Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Jan 24, 2024; 15(1): 32-44
Published online Jan 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i1.32
Published online Jan 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i1.32
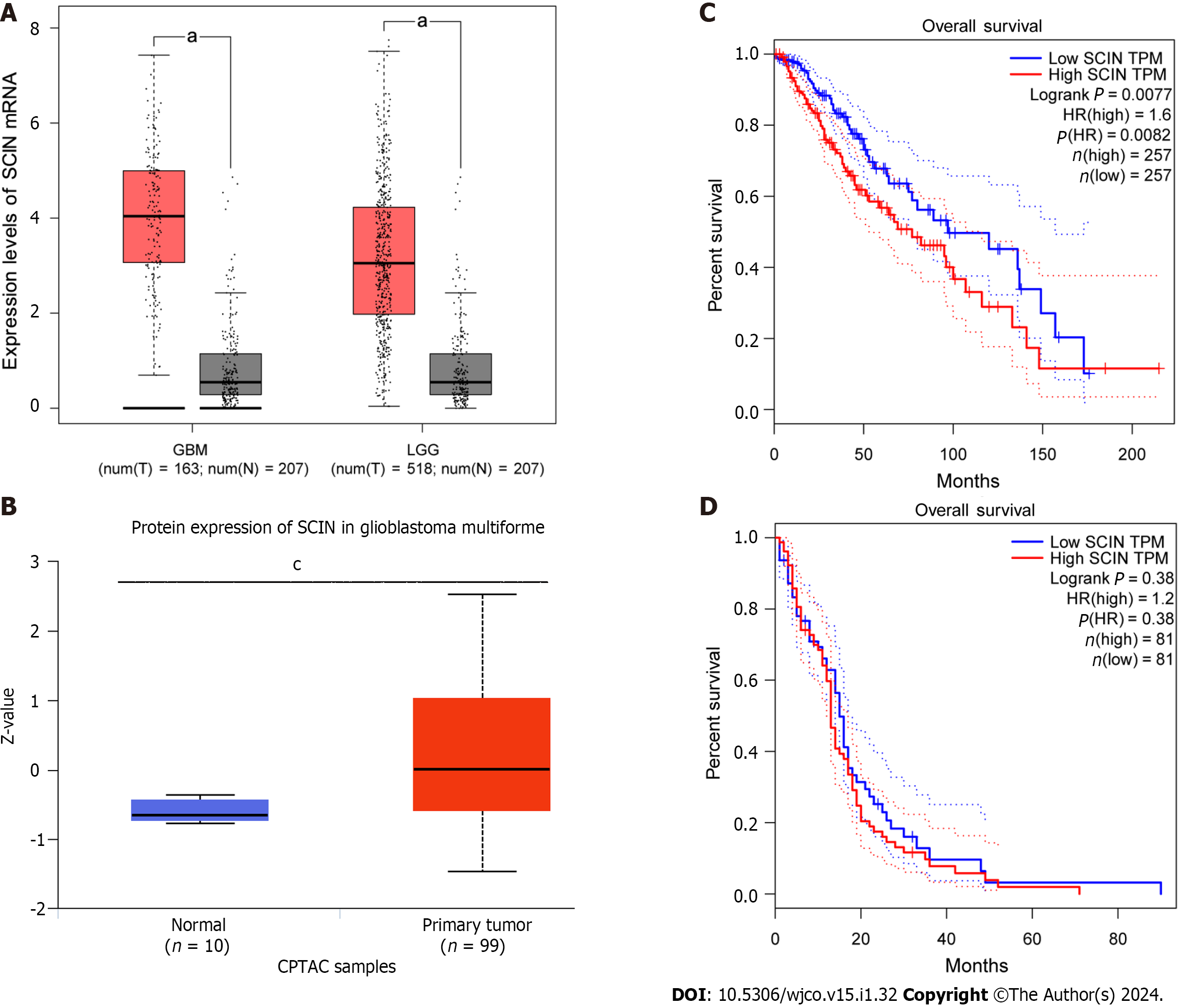
Figure 1 Scinderin expression is upregulated in gliomas and associated with the prognosis of patients with lower-grade glioma.
A: mRNA expression of scinderin (SCIN) in lower-grade glioma (LGG), glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), and corresponding normal tissues, was demonstrated by the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis database. aP < 0.05; B: Protein expression of SCIN in GBM and normal tissues was revealed by the UALCAN database. cP < 0.001; C: Relationship between SCIN mRNA expression and overall survival of LGG patients; D: Relationship between SCIN mRNA expression and overall survival of GBM patients.
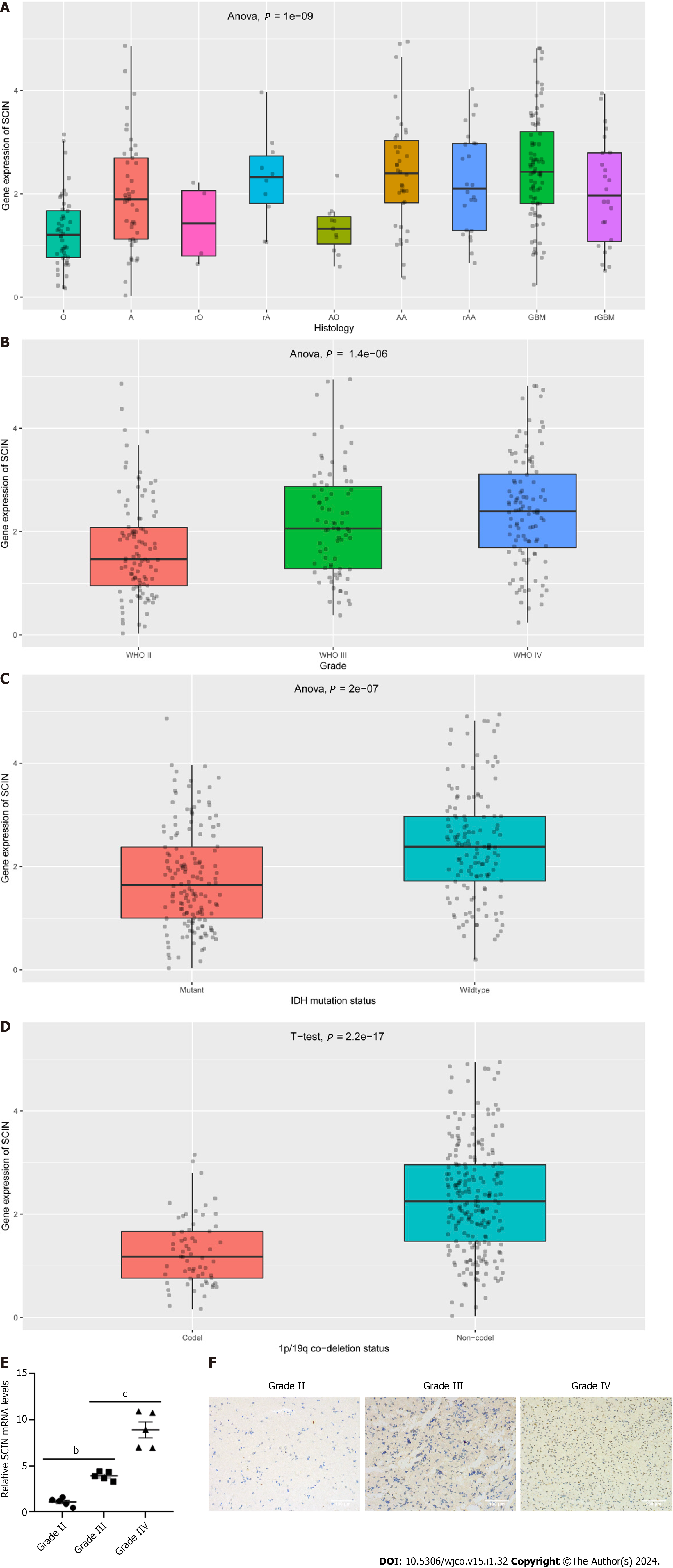
Figure 2 Relationship between scinderin mRNA expression and clinical features of glioma.
A: Expression of scinderin (SCIN) in various types of gliomas; B: Expression of SCIN in World Health Organization II-IV gliomas; C: Expression of SCIN was reduced in gliomas with IDH mutation; D: Expression of SCIN was reduced in gliomas with 1p/19q co-deletion; E: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of the transcriptional levels of SCIN in clinical tissues of Grade II-IV gliomas. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001; F: Representative images of the SCIN protein expression in clinical tissues of Grade II-IV gliomas by immunohistochemical staining. Scale bar: 100 μm.
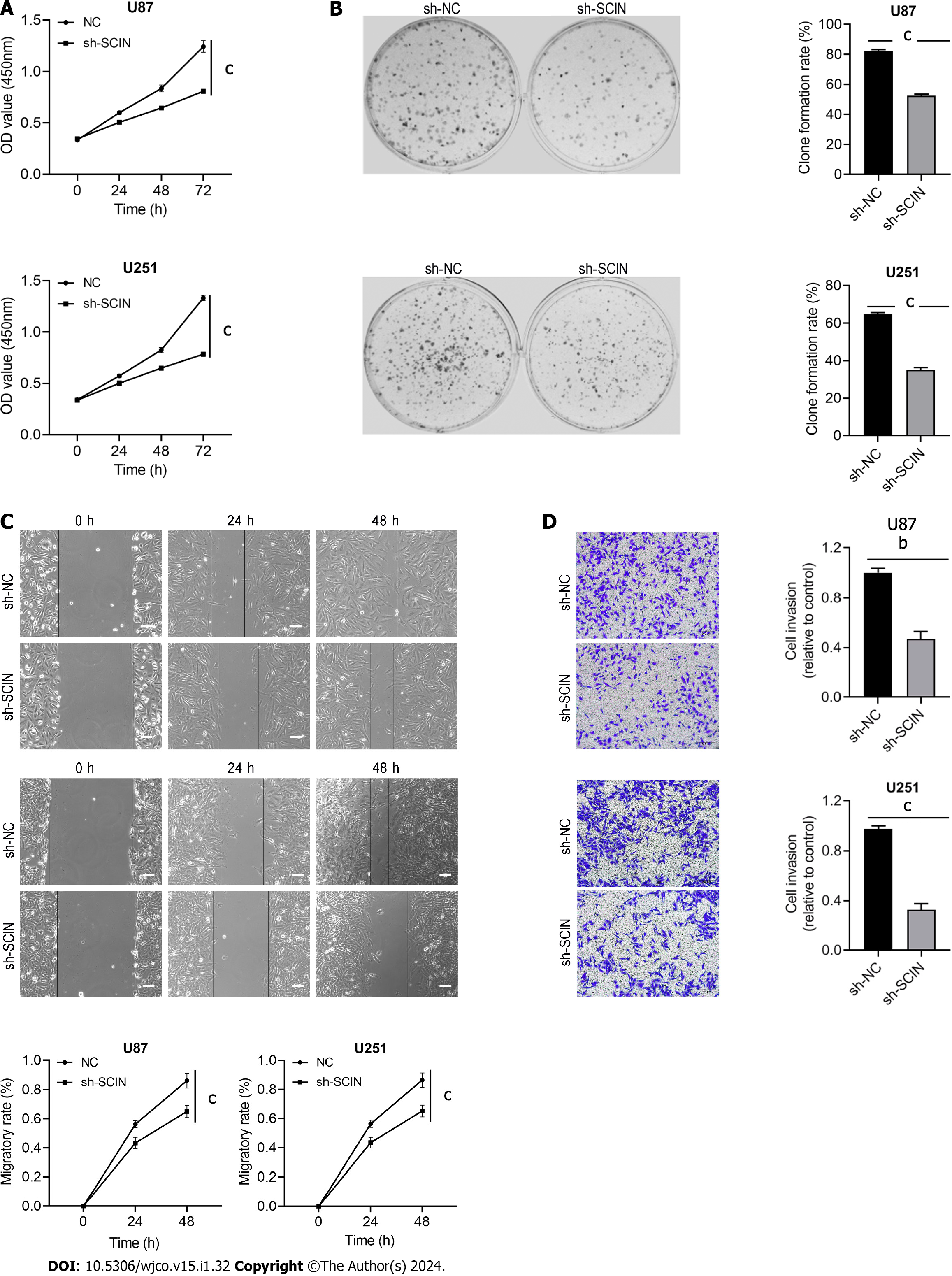
Figure 3 Scinderin silencing inhibits glioma cell malignant behaviors.
A: Cell proliferation was assessed using the Cell Counting Kit-8; B: U87 and U251 cells were transfected with scinderin (SCIN) short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) to determine cell proliferation by colony formation assay; C: Effect of downregulated SCIN on the migration of U87 and U251 was evaluated by a wound-healing assay. Scale bar = 100 μm; D: Transwell assay with Matrigel was performed to examine the invasion property. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
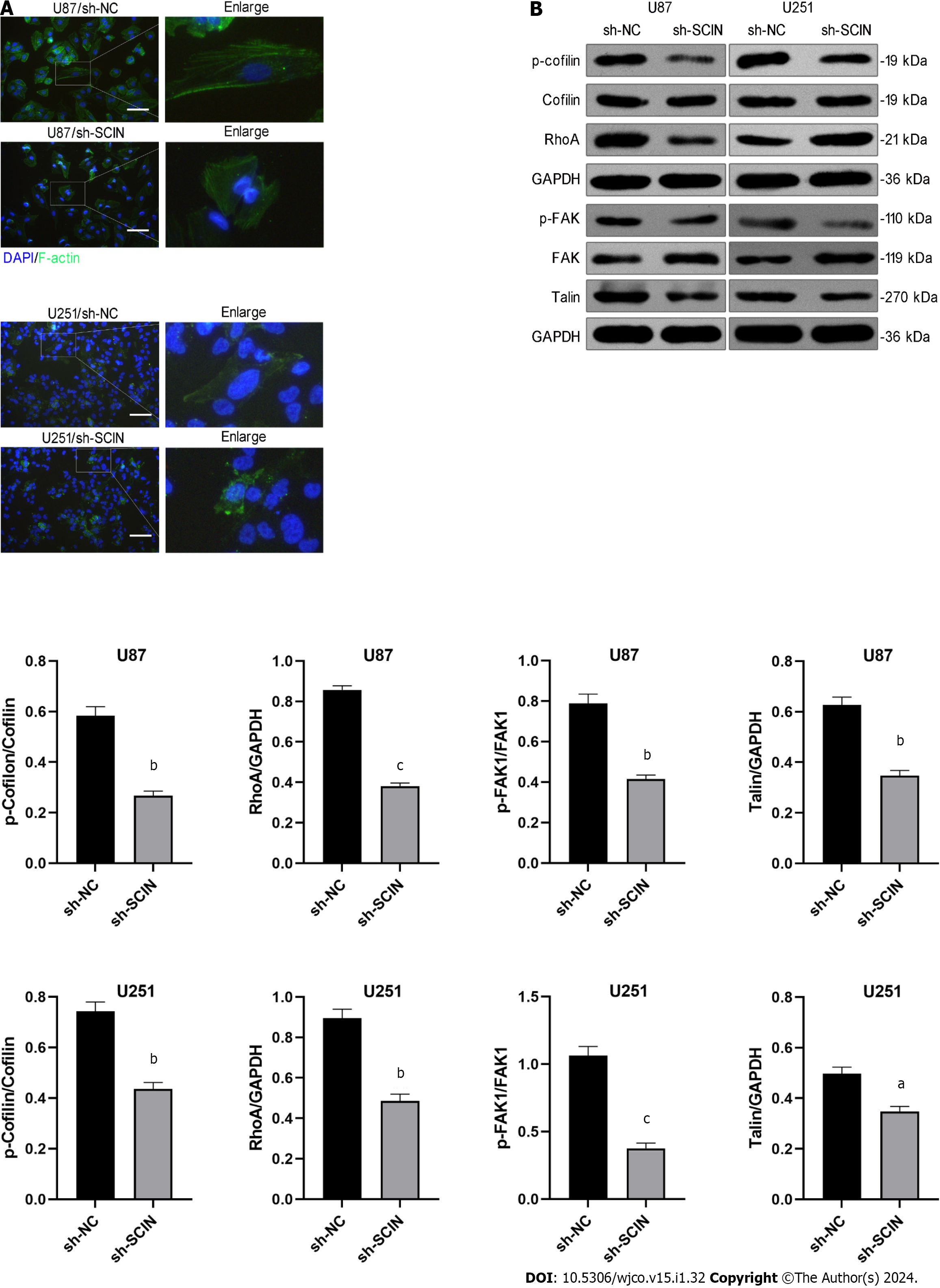
Figure 4 Scinderin silencing promotes F-actin depolymerization and inhibits RhoA/focal adhesion kinase signaling of glioma cells.
A: F-actin cytoskeleton in glioma cells was visualized using Phalloidin staining (green). Scinderin (SCIN) led to a diminution of ruffles and pseudopods on the cell surface; B: Knockdown of SCIN reduced the expression of p-cofilin, RhoA, p-focal adhesion kinase, and Talin, as demonstrated by western blotting. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
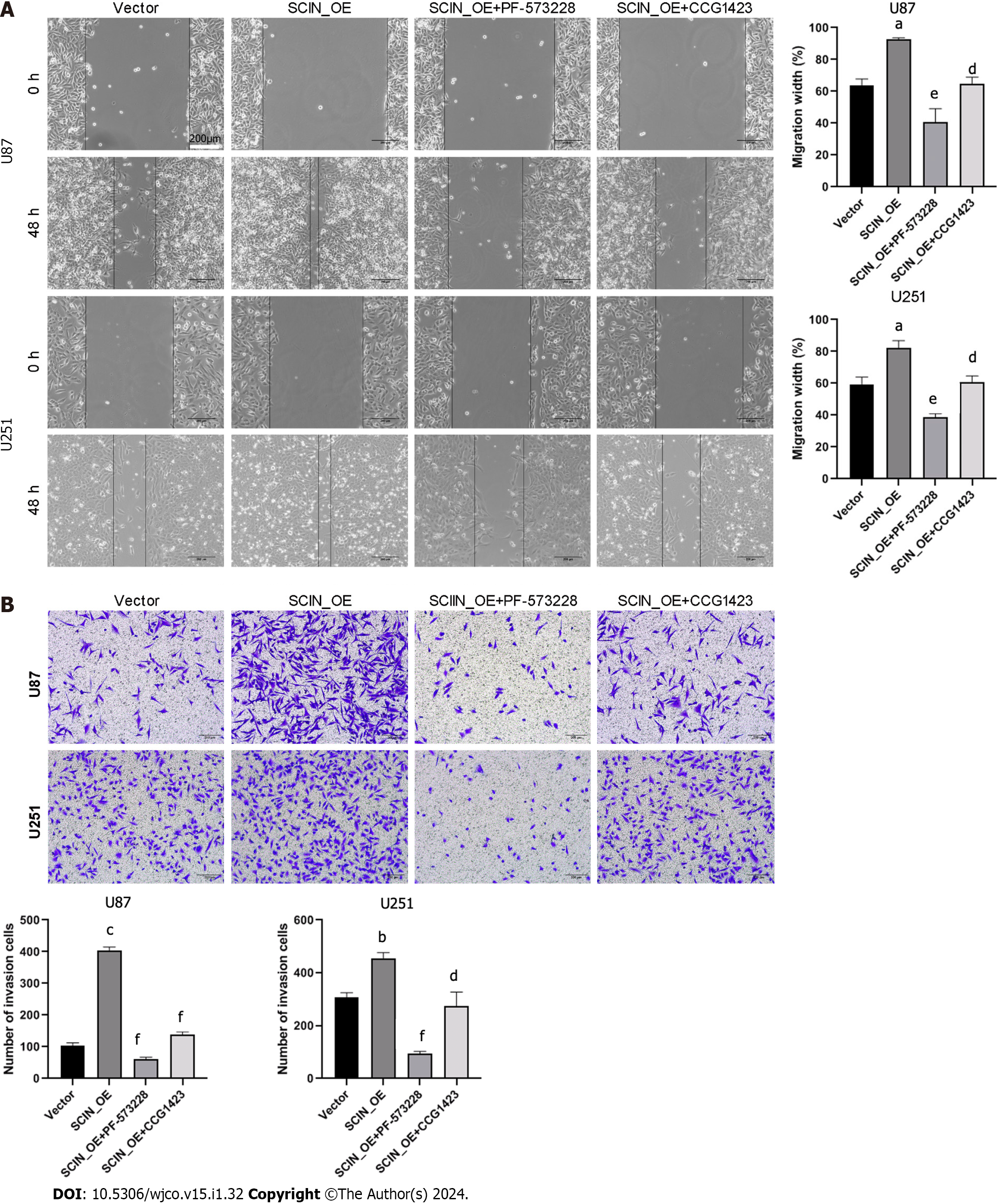
Figure 5 Inhibition of RhoA-focal adhesion kinase signaling reverses scinderin -mediated malignant behaviors in glioma cells.
A: Effects of PF-573228 and Y-27632 on the migration of U87 and U251 cells, evaluated by wound healing assay; B: Transwell assay with Matrigel was performed to examine the invasion property. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs the Vector groups; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs the SCIN_OE groups.
- Citation: Lin X, Zhao Z, Sun SP, Liu W. Scinderin promotes glioma cell migration and invasion via remodeling actin cytoskeleton. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(1): 32-44
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i1/32.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i1.32