Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Cardiol. Aug 26, 2020; 12(8): 409-418
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v12.i8.409
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v12.i8.409
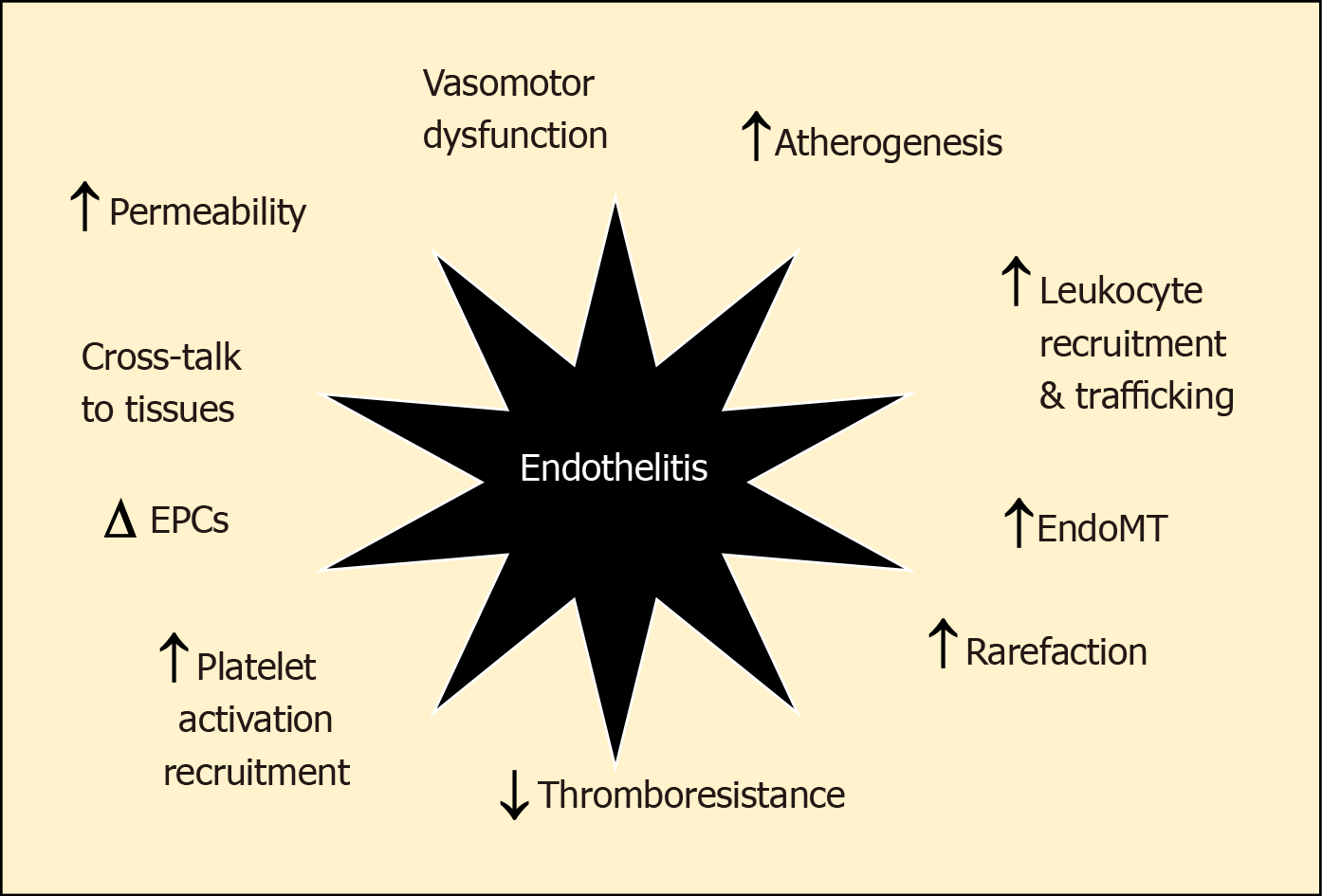
Figure 1 Endothelitis is associated with a range of dysfunctional changes that contribute the development and progression of cardiovascular disease.
EndoMT: Endothelial-mesenchymal transition; EPC: Endothelial progenitor cell.
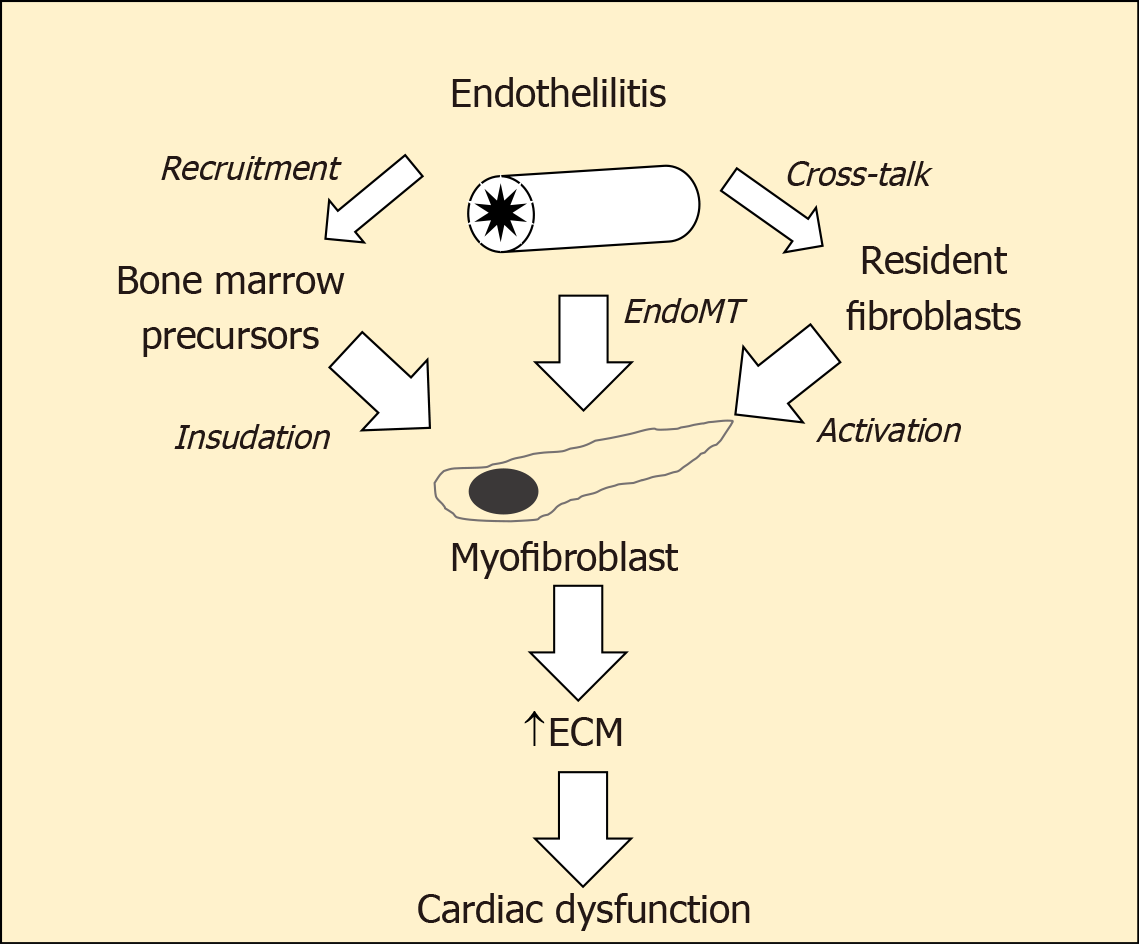
Figure 2 Myofibroblasts the central players in cardiac fibrogenesis.
ECM: Extracellular matrix; EndoMT: Endothelial-mesenchymal transition; EPC: Endothelial progenitor cell.
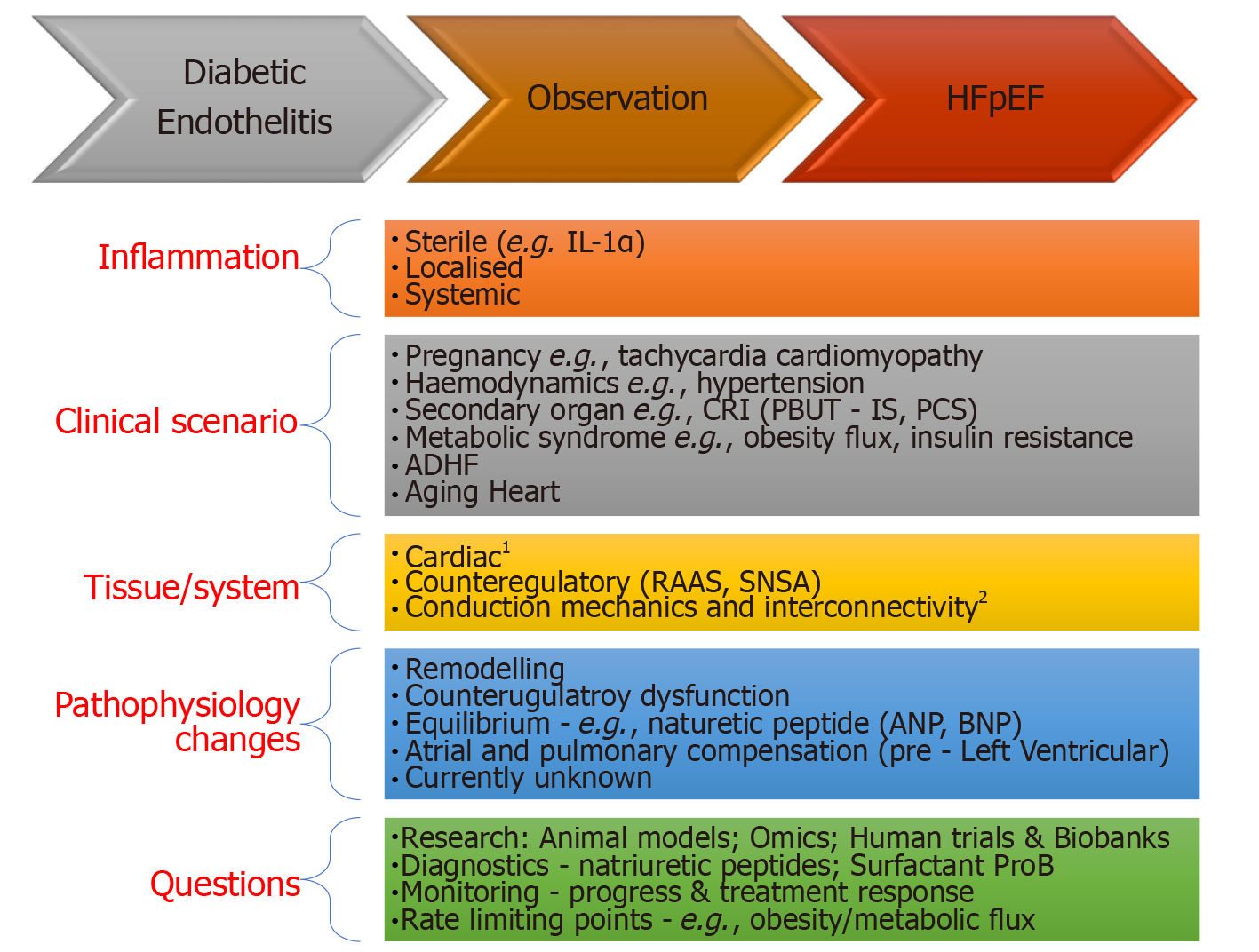
Figure 3 Theoretical bench to bedside flow chart for some commonly encountered clinical scenarios.
1Cytoskeleton (e.g., Rho kinase activity), contractile apparatus (e.g., Titin phosphorylation), mitochondrial energetics, AGE. 2Ventricular atrial coupling; Microvasculature; Pericardial restraint; Chronotropic reserve. ADHF: Acute decompensated heart failure; AGE: Advanced glycation end products; ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP: Brain natriuretic peptide; IL-1α: Interleukin 1 alpha; CRI: Chronic renal impairment/insufficiency; IS: Indoxyl sulphate; PBUT: Protein bound uremic toxins; PCS: P-cresyl sulphate; RAAS: Renin angiotensin aldosterone syndrome; SNSA: Sympathetic nervous system activity.
- Citation: Thomas MC, Iyngkaran P. Forensic interrogation of diabetic endothelitis in cardiovascular diseases and clinical translation in heart failure. World J Cardiol 2020; 12(8): 409-418
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v12/i8/409.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v12.i8.409