Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. May 26, 2014; 6(5): 304-313
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i5.304
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i5.304
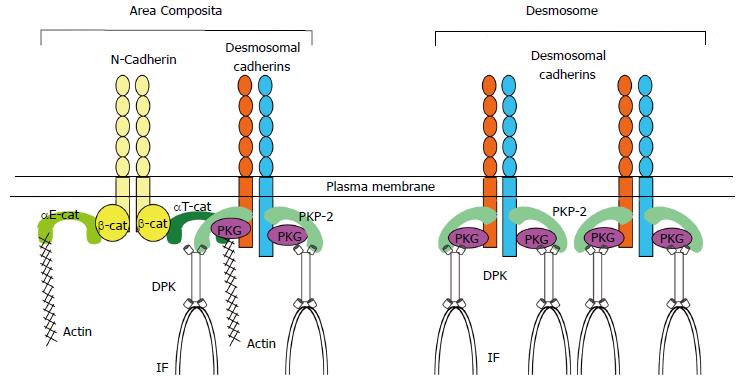
Figure 1 Components of area composita in the heart.
Area composita is a mixed-type junctional structure composed of both desmosomal and adherens junctional proteins. Both αE-catenin and αT-catenin are present in the area composita at the cardiac intercalated disc. However, only αT-catenin was shown to interact directly with desmosomal protein PKP2. PKP2: Plakophilin-2; DPK: Desmoplakin; IF: Intermediate filaments.
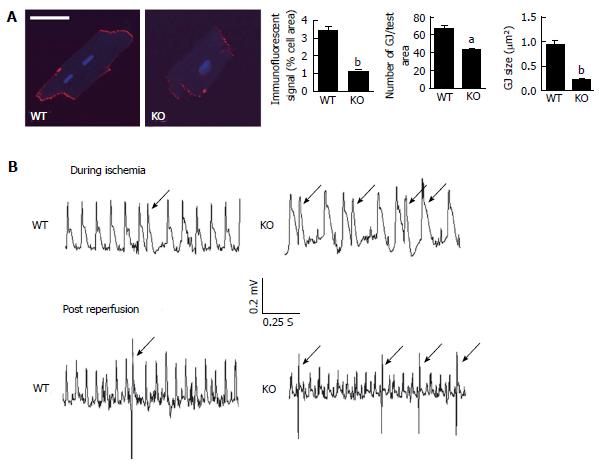
Figure 2 Loss of αT-catenin in the mouse heart leads to reduced expression of Cx43 and ventricular arrhythmia following acute ischemic injury.
A: Adult cardiomyocytes isolated from wildtype (WT) and αT-catenin knockout (KO) hearts were immunostained for Cx43. Ten cardiomyocytes from each animal were examined for five or more contiguous pixels of high signal intensity. The amount of specific immunoreactive signal at intercalated disc (ID) for Cx43, the number of Cx43-containing plaques (gap junction, GJ) and their size (GJ size) were quantified and are shown in the panel at right. Scale bar; 50 um. The error bars represent the s.e.m. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; B: Representative telemetry ECGs of different patterns of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs, arrow) during ischemia-reperfusion (I-R) injury in WT and αT-catenin KO mice. Mice from WT and αT-catenin KO were subjected to ligation of the left anterior descending artery for 30 min and 7 d reperfusion. A miniaturized telemetry ECG transmitter was implanted before I-R.
- Citation: Li J. Alterations in cell adhesion proteins and cardiomyopathy. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(5): 304-313
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i5/304.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i5.304