Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Apr 15, 2012; 3(2): 51-59
Published online Apr 15, 2012. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v3.i2.51
Published online Apr 15, 2012. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v3.i2.51
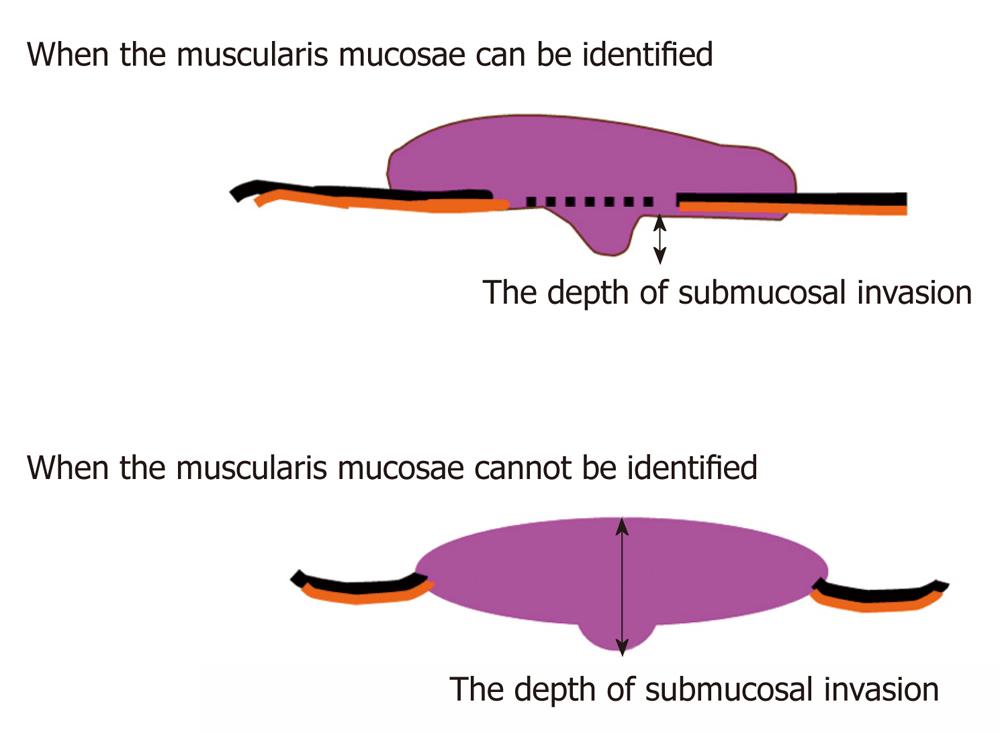
Figure 1 The Japanese system for measuring the depth of submucosal invasion in submucosally invasive cancer.
When the muscularis mucosae can be identified, it is used as the baseline and the vertical distance from this line to the deepest extent of invasion represents the depth of submucosal invasion. When the muscularis mucosae cannot be identified due to carcinomatous invasion, the most superficial aspect of the submucosally invasive cancer is used as the baseline and the vertical distance from this line to the deepest extent of invasion is the depth of submucosal invasion.
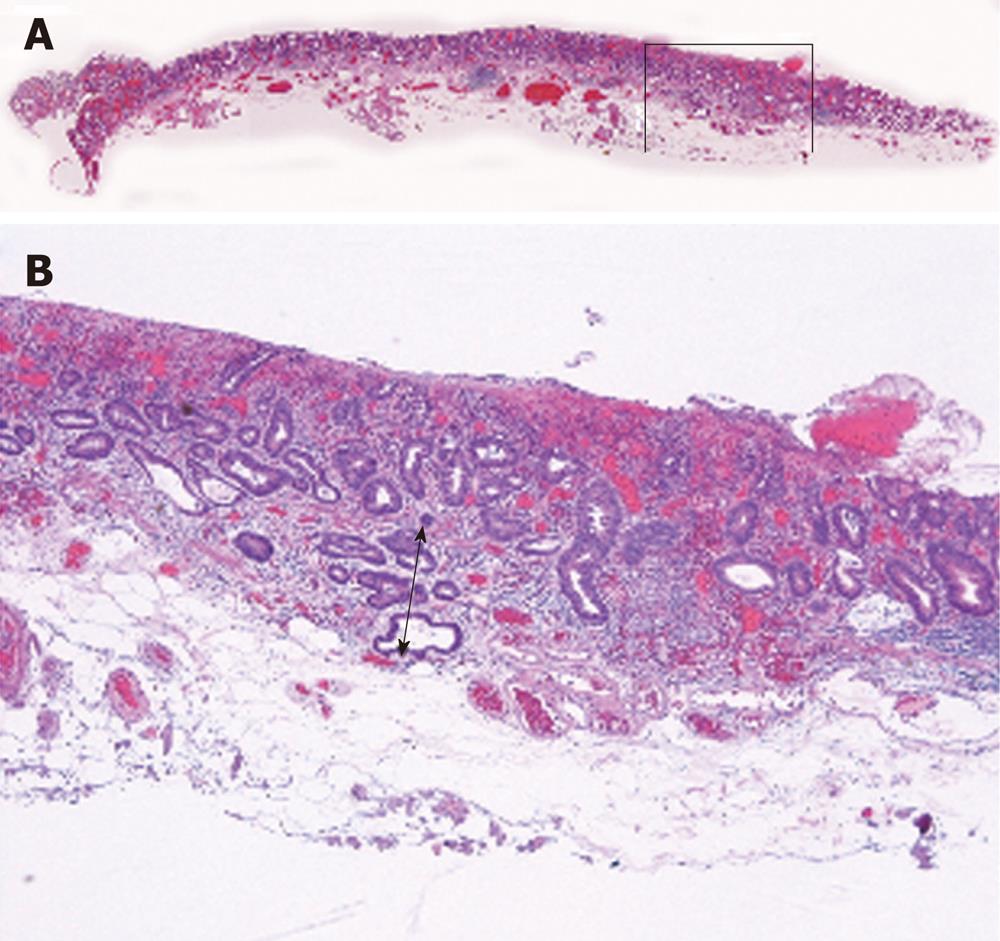
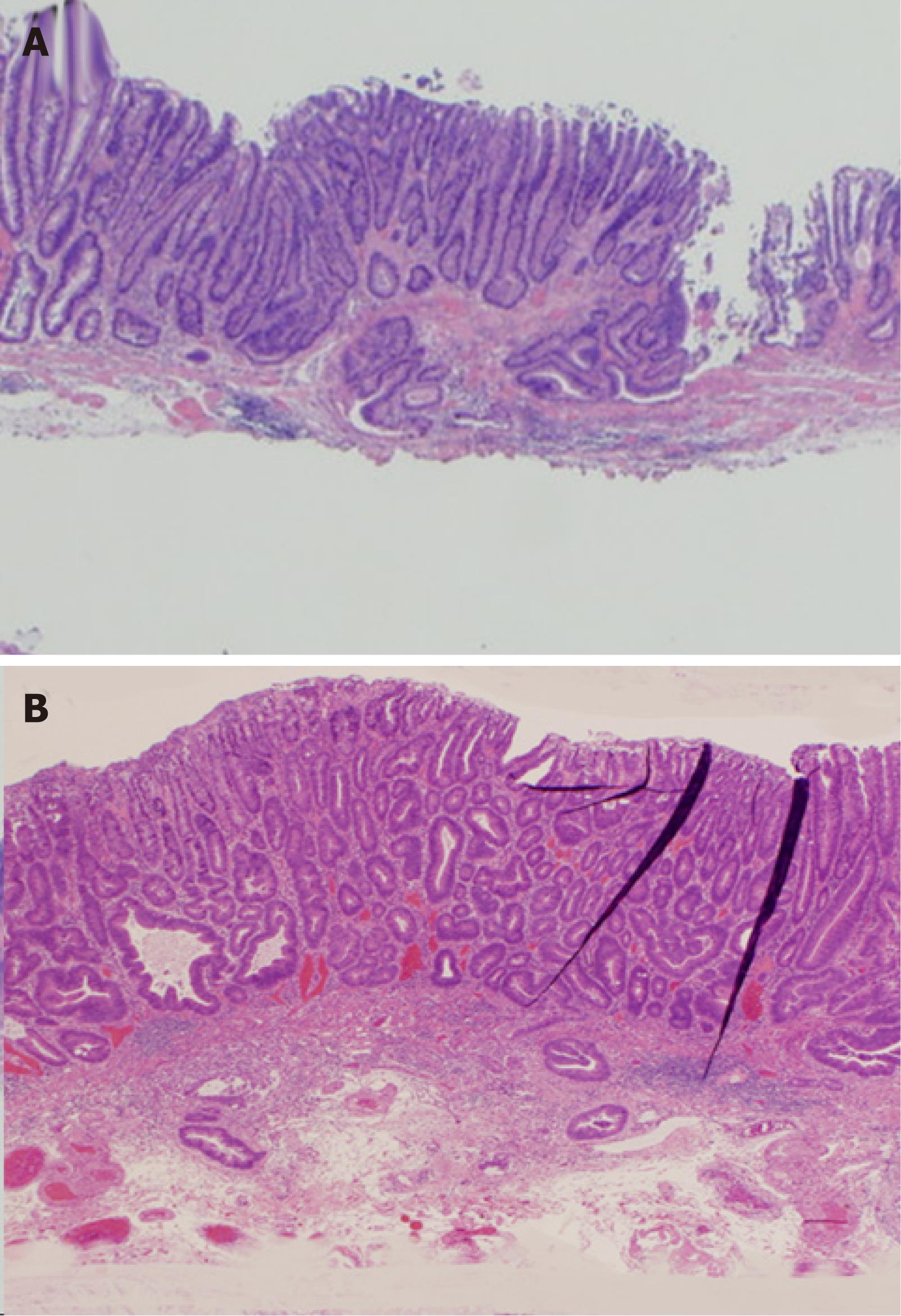
Figure 2 A submucosally invasive cancer with identifiable muscularis mucosae.
A: Submucosal invasion (black box) with partial destruction of the muscularis mucosae was detected by histological examination of hematoxylin and eosin stained sections; B: The muscularis mucosae was identified. The depth of submucosal invasion was 500 μm (black arrow).
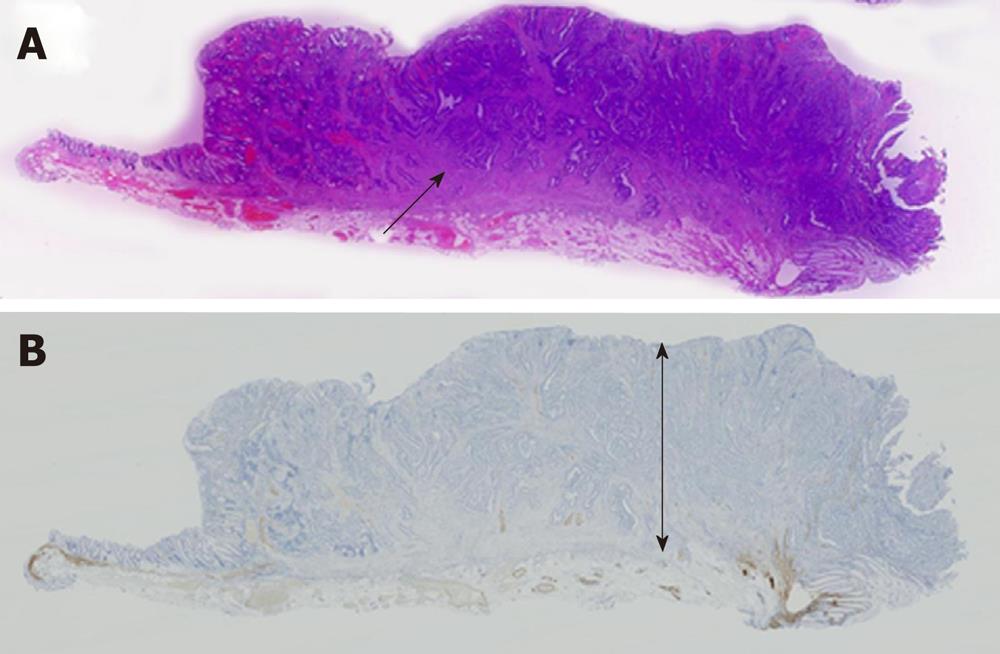
Figure 3 A submucosally invasive cancer with unidentifiable muscularis mucosae.
A: Submucosal invasion (black arrow) with complete destruction of the muscularis mucosae was detected by histological examination of hematoxylin and eosin stained sections; B: Immunohistological staining for desmin showed that the muscularis mucosae could not be identified. The depth of submucosal invasion was 3500 μm (black arrow).
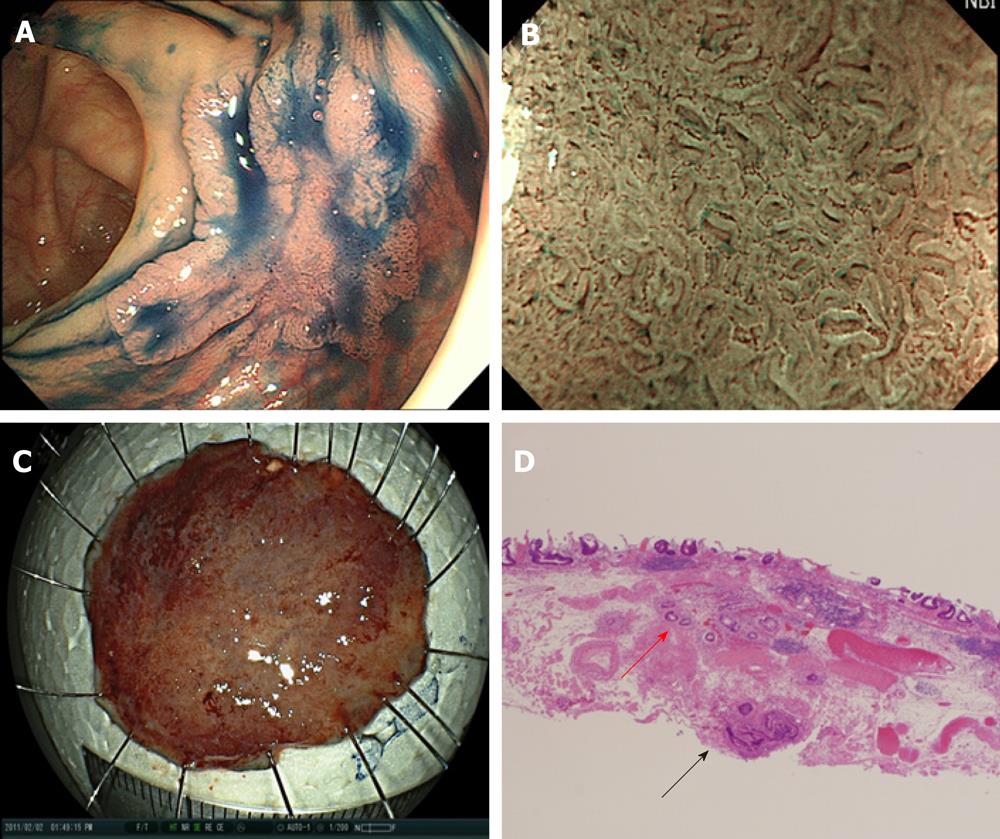
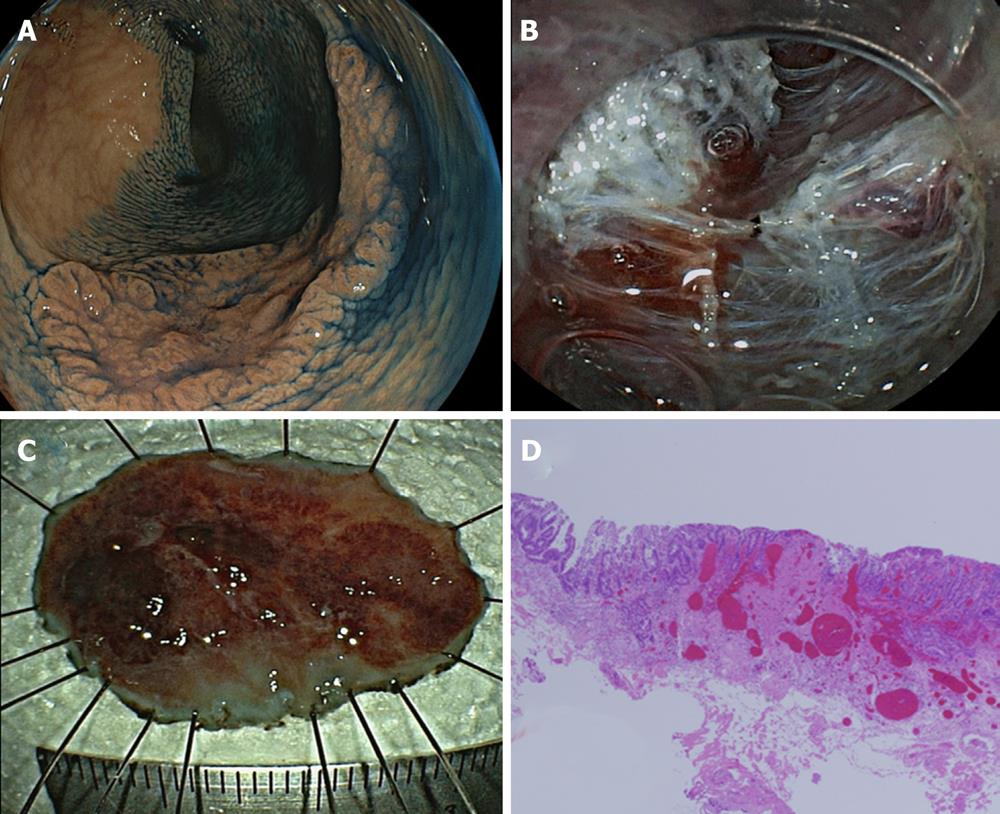
Figure 4 A submucosally invasive cancer with venous infiltration.
A: A tumor graded 0-IIa, measuring 20 mm, located in the ascending colon. The surface of the tumor was slightly depressed (shown by indigo carmine dye); B: Magnifying endoscopy with NBI revealed Type C1/C2 according to Hiroshima classification[43]. The tumor was diagnosed as shallow submucosally invasive cancer and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) was performed; C: En bloc resection was performed. The ESD operation time was 50 min; D: The histopathological diagnosis of the specimen resected by ESD was massive submucosally invasive cancer. The depth of submucosal invasion was 1300 μm and both a positive vertical margin of the tumor (black arrow) and venous infiltration (red arrow) were detected. The appropriate depth of dissection allowed detection of the positive vertical margin and venous infiltration. Additional surgical intervention was performed and no residual tumor or lymph node metastasis was detected. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; NBI: Narrow band imaging.
Figure 5 A submucosally invasive cancer with severe fibrosis.
A: A tumor graded 0-IIa, measuring 35 mm, located in the descending colon. The surface of the tumor was slightly depressed. The tumor was diagnosed by magnifying endoscopy as shallow submucosally invasive cancer and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) was performed; B: Severe fibrosis was detected during ESD and was dissected with a scissor-type knife; C: En bloc resection was performed. The ESD operation time was 160 min. There was no perforation or postoperative hemorrhage; D: Histopathological diagnosis of the specimen resected by ESD was shallow submucosally invasive cancer. The depth of submucosal invasion was 800 μm, and there was severe fibrosis in the submucosa. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Figure 6 The depth of submucosal dissection in resection of submucosally invasive cancer by endoscopic submucosal dissection.
A: The dissection in this case was too shallow. Insufficient submucosa is seen in the resected specimen, which was dissected at the submucosa slightly below the muscularis mucosae. Submucosal invasion can be detected; however, the presence of venous-lymphatic invasion cannot be evaluated; B: This case was dissected appropriately. An adequate amount of submucosa is seen in the resected specimen, which was dissected at the middle-deep submucosa sufficiently below the muscularis mucosae. Both submucosal invasion and venous-lymphatic invasion can be detected.
- Citation: Yoshida N, Naito Y, Yagi N, Yanagisawa A. Importance of histological evaluation in endoscopic resection of early colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2012; 3(2): 51-59
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v3/i2/51.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v3.i2.51