Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Pediatr. Sep 9, 2025; 14(3): 104951
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i3.104951
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i3.104951
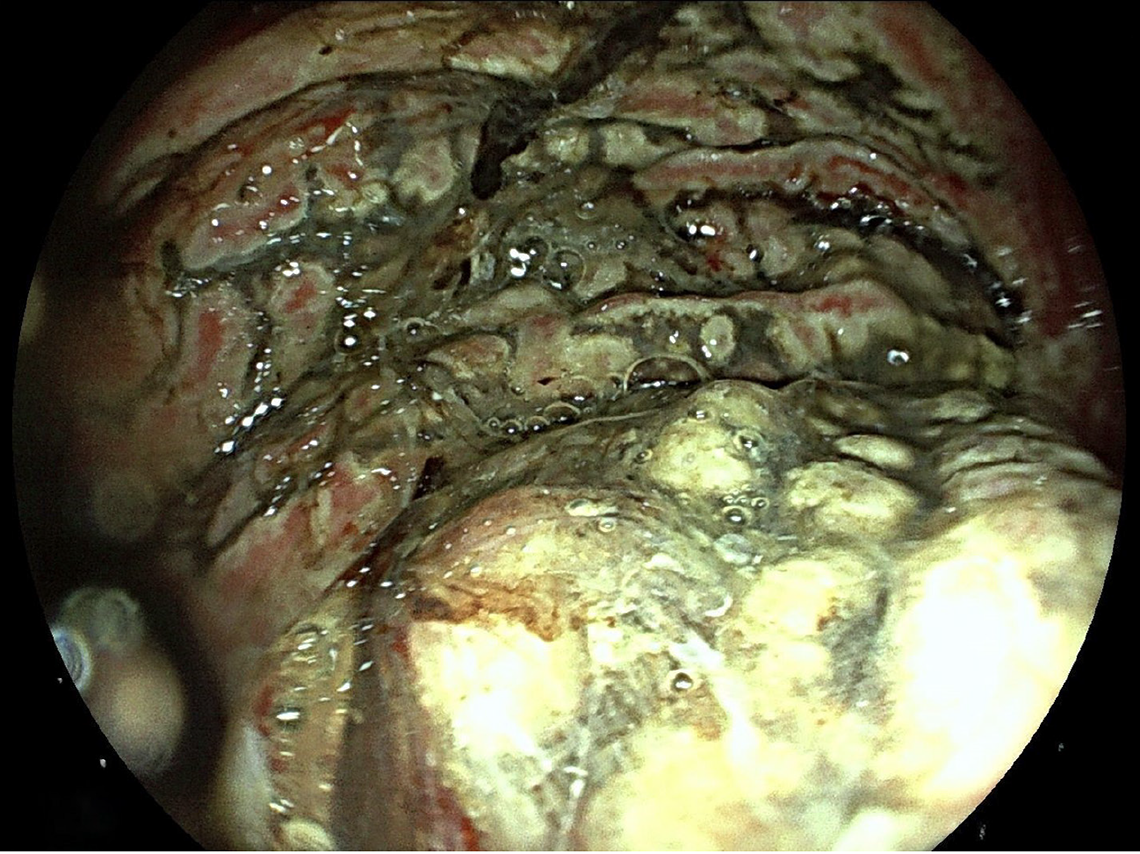
Figure 1 Endoscopic images showing extensive gastric necrosis on esophagogastroduodenoscopy, obtained 20 hours after the ingestion of caustic substances in a 2-year-old boy.
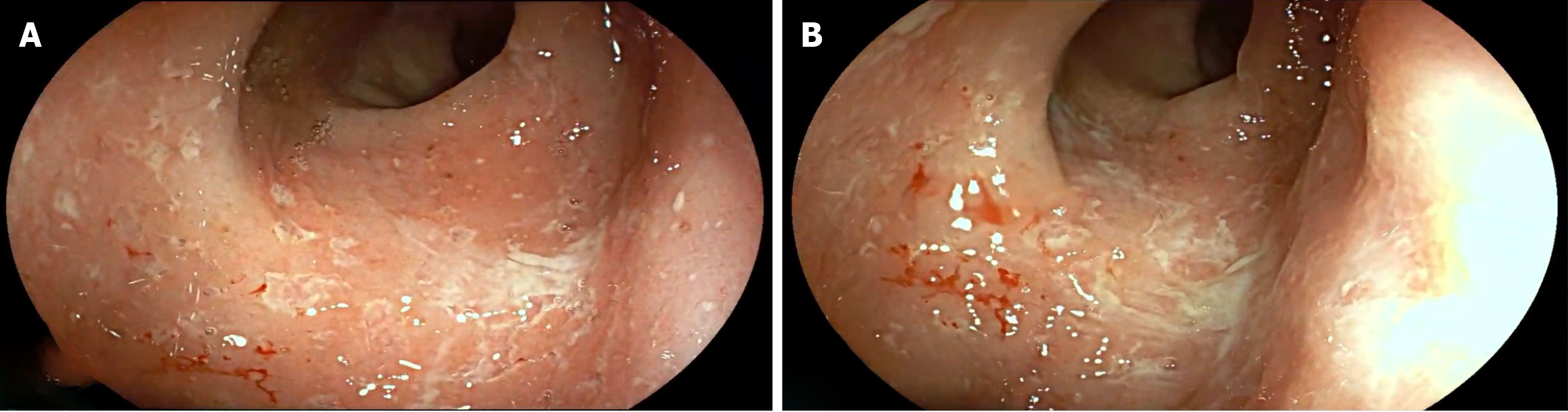
Figure 2 Colonoscopic pictures of Crohn's disease in a 7-year-old boy.
A and B: Multiple rectal ulcers.
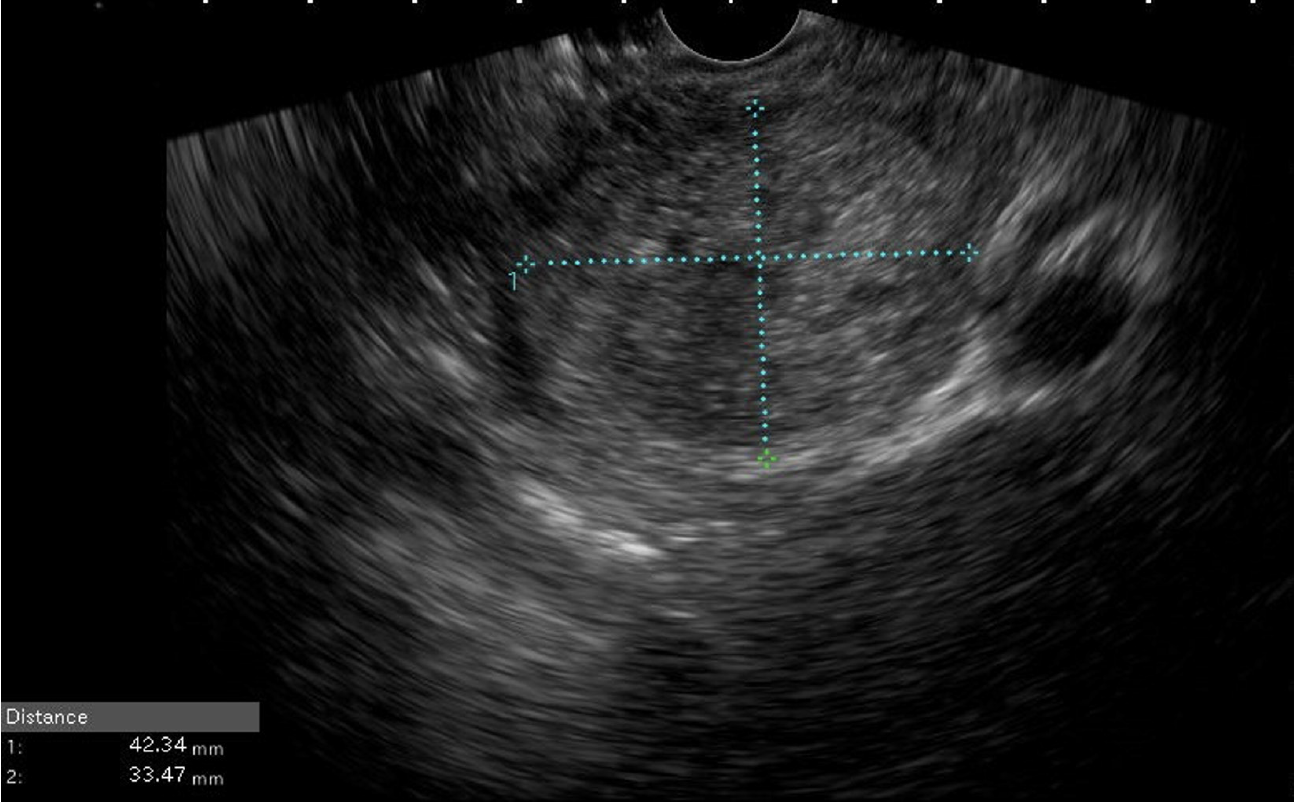
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasound image of pancreatic body solid pseudo papillary neoplasm in a young female (15 years old).
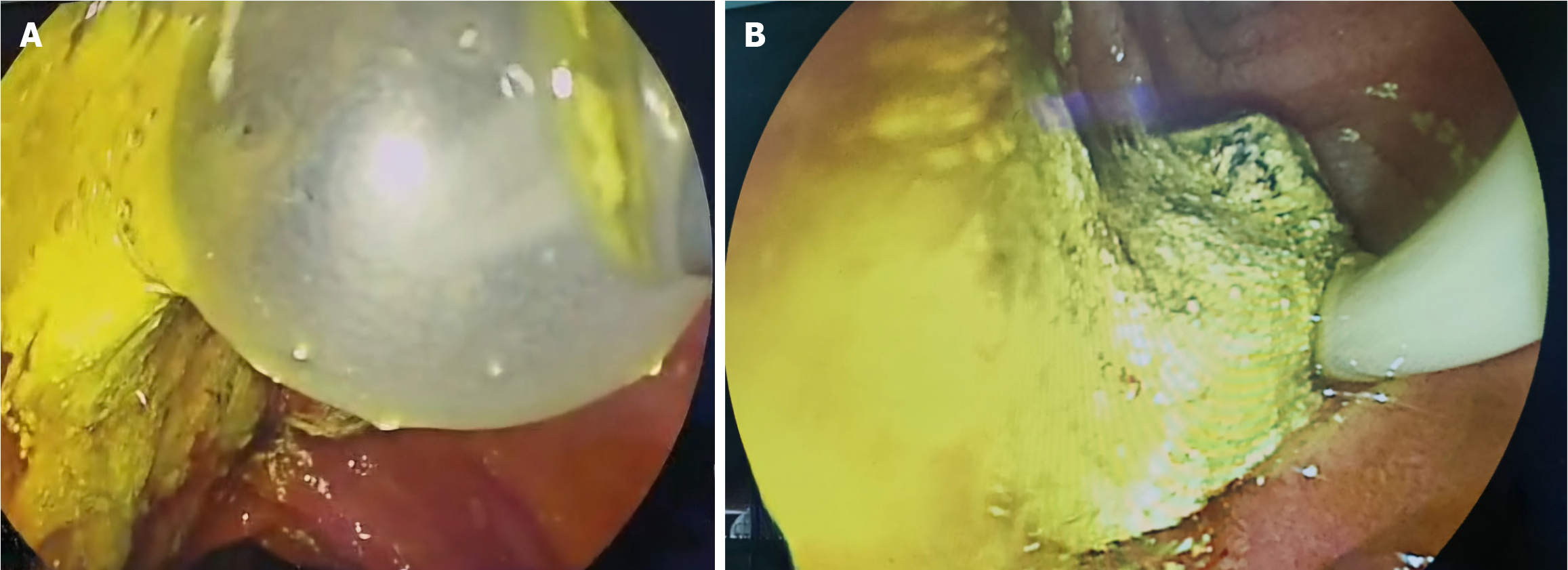
Figure 4 Image of bile duct stones removed by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in a 13-year-old girl admitted for biliary cholangitis.
A: Stones removed with balloon; B: Small bile duct stones.
- Citation: Okasha HH, El-Meligui A, Ghoneem E, Alyouzbaki AZ, Ait Errami A, Delsa H. Paediatric digestive endoscopy: From conventional endoscopy to endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. World J Clin Pediatr 2025; 14(3): 104951
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v14/i3/104951.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v14.i3.104951