Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Pediatr. Sep 9, 2025; 14(3): 105290
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i3.105290
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i3.105290
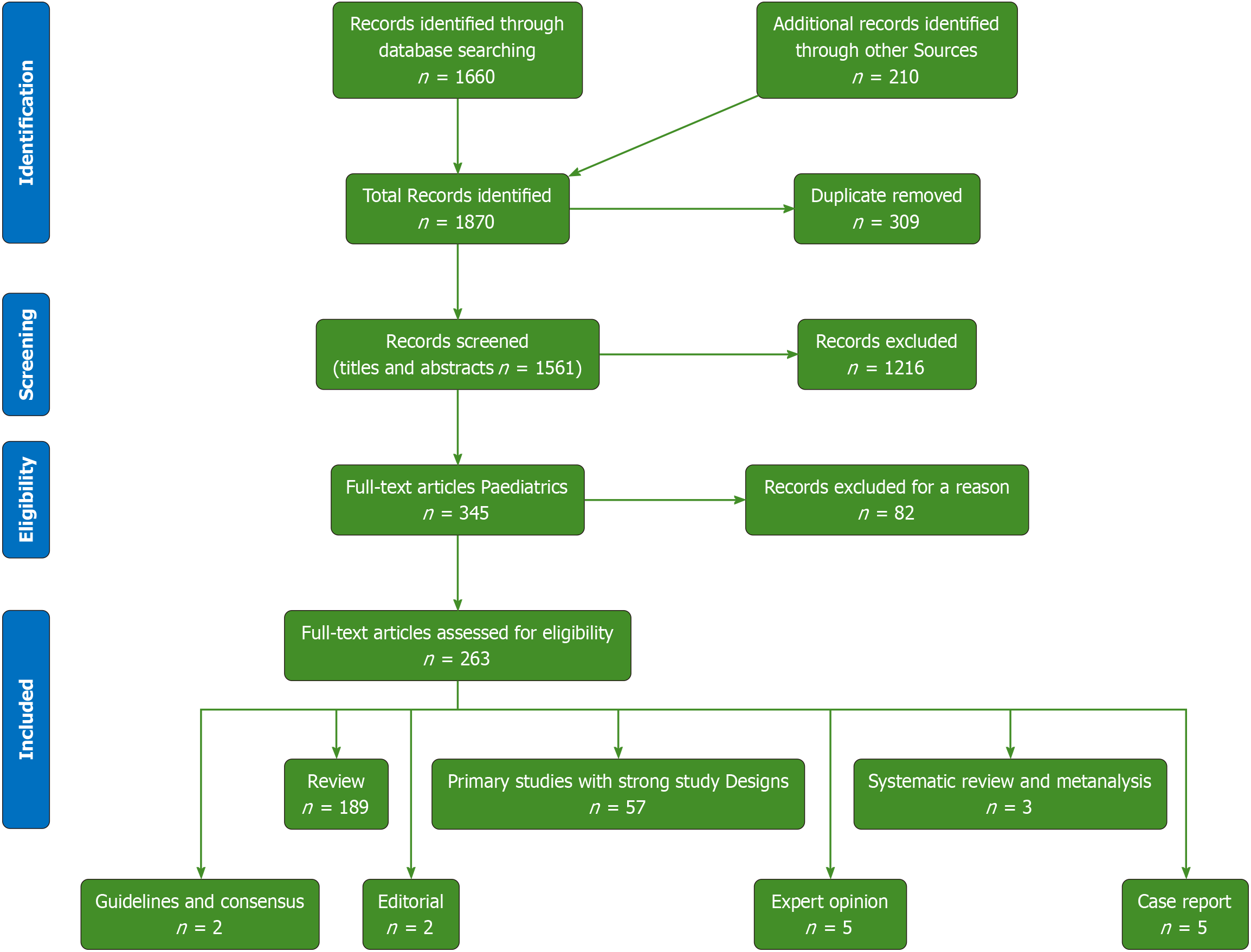
Figure 1 The flow chart of the study.
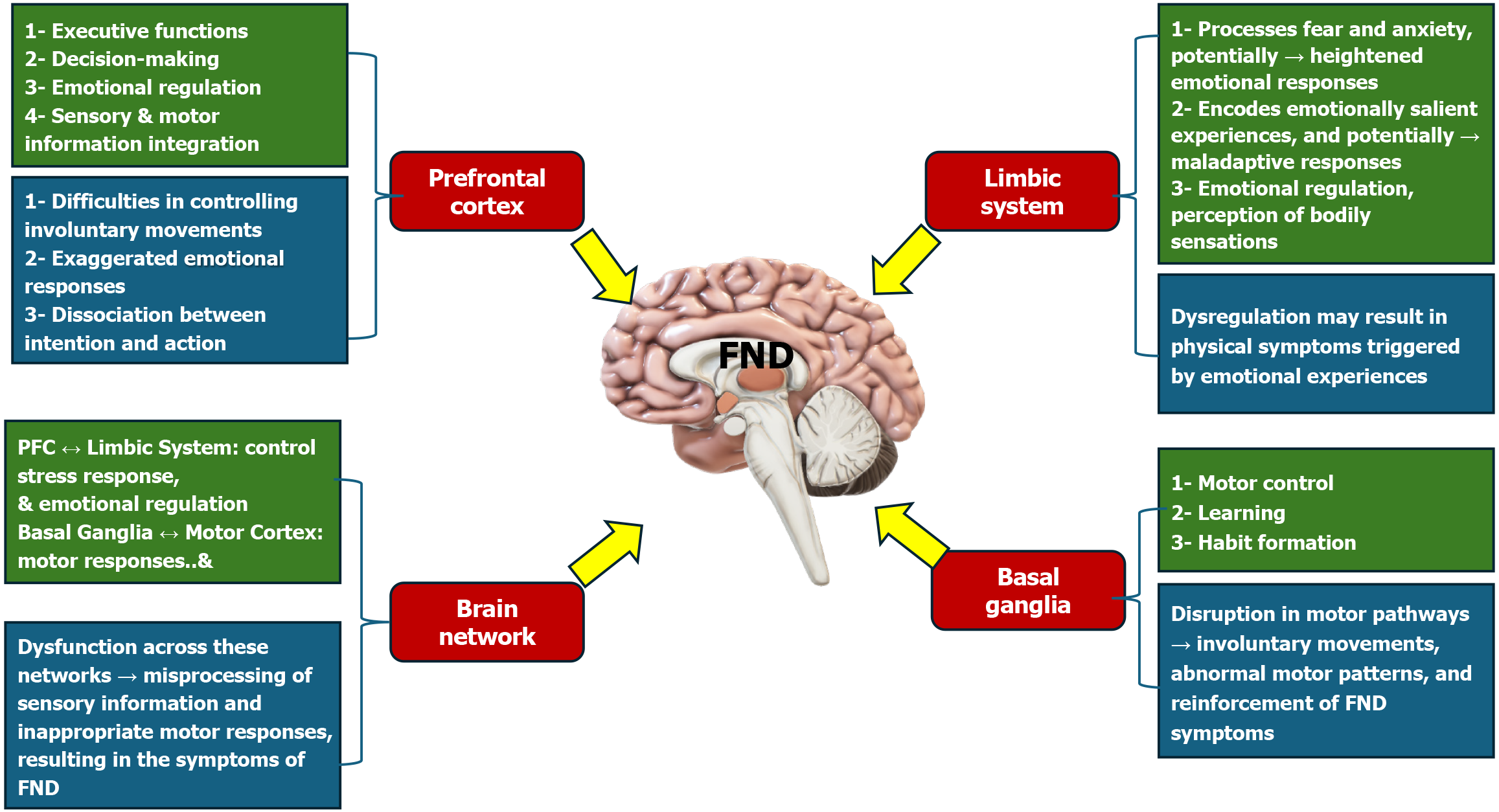
Figure 2 The role of brain networks in functional neurological disorder.
This diagram illustrates the interconnected role of various brain networks in developing and manifesting functional neurological disorder (FND). The prefrontal cortex, limbic system, and basal ganglia are highlighted as key regions that contribute to the symptoms of FND through their respective functions and interactions. Prefrontal cortex: Involved in executive functions, decision-making, emotional regulation, and integration of sensory and motor information. Dysfunctions in this area can lead to difficulties in controlling involuntary movements, exaggerated emotional responses, and dissociation between intention and action. Limbic system: Responsible for processing emotions, memories, and stress responses. Dysregulation in this system, particularly in the amygdala, hippocampus, and cingulate cortex, can cause physical symptoms triggered by emotional experiences. Basal ganglia: Plays a critical role in motor control, learning, and habit formation. Abnormalities in this region can lead to involuntary movements, abnormal motor patterns, and reinforcement of FND symptoms. Interconnectivity and network dysfunction: The diagram also emphasizes the complex interplay between these networks, where disruptions in communication can lead to the misprocessing of sensory information and inappropriate motor responses, which are characteristic of FND. The interconnected nature of these brain regions suggests that FND symptoms arise from widespread network dysfunction rather than isolated brain abnormalities. FND: Functional neurological disorder.
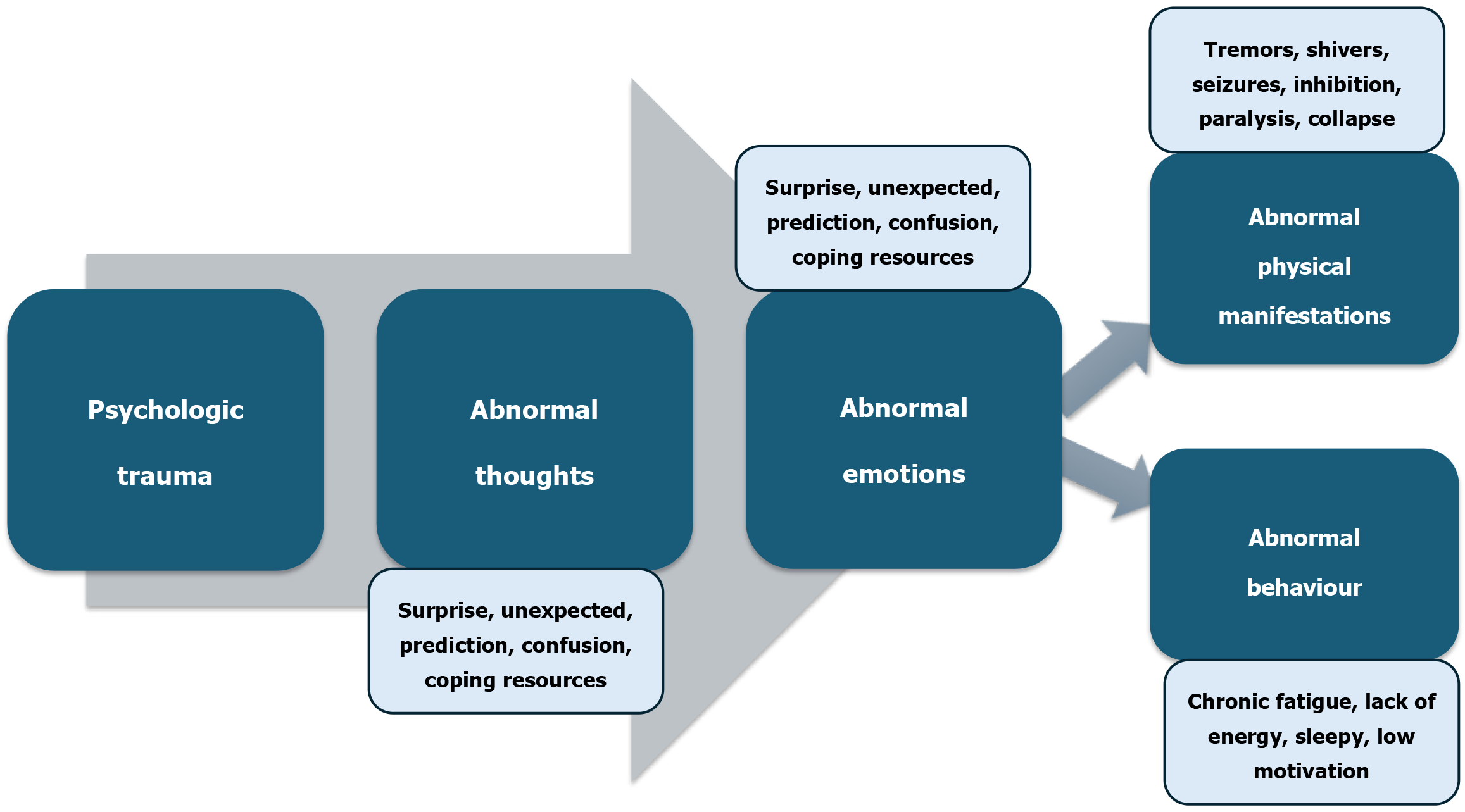
Figure 3 The cascade of developing functional neurogenic disorders after psychological trauma.
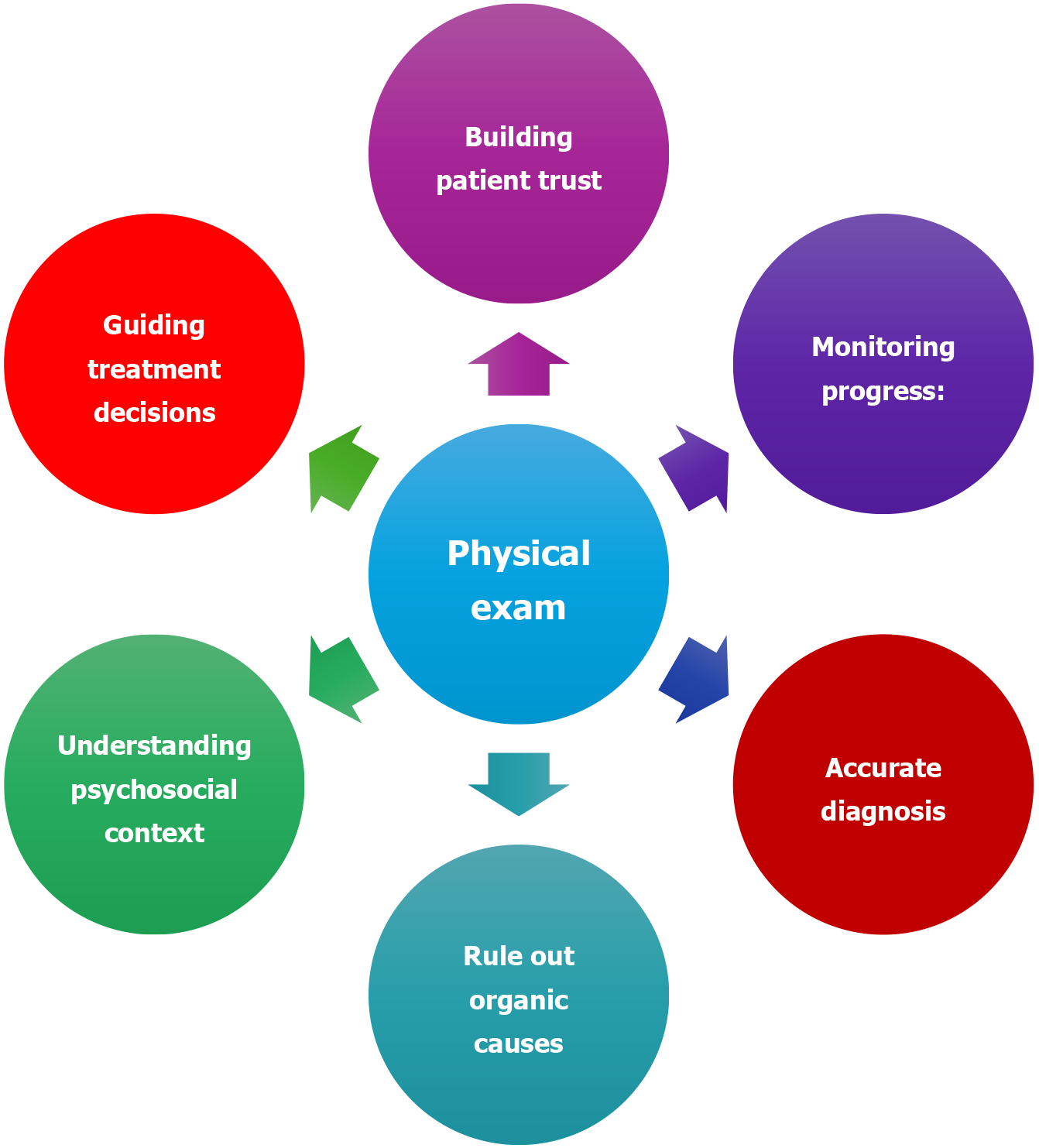
Figure 4 Importance of a thorough clinical assessment in functional neurogenic disorders.
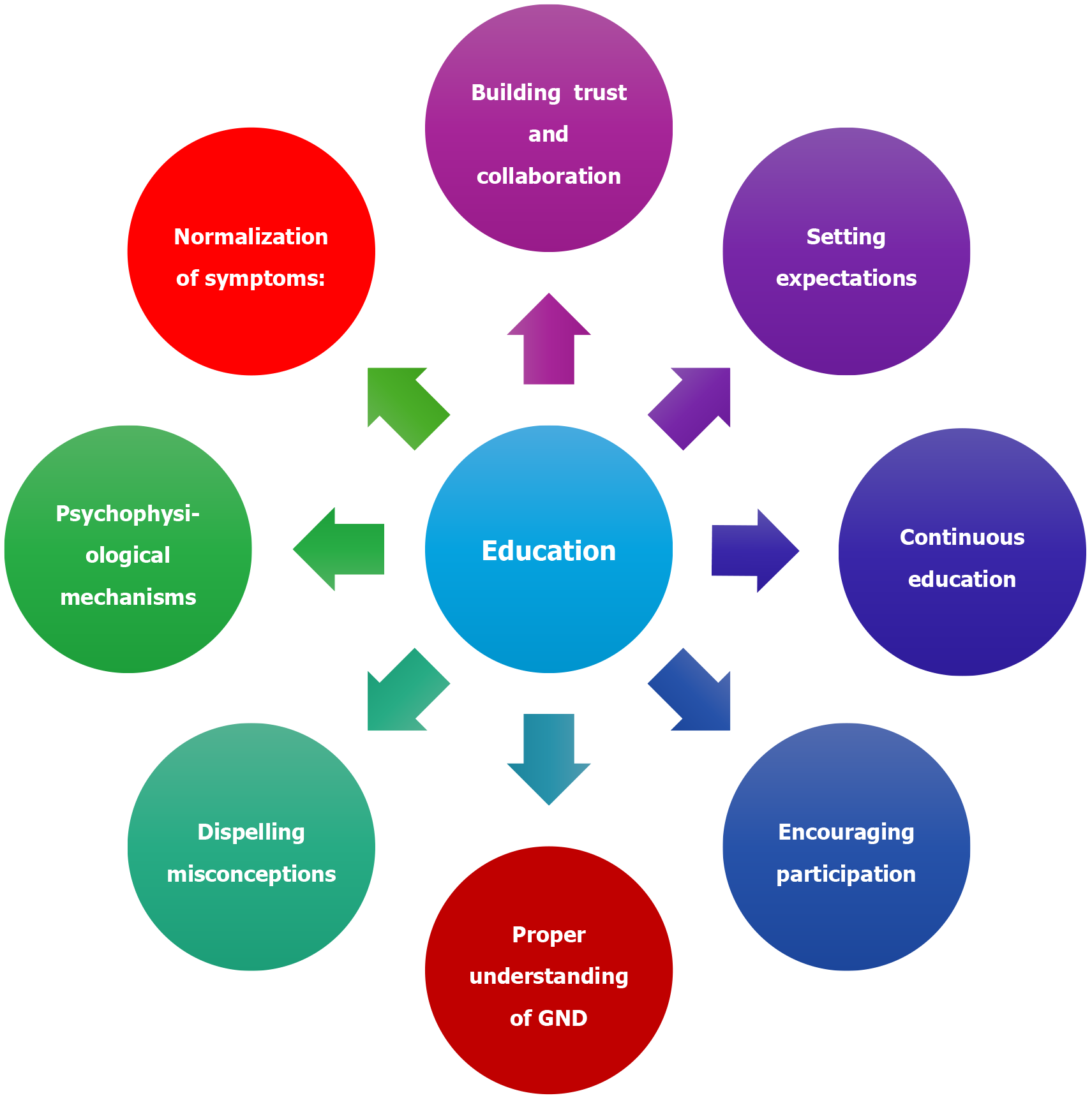
Figure 5 Pillars of education and communication with patients and families in pediatric functional neurogenic disorders.
- Citation: Al-Beltagi M, Saeed NK, Bediwy AS, Bediwy EA, Elbeltagi R. Unraveling functional neurological disorder in pediatric populations: A systematic review of diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. World J Clin Pediatr 2025; 14(3): 105290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v14/i3/105290.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v14.i3.105290