Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Sep 20, 2025; 15(3): 108025
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.108025
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.108025
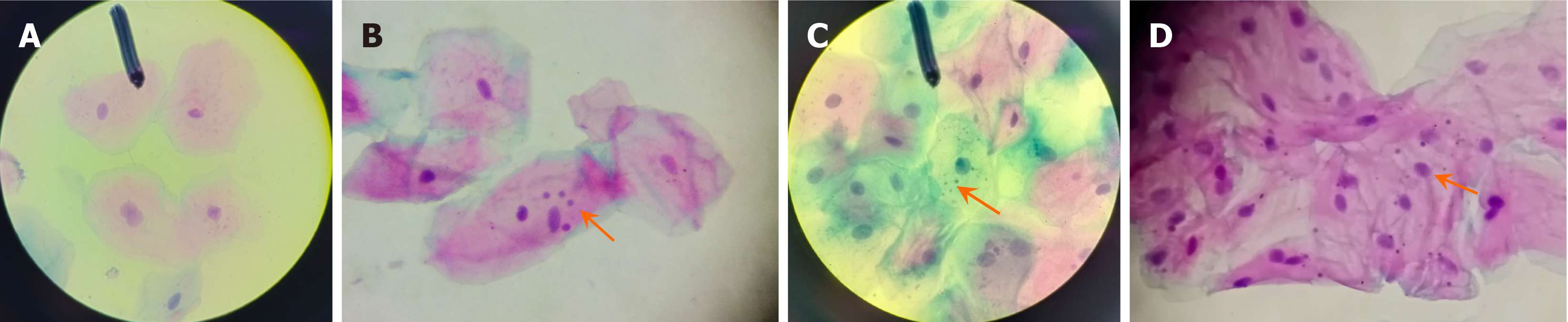
Figure 1 Samples examined under 40 × magnification, categorized by the number of micronuclei.
A: Absent; B: Rare; C: Moderate; D: Abundant. Indicators highlight the presence of micronuclei in each image.
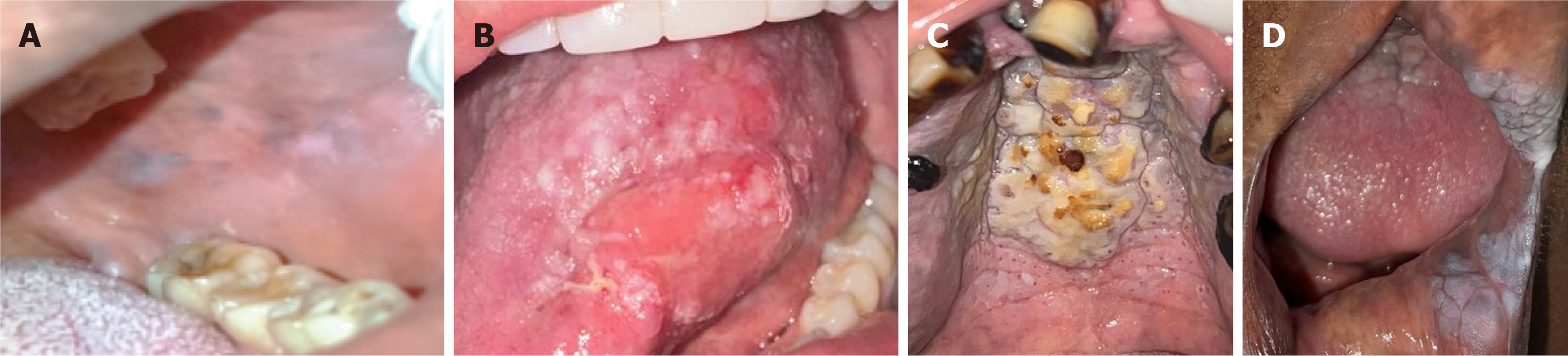
Figure 2 Intraoral photographs of observed lesions.
A: Buccal mucosal leukoedema in a to-bacco smoker; B: In situ carcinoma of the tongue in an electronic cigarette user; C: Palate of an in-verted smoker; D: Verrucous leukoplakia in an inverted smoker.
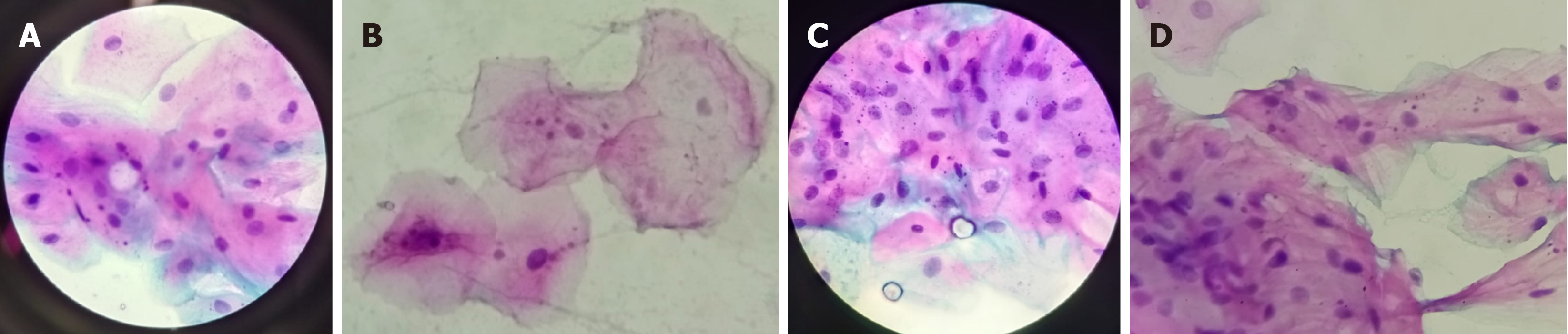
Figure 3 Data on micronucleus occurrence.
A: Conventional smokers (moderate occurrence); B: Marijuana smokers (low occurrence); C: Reverse smokers (abundant occurrence); D: E-cigarette smokers (moderate occurrence).
- Citation: Álvarez-Martínez E, Porto-Puerta IE, Ardila CM. Genotoxic damage assessment using the micronucleus assay in buccal mucosa of different types of smokers: A cross-sectional study. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(3): 108025
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v15/i3/108025.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.108025