Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Oncol. May 10, 2011; 2(5): 203-216
Published online May 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i5.203
Published online May 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i5.203
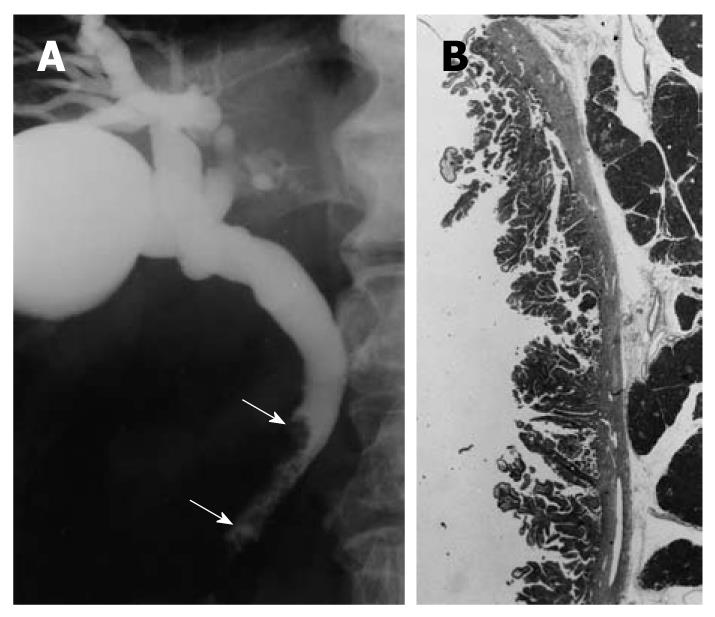
Figure 1 Cholangiographic finding of extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma in the nonicteric stage.
A: Cholangiography shows a papillary tumor at the distal common bile duct (arrows); B: The histologic findings of the resected specimen showed papillary adenocarcinoma confined to the mucosal layer (hematoxylin and eosin, × 1).
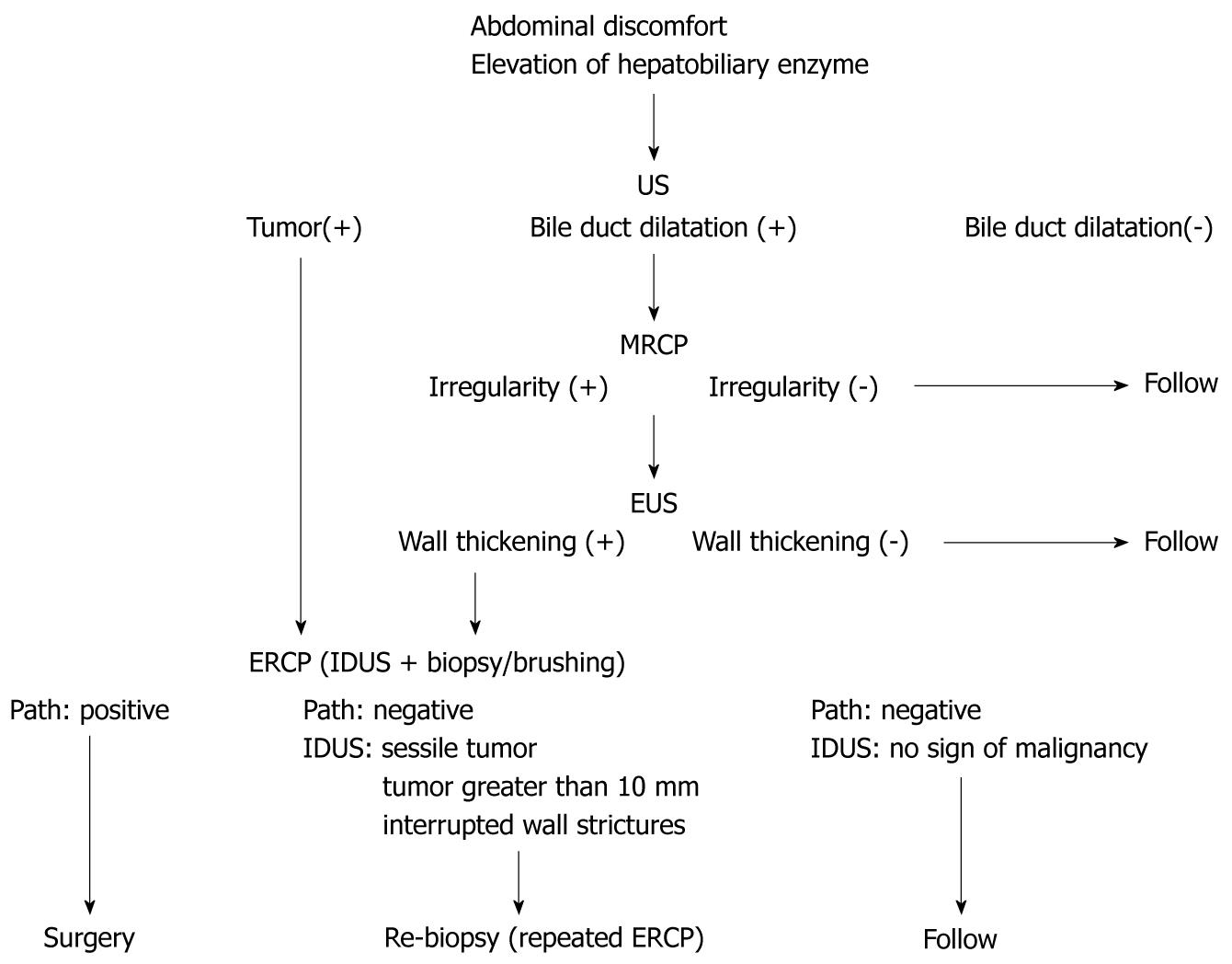
Figure 2 Diagnostic methods for extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma without jaundice.
US: Ultrasonography; MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasonography; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; IDUS: Intraductal ultrasonography.
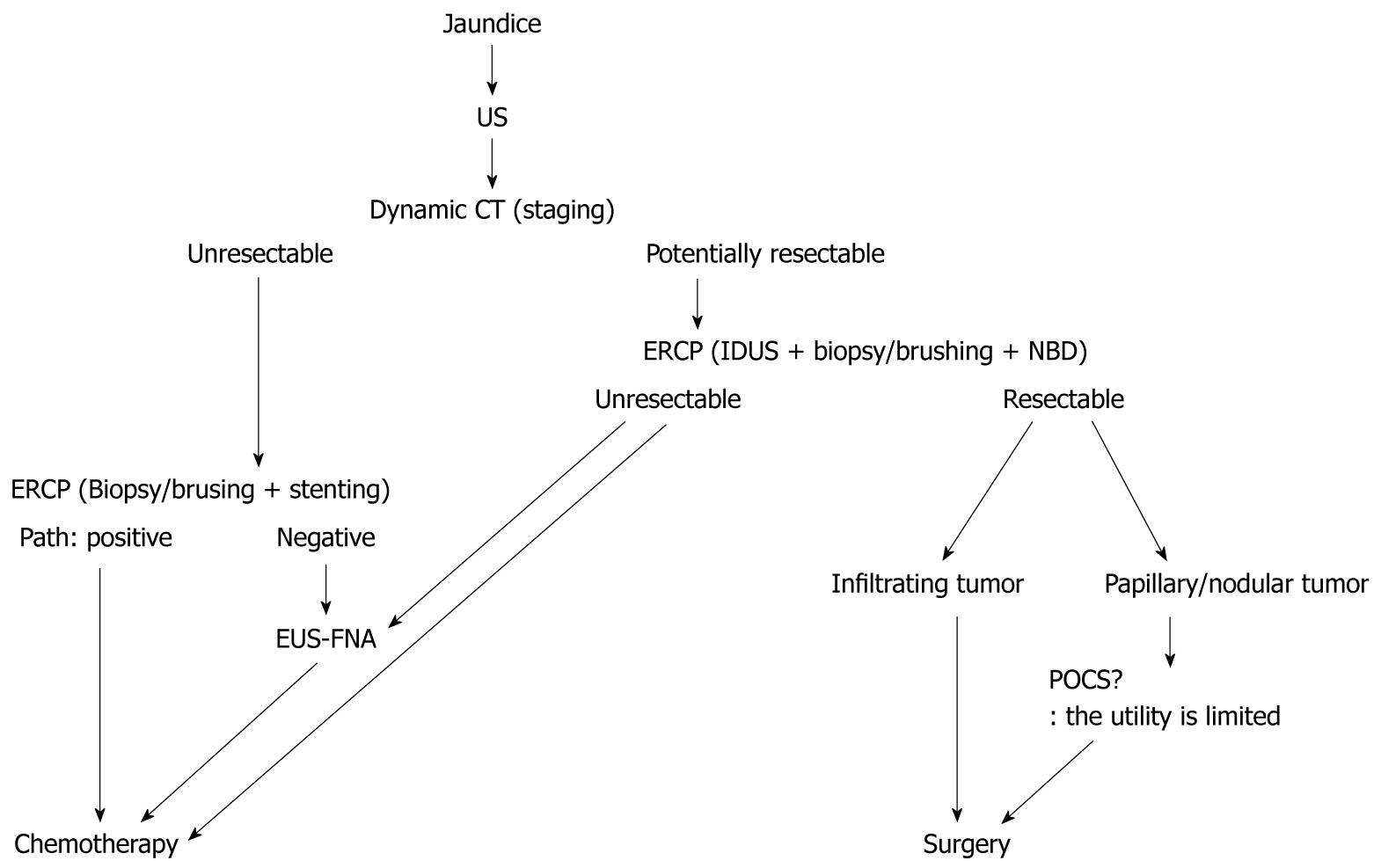
Figure 3 Diagnostic methods for extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma with jaundice.
US: Ultrasonography; CT: Computed tomography; NBD: Naso-biliary drainage; EUS-FNA: Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; IDUS: Intraductal ultrasonography; POCS: Peroral cholangioscopy.
- Citation: Tamada K, Ushio J, Sugano K. Endoscopic diagnosis of extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma: Advances and current limitations. World J Clin Oncol 2011; 2(5): 203-216
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v2/i5/203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v2.i5.203