Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2014; 5(3): 133-146
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.133
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.133
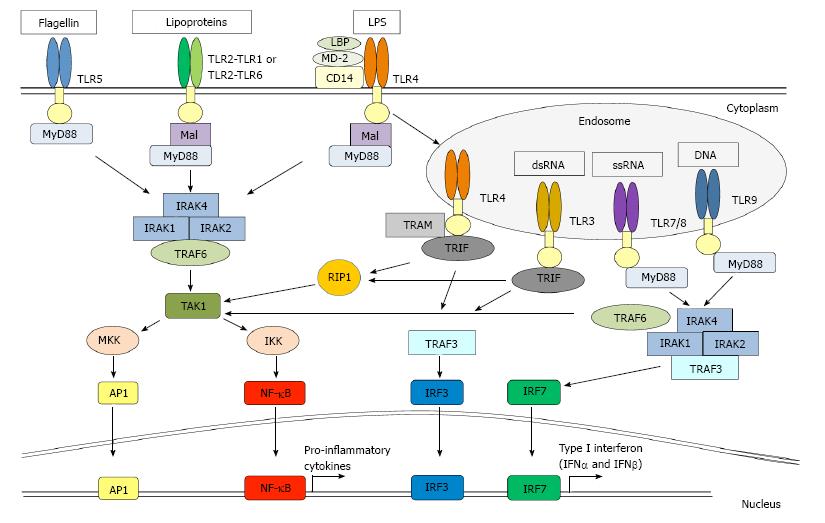
Figure 1 Toll-like receptor signalling.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are type I transmembrane proteins, consisting of a leucine-rich repeat-containing ectodomain involved in pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) recognition, a transmembrane region and an intracellular portion that harbours a Toll-IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain involved in adapter protein recruitment and the activation of downstream signalling pathways. TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5 and TLR6 bind to their ligands on the cell surface and recognize microbial membrane components. TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9 are found in intracellular vesicles and are mainly involved in the recognition of microbial nucleic acids. TLR signalling is initiated by ligand-induced receptor dimerization and TIR engagement with the adapter proteins MyD88 or TRIF. TLR4 localises from the cell membrane to endosomes to change signalling through MyD88 to TRIF. MyD88 is a central TLR adapter protein utilized by all TLRs, with the exception of TLR3, and transmits signals that result in the induction of inflammatory cytokines. The association between a TLR and MyD88 recruits members of the IRAK family. IRAK1 and IRAK4 are sequentially phosphorylated and dissociated from MyD88. This results in the activation of TRAF6, which in turn activates TAK1. TAK1 activates the IKK complex. In most resting cells, NF-κB is bound to the inhibitory IκB proteins (IκBα and IκBβ) in the cytoplasm. Upon activation of the IKK complex, IĸB becomes phosphorylated and degraded, thus releasing NF-κB for translocation to the nucleus, where it interacts with promoters harboring ĸB binding elements. In addition, TAK1 stimulation results in the induction of MAP kinases kinases (MKKs) that activate p38, JNK and ERK, resulting in the subsequent activation of AP-1. In the case of TLR4, and to a lesser extent TLR2, the activation of this pathway involves the bridging adapter protein MAL, which links MyD88 to the TLR. The adapter protein TRIF is involved in the MyD88-independent TLR4 pathway, as well as the TLR3 signalling pathway. TRAM links TRIF to TLR4. Endosomal TLR-mediated signalling leads to the induction of type I interferon through the activation of the transcription factors IRF3 and IRF7.
-
Citation: Smith SM. Role of Toll-like receptors in
Helicobacter pylori infection and immunity. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014; 5(3): 133-146 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v5/i3/133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.133