Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Clin Infect Dis. Nov 25, 2015; 5(4): 86-93
Published online Nov 25, 2015. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v5.i4.86
Published online Nov 25, 2015. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v5.i4.86
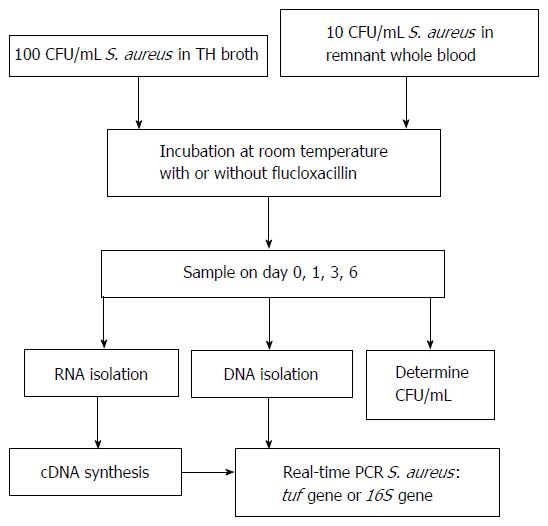
Figure 1 Overview of the experimental setup.
CFU: Colony forming unit; S. aureus: Staphylococcus aureus; TH: Todd Hewitt; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
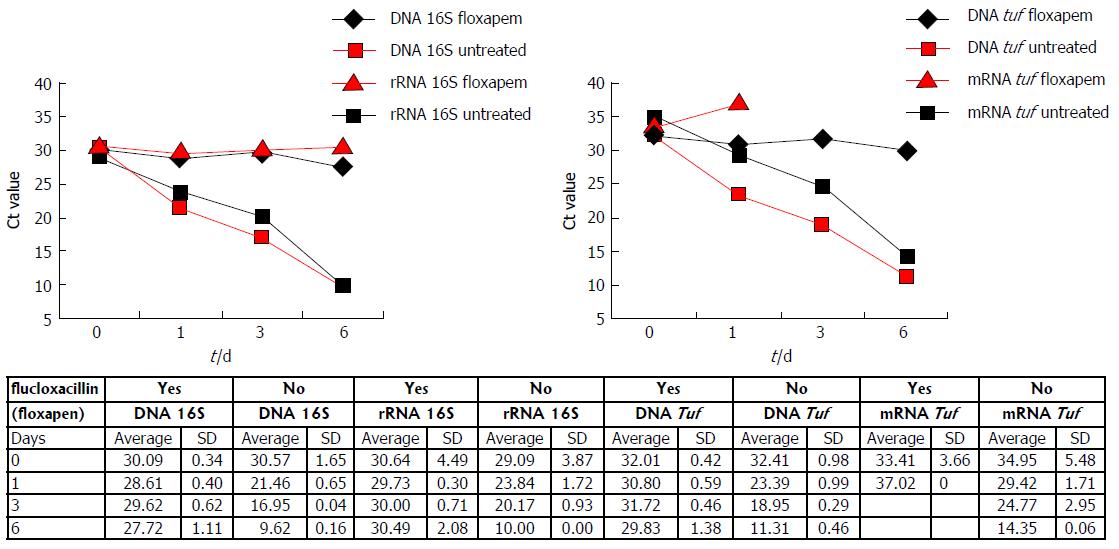
Figure 2 Staphylococcus aureus polymerase chain reaction results with and without flucloxacillin treatment in Todd Hewitt broth.
S. aureus bacteria (100 CFU/mL) continue to grow in absence of flucloxacillin and as a result DNA and RNA levels of both tuf and 16S increase in time (Ct values decrease). When flucloxacillin is added 16S DNA, 16S rRNA, and tuf DNA levels remain relatively stable in time. Whereas tuf DNA is still detectable, tuf mRNA is not detectable on day 3 and 6 after flucloxacillin treatment. The experiment was performed twice. Ct values are depicted. CFU: Colony forming unit; S. aureus: Staphylococcus aureus.
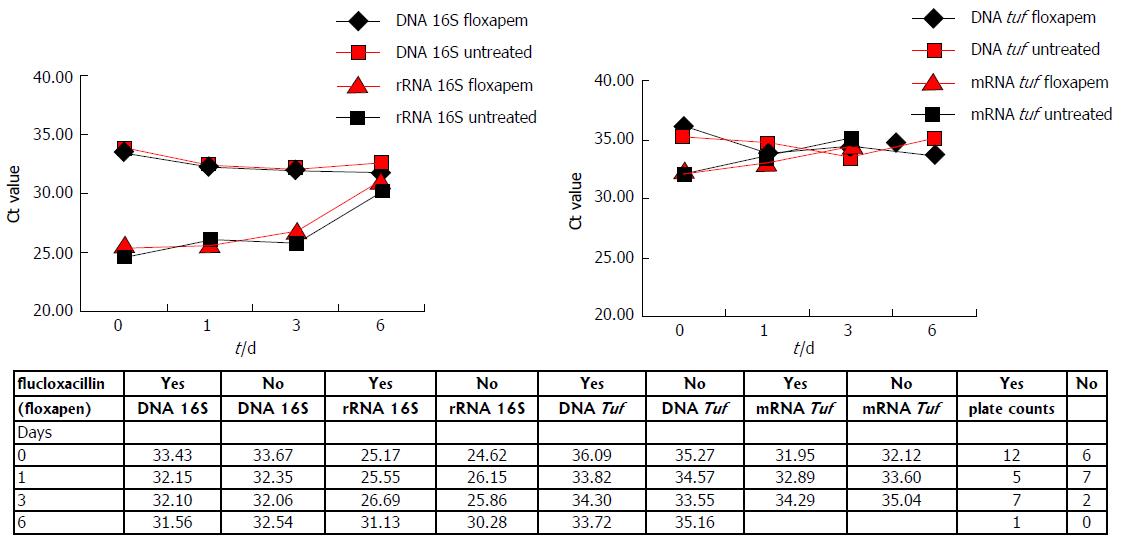
Figure 3 Staphylococcus aureus polymerase chain reaction results with and without flucloxacillin treatment in whole blood.
Both 16S and tuf DNA levels remain relatively stable in time in presence and absence of flucloxacillin. 16S rRNA and tuf mRNA show an increase in Ct values (reduction in RNA level). Tuf mRNA was not detectable on day 6. Ct values and CFU/mL (plate counts) are depicted.
-
Citation: Loonen AJ, Wolffs PF, de Bresser M, Habraken M, Bruggeman CA, Hermans MH, van den Brule AJ.
Tuf mRNA rather than 16S rRNA is associated with culturableStaphylococcus aureus . World J Clin Infect Dis 2015; 5(4): 86-93 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3176/full/v5/i4/86.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5495/wjcid.v5.i4.86