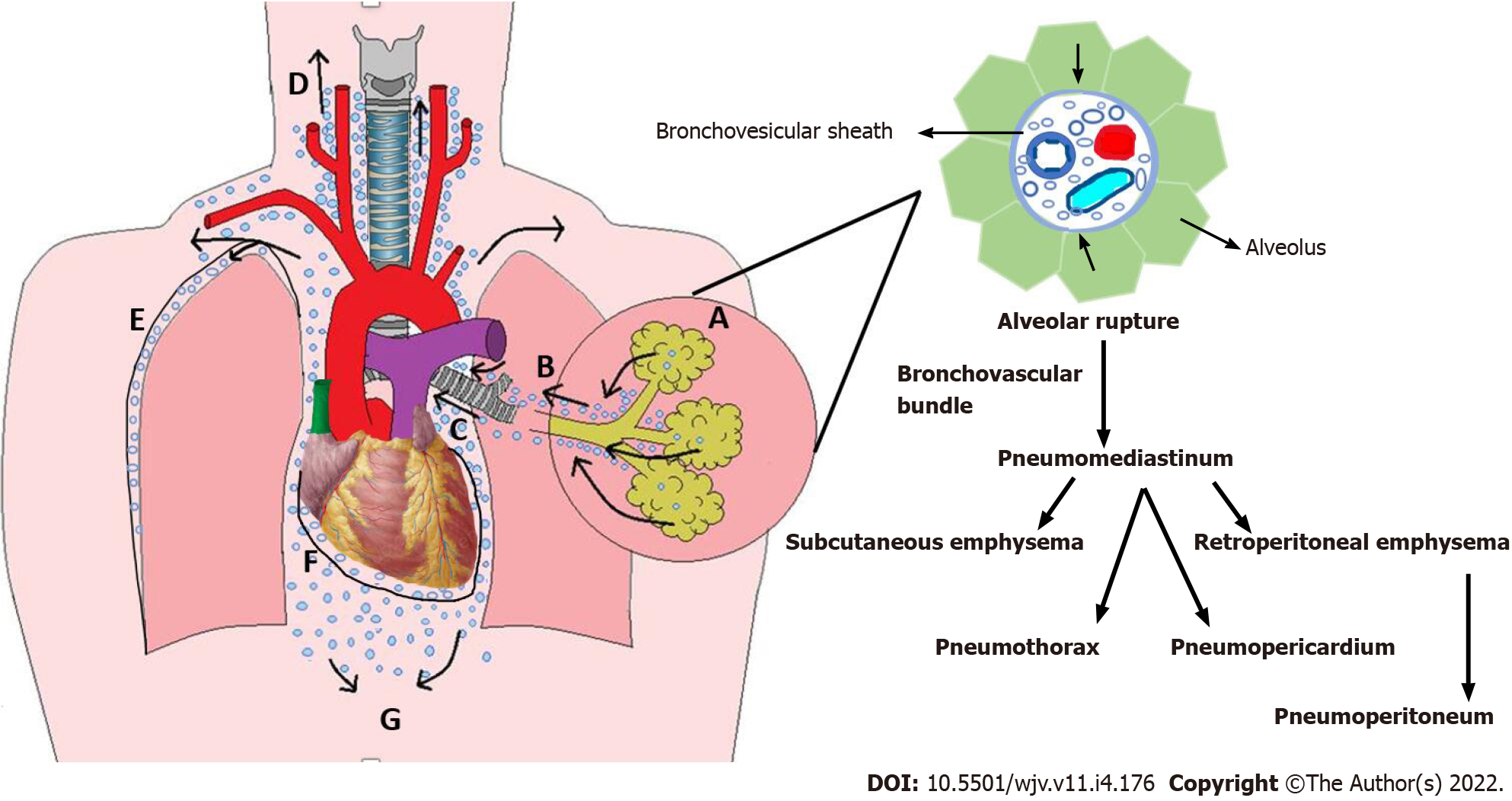
Figure 1 Macklin effect.
A: Macklin effect - Increase in pressure gradient between the damaged marginal alveoli and lung interstitium due to increase in intrathoracic pressure and or decrease pulmonary intravascular pressure, leads to alveoli rupture and development of interstitial emphysema; B: Air disseminates in the peribronchovascular space up to the pulmonary hila; C: Pnemomediastinum; D: Subcutaneous emphysema; E: Pneumothorax; F: Pneumopericardium; G: Retroperitoneal emphysema.
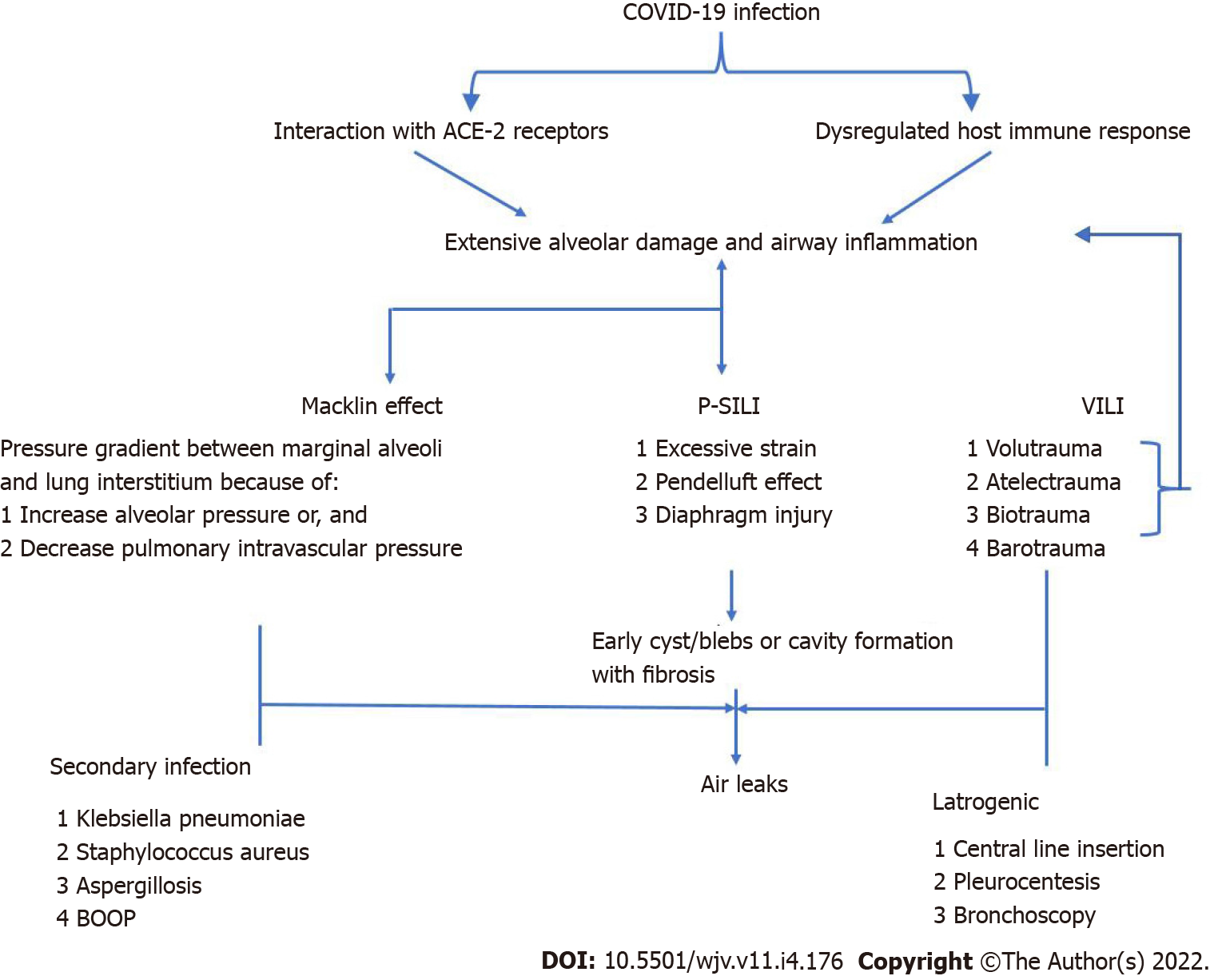
Figure 2 Pathogenesis of air leaks in coronavirus disease 2019.
COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; ACE-2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2; P-SILI: Patient self-inflicted lung injury; VILI: Ventilator-induced lung injury.
- Citation: Juneja D, Kataria S, Singh O. Air leaks in COVID-19. World J Virol 2022; 11(4): 176-185
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i4/176.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i4.176