Copyright
©2013 Baishideng.
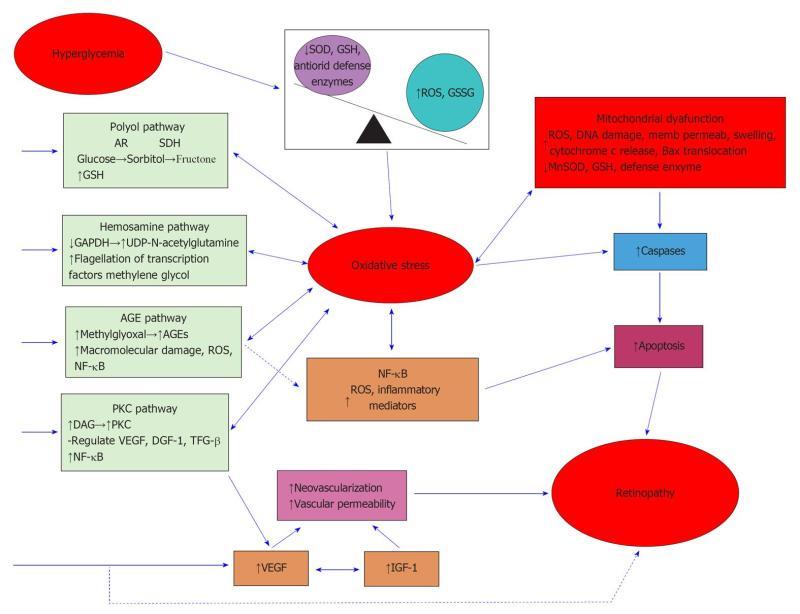
Figure 1 Oxidative stress mediated dysmetabolisms in diabetic retinopathy.
AR: Aldose reductase; SDH: Sorbitol dehydrogenase; GSH: Glutathione; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; AGEs: Advanced glycation end product; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB; PKC: Protein kinase C; DAE: Diacylglycerol; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; DGF-1: Dispersed gene family-1; TFG-β: Transforming growth factor-β; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSSG: Oxidant glutathione; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; MnSOD: Manganese superoxide dismutase. Reproduced with permission from[200].
Figure 2 Chemical structure of hesperidin (A) and hesperetin (B).
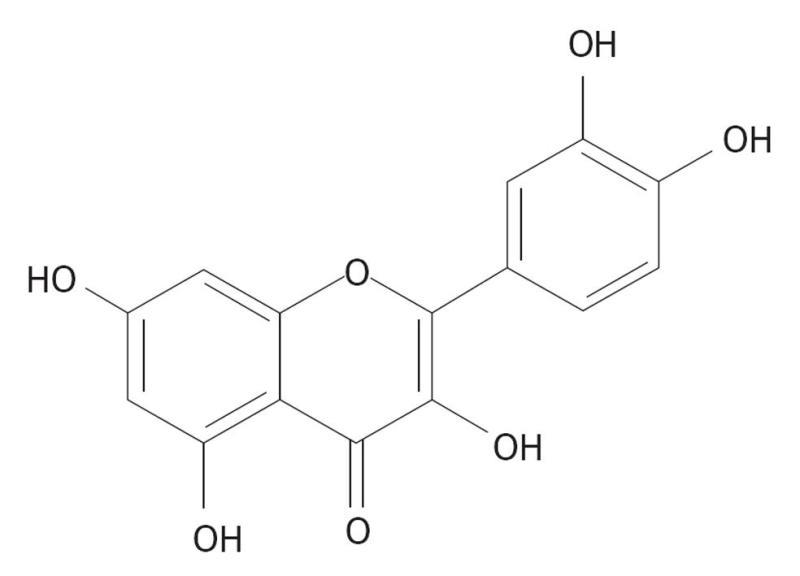
Figure 3 Chemical structure of quercetin [2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one].
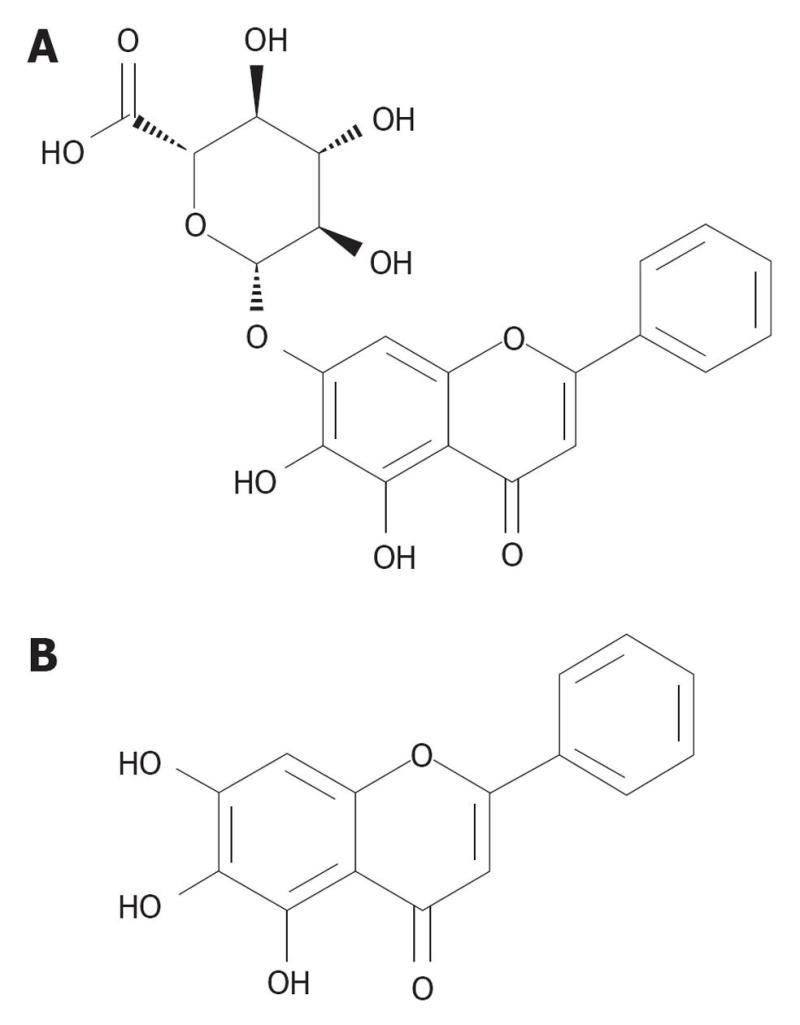
Figure 4 Chemical structure of (A) Baicalein (Baicalein 7-O-glucuronide; 5,6-Dihydroxy-4-oxygen-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-7-beta-D-glucopyranose acid) (B) baicalein (5,6,7-Trihydroxy-2-phenyl-chromen-4-one).
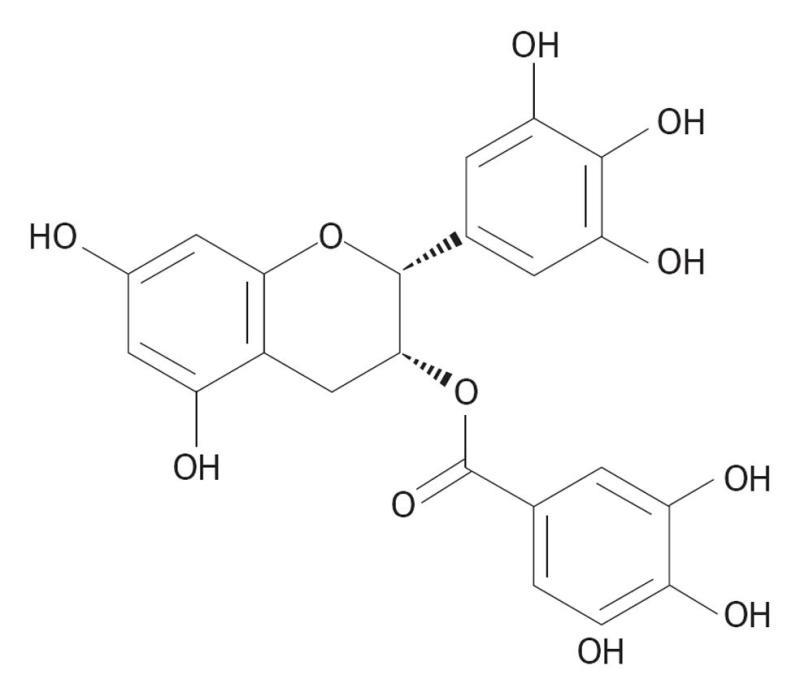
Figure 5 Chemical structure of epigallocatechin gallate [(2R,3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)chroman-3-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate.
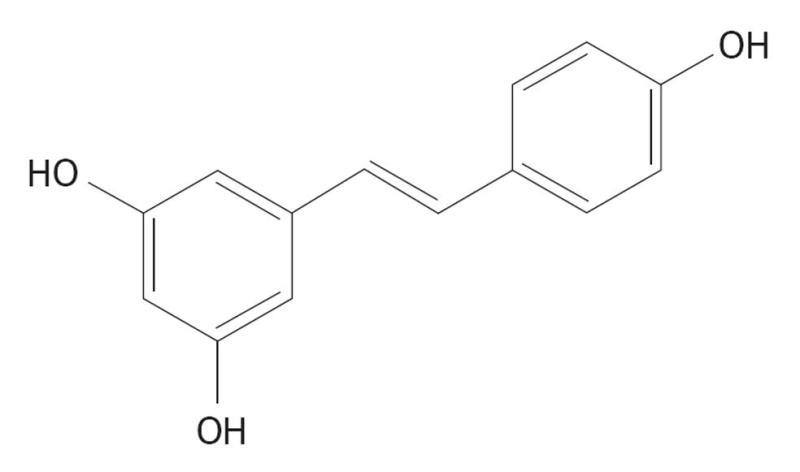
Figure 6 Chemical structure of Resveratrol is 3,5,4'-trihydroxystilbene.
- Citation: Adelli GR, Srirangam R, Majumdar S. Phytochemicals in ocular health: Therapeutic potential and delivery challenges. World J Pharmacol 2013; 2(1): 18-34
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v2/i1/18.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v2.i1.18