Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Oct 15, 2011; 2(5): 72-81
Published online Oct 15, 2011. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v2.i5.72
Published online Oct 15, 2011. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v2.i5.72
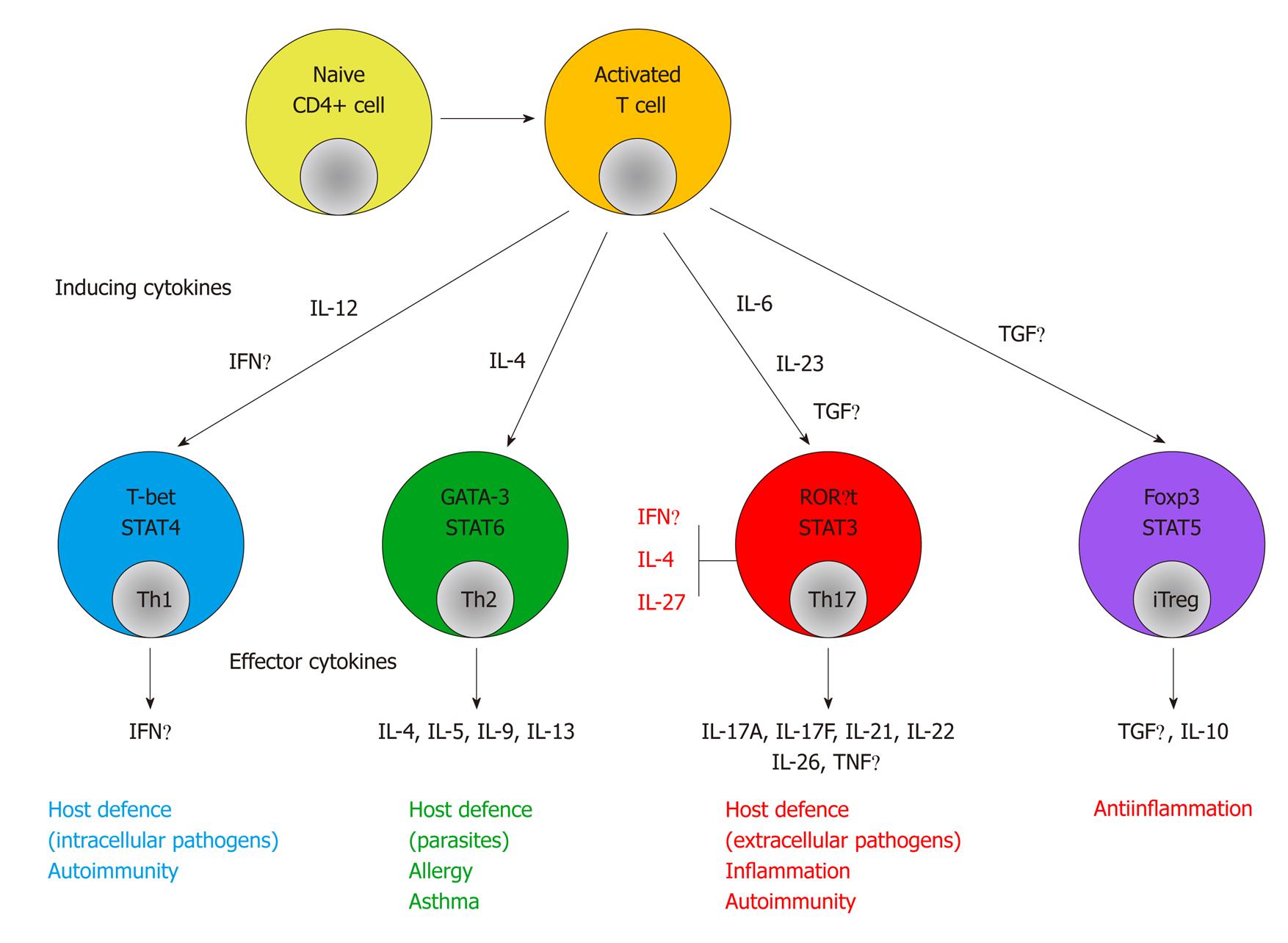
Figure 1 Development of Th1, Th2, Th17 and induced Treg cells from naïve CD4+ T cells.
Cytokines that inhibit the development of Th17 cells are marked in red. CD: Crohn’s disease; T-bet: T box expressed in T cells; GATA: GATA-binding protein; ROR: Retinoid-related orphan receptor; Foxp3: Forkhead box P3; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
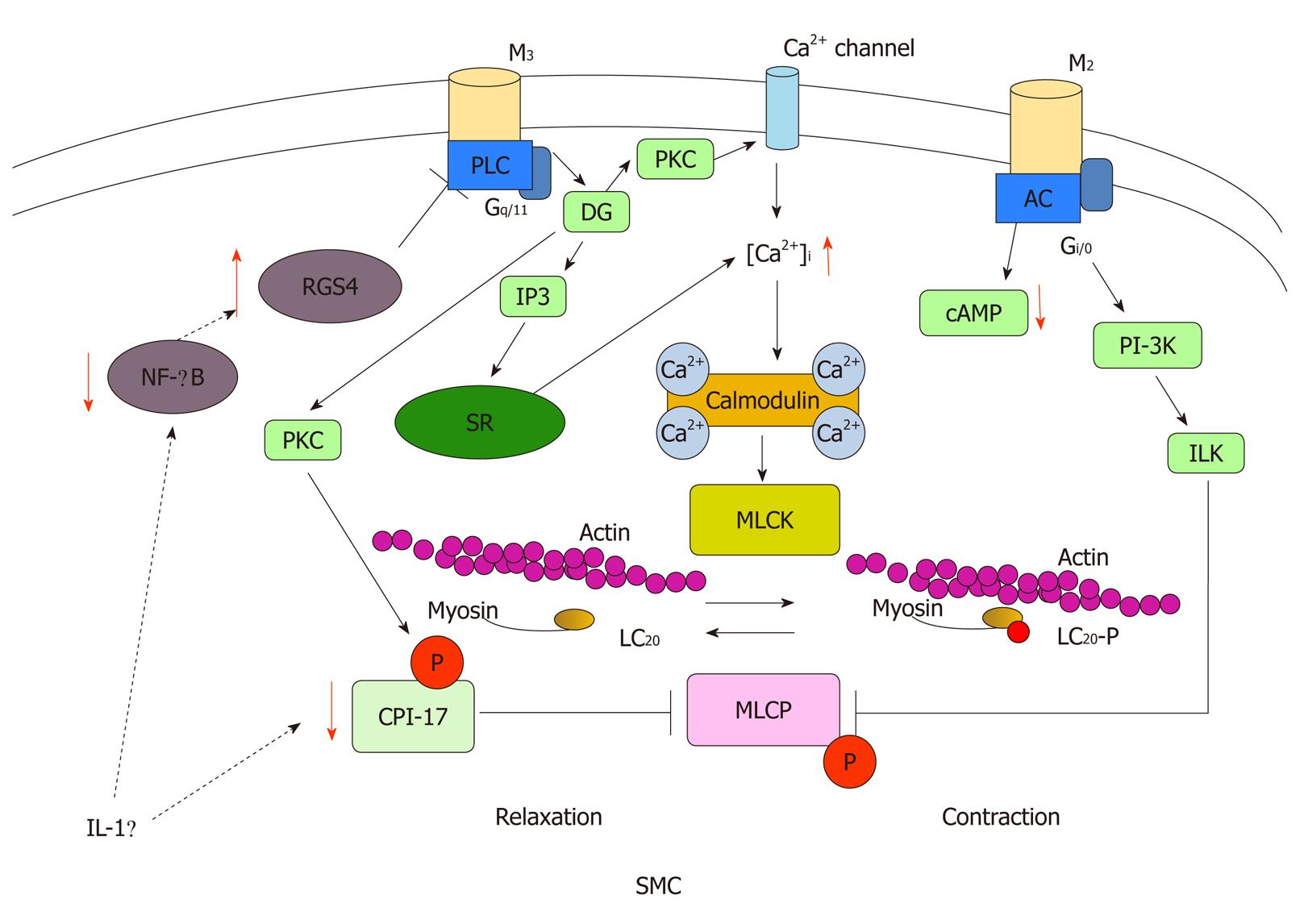
Figure 2 Muscarinic receptor signaling pathways.
Gastrointestinal smooth muscle expresses both M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors. The M3 receptors are coupled to Gq/11, which activates phospholipase C (PLC) and produce inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DG). These second messengers elicit the activation of PKC and trigger an increase in [Ca2+]i. M2 receptors are coupled to Gi/o, accompanied by adenylcyclase (AC), which causes a decrease in cAMP level and activation of phosphoinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and integrin-linked kinase (ILK). Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS4) plays an important role in regulating smooth muscle contraction. To initiate contraction, increases in [Ca2+]i activate MLCK, a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent enzyme. MLCK phosphorylates LC20 on Ser-19, which results in contraction of smooth muscle through increases in myosin ATPase activity and cross-bridge cycling. MLCP is responsible for the dephosphorylation of LC20, which results in relaxation of smooth muscle. It is the balance between MLCK and MLCP activities that dictates the contractile activity of smooth muscle. Although MLCK is Ca2+/calmodulin dependent, MLCP functions independently of Ca2+/calmodulin and is regulated directly by phosphorylation of the myosin targeting subunit of MLCP and/or indirectly via phosphorylation of CPI-17. IL-1β upregulates RGS4 expression by inhibiting NF-κB activation. IL-1β also downregulates CPI-17 expression leading to muscle relaxation. PKC: Protein kinase C; MLCK: Myosin light chain kinase; MLCP: Myosin light chain phosphatase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB.
- Citation: Akiho H, Ihara E, Motomura Y, Nakamura K. Cytokine-induced alterations of gastrointestinal motility in gastrointestinal disorders. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2011; 2(5): 72-81
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v2/i5/72.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v2.i5.72