Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hematol. Jan 17, 2023; 10(2): 15-24
Published online Jan 17, 2023. doi: 10.5315/wjh.v10.i2.15
Published online Jan 17, 2023. doi: 10.5315/wjh.v10.i2.15
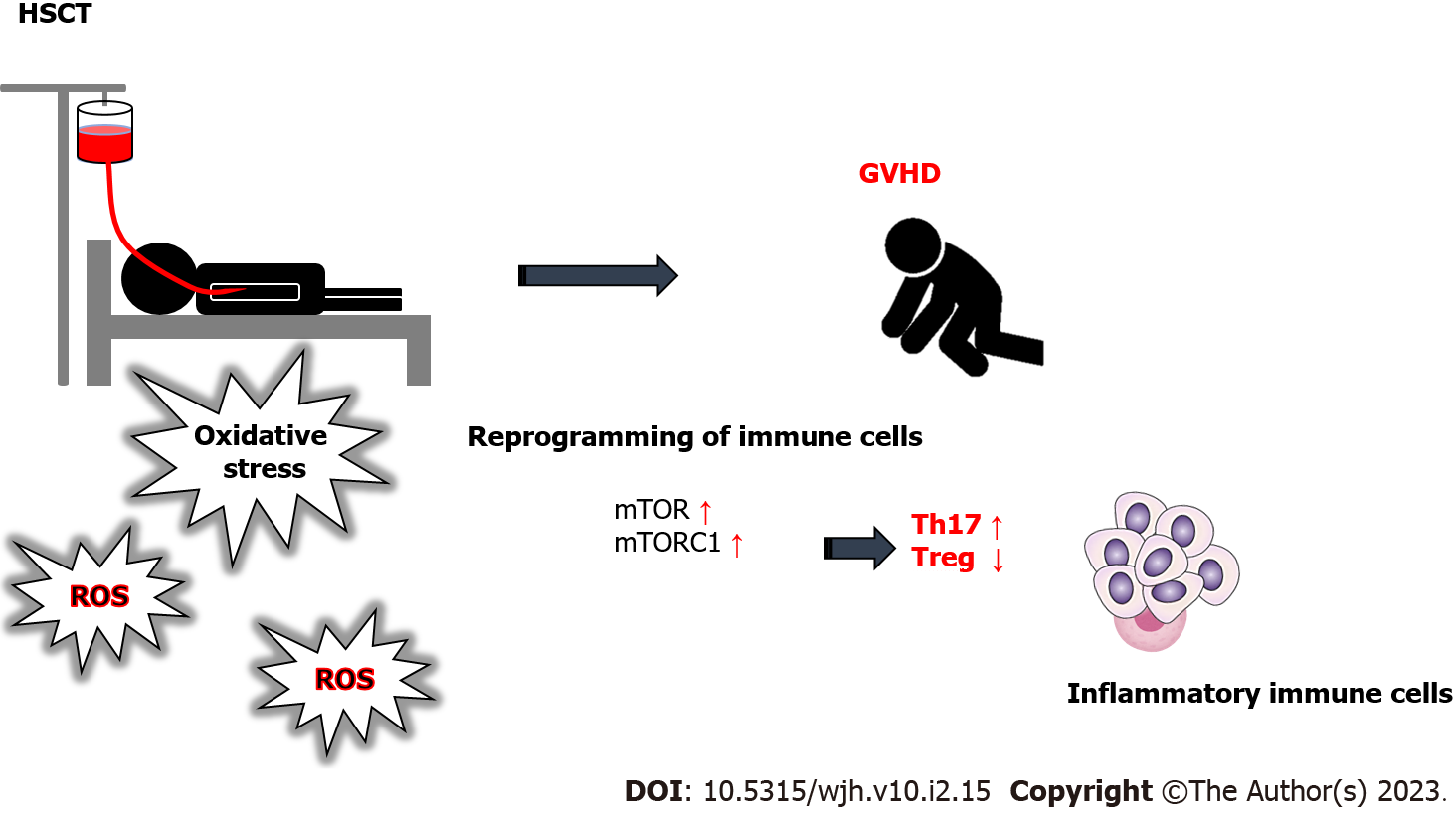
Figure 1 Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients likely to suffer from the graft-versus-host disease.
Oxidative stress, reactive oxygen species, and/or inflammation may be all involved in the pathogenesis of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) following the expansion of Th17 cells, which may help increase GVHD severity through the activation of pathogenic inflammatory immune cells. Arrowhead means stimulation and/or augmentation. Hammerhead represents inhibition. Note that some critical intracellular molecular pathways such as those related to mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) or mTORC have been omitted for clarity. ROS: Reactive oxygen species; GVHD: Graft-versus-host disease; HSCT: Hematopoietic cell transplantation.
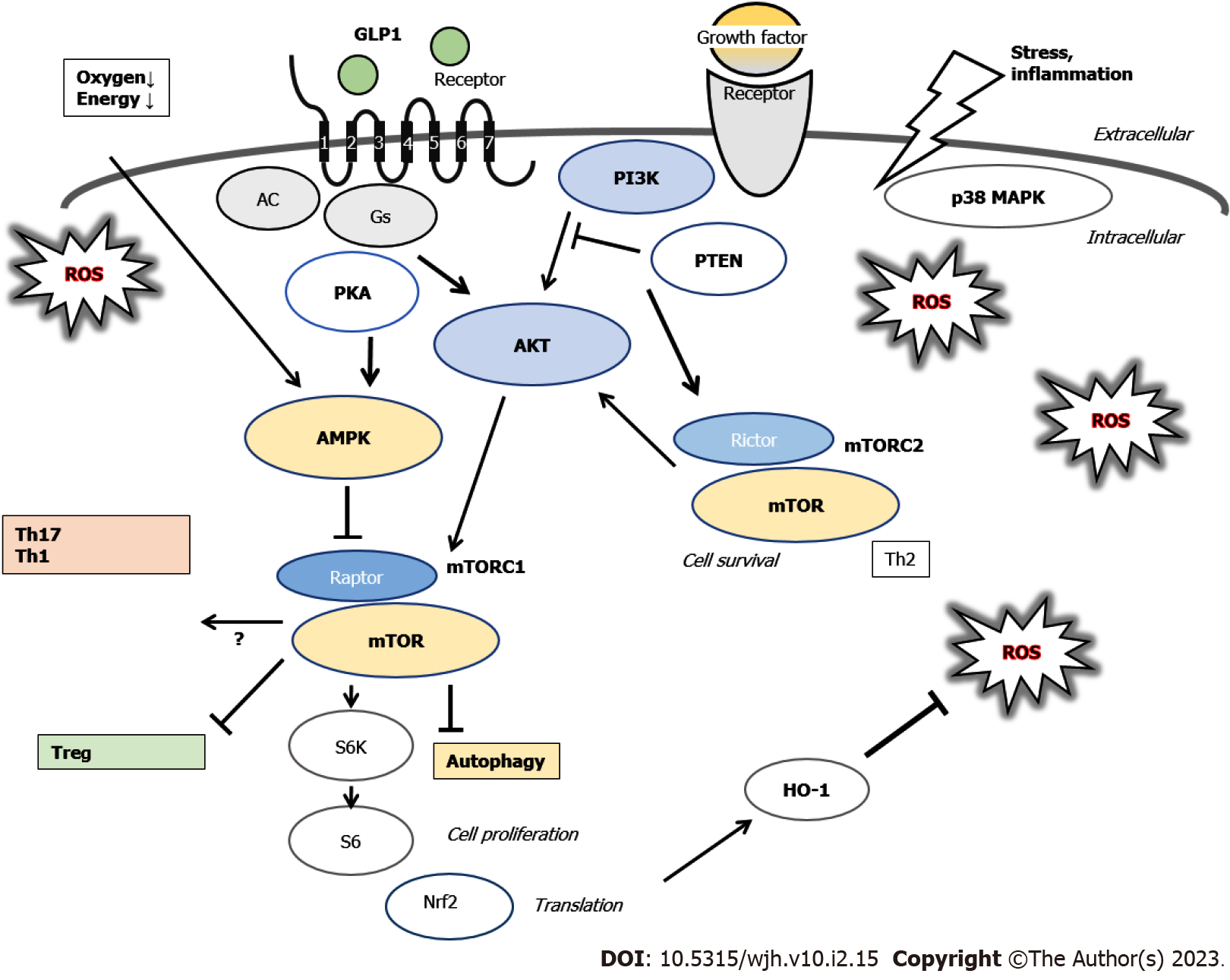
Figure 2 Several modulator molecules linked to the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR)/mTORC1 signaling pathway for the alteration of Th17, Th1, and/or Treg cells are demonstrated.
Example molecules known to act on the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/mTOR and/or PI3K/AKT signaling pathway are also shown. Note that some critical events such as immune activation and/or cytokine-induction in cases of inflammation and/or oxidative stress have been omitted for clarity. Arrowhead means stimulation whereas hammerhead represents inhibition. GLP1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; PKA: Protein kinase A; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; mTOR: Mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10.
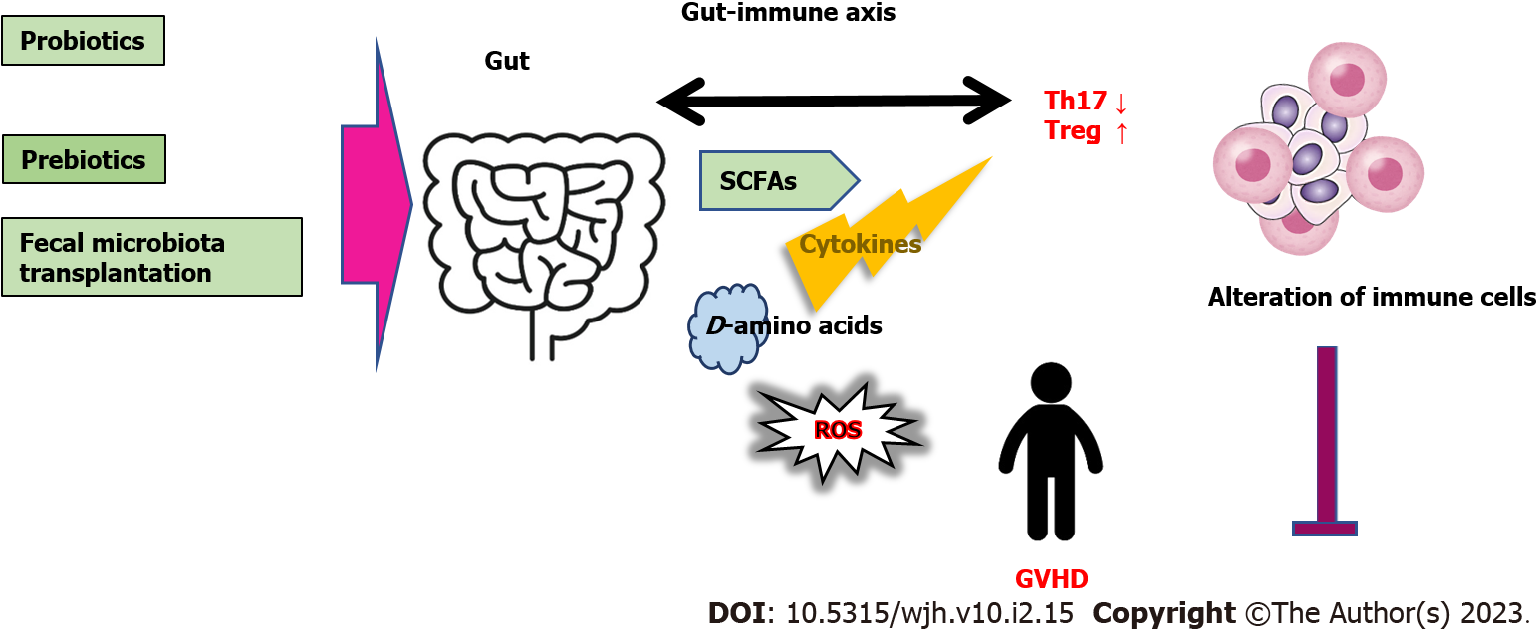
Figure 3 The gut microbiota could support to take a favorable action against the disease-progression of graft-versus-host disease by affecting the gut-immune axis, which may contain the inhibition or production of cytokines, reactive oxygen species, hort-chain fatty acids, and certain D-amino acids.
Probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation might be potential therapy for the alteration of gut microbiota. Arrowhead indicates stimulation whereas hammerhead shows inhibition. Note that several important activities such as cytokine-induction or anti-inflammatory reaction have been omitted for clarity. FMT: Fecal microbiota transplantation; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; GVHD: Graft-versus-host disease; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; SCFAs: Short chain fatty acids; Th17: Type 17 T helper cell; Treg: Regulatory T cell; GVHD: Graft-versus-host disease.
- Citation: Yoshikawa S, Taniguchi K, Sawamura H, Ikeda Y, Tsuji A, Matsuda S. Advantageous tactics with certain probiotics for the treatment of graft-versus-host-disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. World J Hematol 2023; 10(2): 15-24
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6204/full/v10/i2/15.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5315/wjh.v10.i2.15