Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Biol Chem. Jan 27, 2022; 13(1): 1-14
Published online Jan 27, 2022. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v13.i1.1
Published online Jan 27, 2022. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v13.i1.1
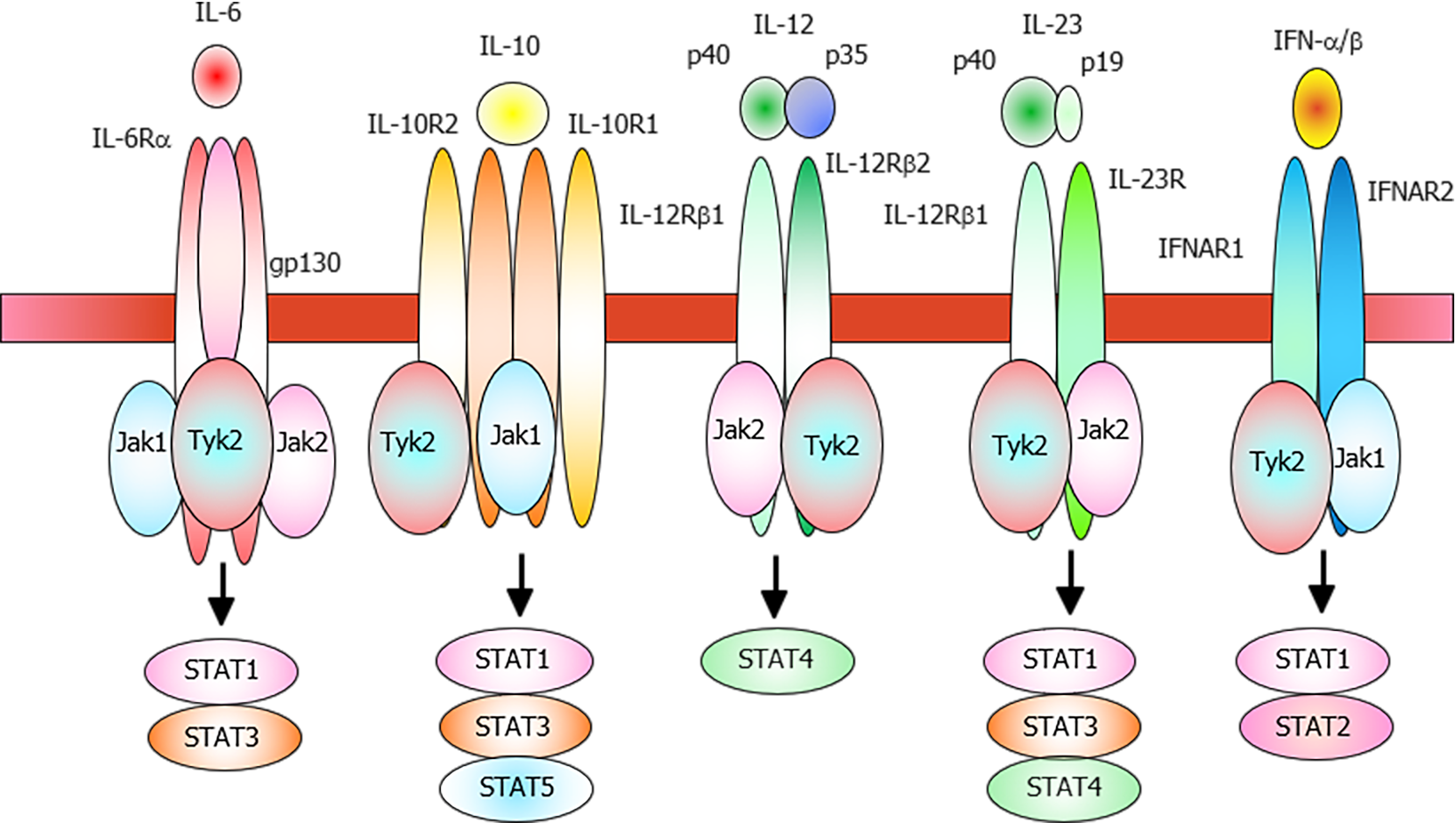
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the tyrosine kinase 2-related cytokine receptors.
The IL-6 receptor, which comprises IL6RA (gp80) and IL6RB (gp130) subunits, activates signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1 and STAT3 through interactions with Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2), Janus family of protein tyrosine kinases 1 (Jak1), and Jak2. The IL-10 receptor, which comprises IL-10R1 and IL10-R2 subunits, activates STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5 through interactions with Tyk2 and Jak1. IL-12 is a heterodimeric cytokine comprising the IL-12p35 and IL-12p40 subunits. The IL-12 receptor, which comprises IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ2, mainly activates STAT4 through interactions with Tyk2 and Jak2. The IL-12p40 component of IL-23 can dimerize with IL-23p19 to form IL-23. The IL-23 receptor, which comprises IL-12Rβ1 and IL-23R subunits, activates STAT1, STAT3, and STAT4 through interactions with Tyk2 and Jak2. The type I IFN receptor, which comprises IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 subunits, activates STAT1 and STAT2 through interactions with Tyk2 and Jak1. STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; Tyk2: Tyrosine kinase 2; Jak1: Janus family of protein tyrosine kinases 1.
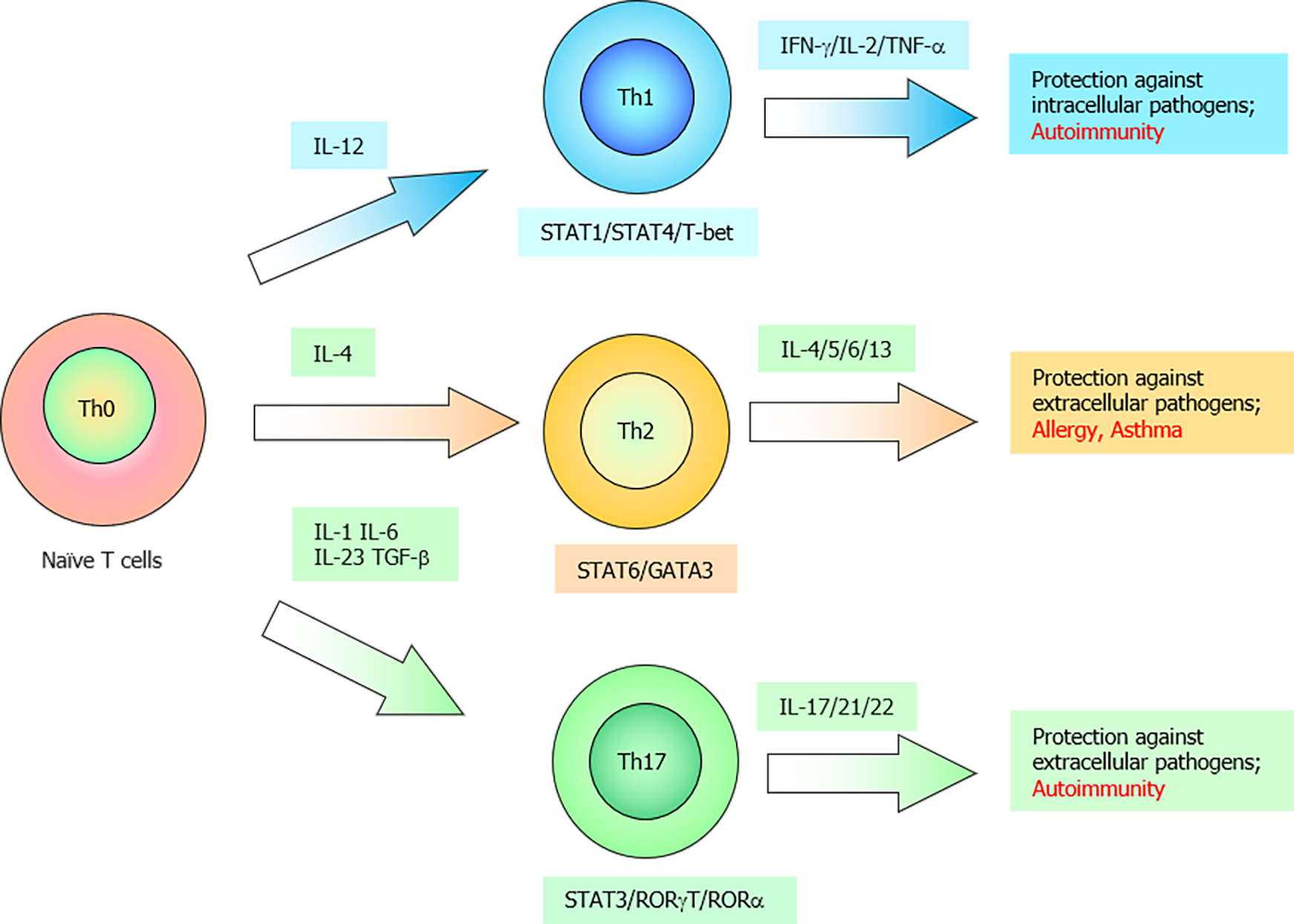
Figure 2 Schematic representation of naïve T cell differentiation into T helper 1, T helper 2, or T helper 17 cells depending on the cytokine profile.
IL-12 promotes the differentiation of naïve T cells into Th1 cells. Th1 cells promote the clearance of intracellular pathogens and induce autoimmunity through the production of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α. Th1 differentiation is regulated by transcription factors such as signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1, STAT4, and T-bet. IL-4 promotes the differentiation of naïve T cells into Th2 cells. Th2 cells promote the clearance of extracellular pathogens and induce allergic responses through the production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, and IL-13. Th2 differentiation is regulated by transcription factors such as STAT6 and GATA3. TGF-β, IL-6, and IL1 promote the differentiation of naïve T cells into Th17 cells, while IL-23 can maintain the Th17 phenotype. Th17 cells promote the clearance of extracellular pathogens and induce autoimmunity through the production of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-22. Th2 differentiation is regulated by transcription factors, such as STAT3, RORγt and RORα.
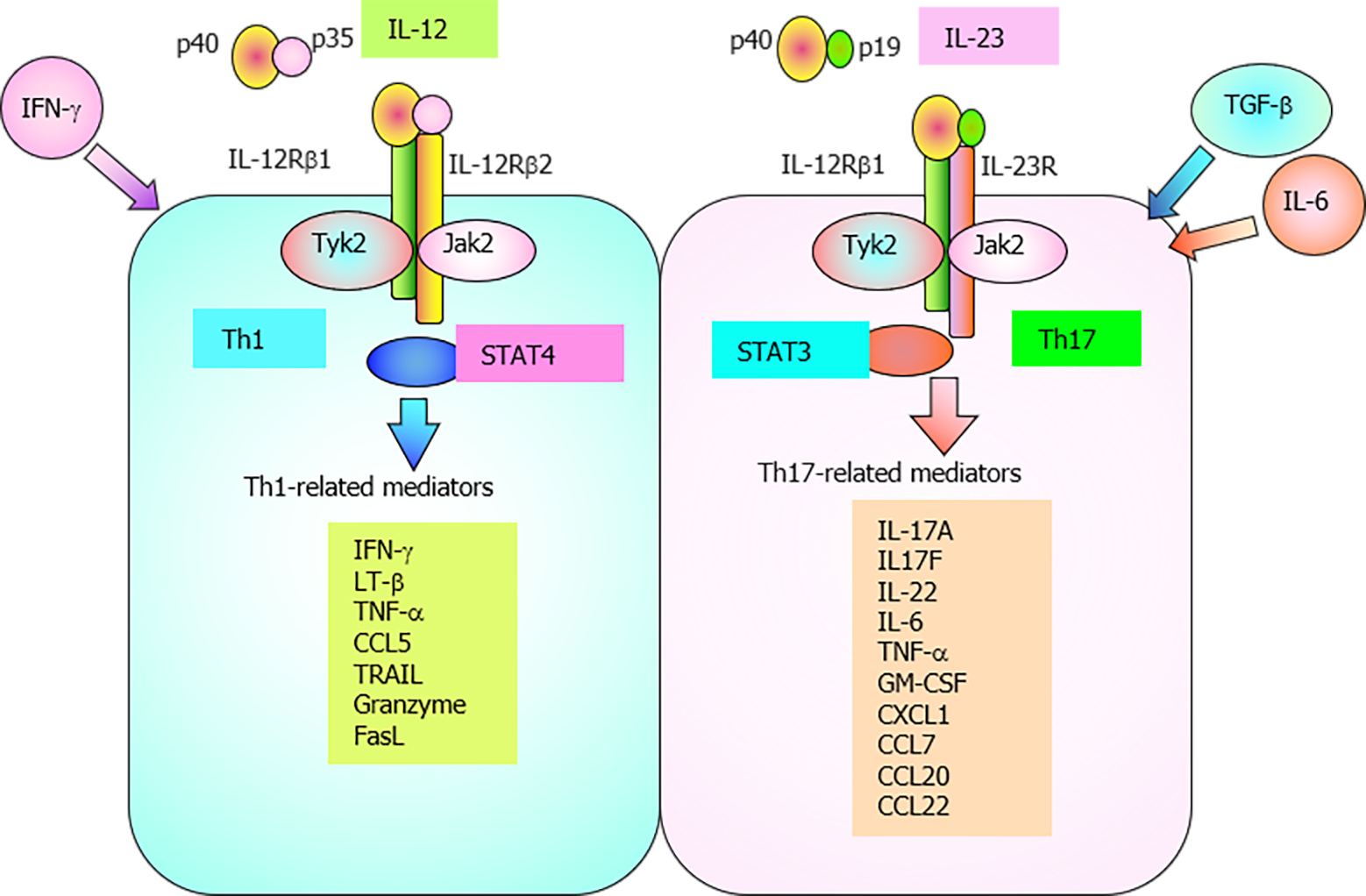
Figure 3 Illustration of interleukin-12 and interleukin-23, as well as their receptors and downstream signaling pathways.
IL-12 and IL-23 share the p40 subunit, while their receptors share the IL-12Rβ1 subunit. The binding of IL-12 to its receptor induces the activation of Jak2 and Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2), which results in signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)4 phosphorylation. Activated STAT4 promotes the differentiation of naïve Th cells into Th1 cells, which subsequently produce IFN-γ that is required for the development of Th1 immune response. The binding of IL-23 to its receptor induces the activation of Jak2 and Tyk2, which results in STAT3 phosphorylation. IL-23 induces the expression of IL-17A, IL-17F, and/or IL-22 and stabilizes Th17 cells. STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
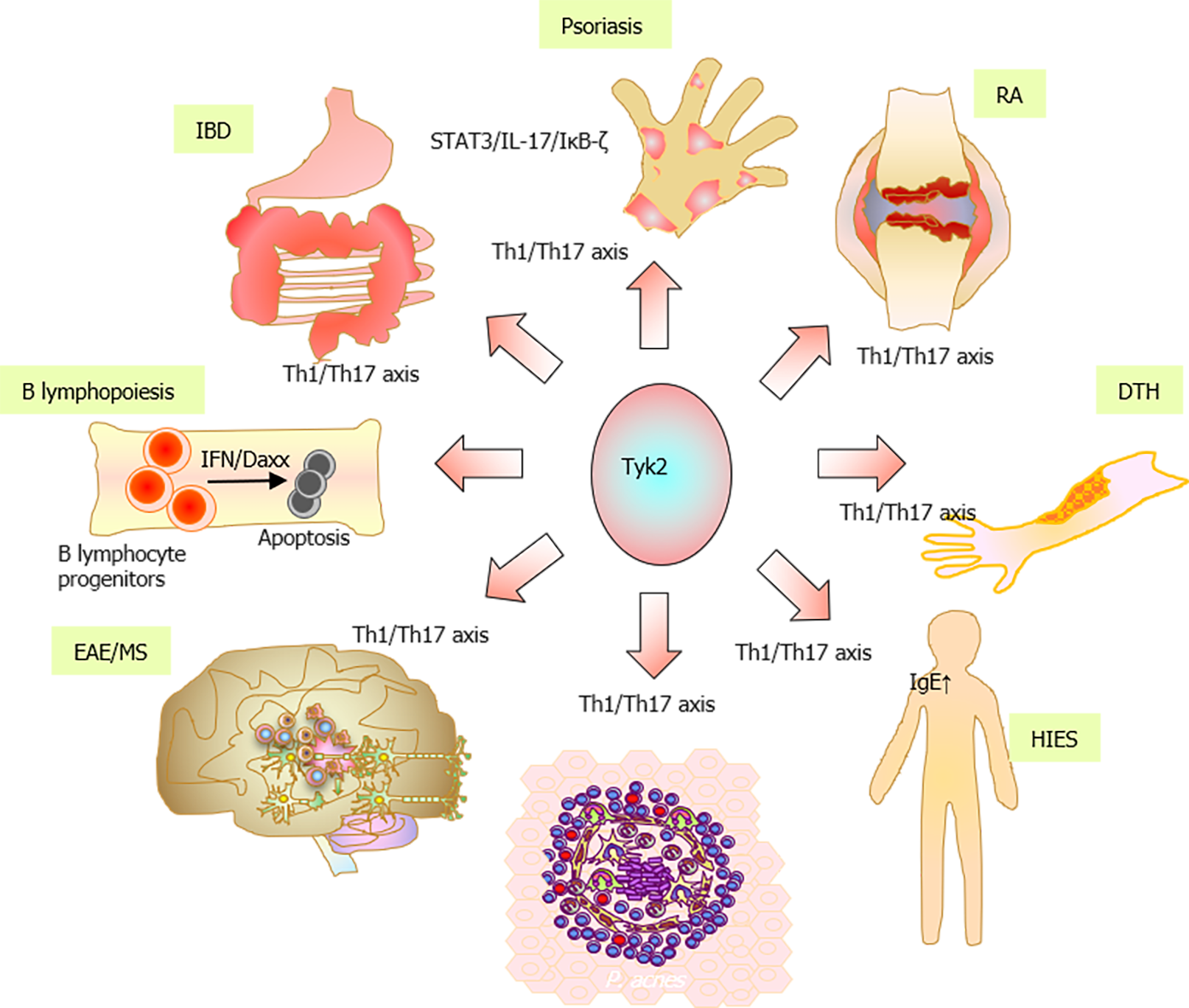
Figure 4 Schematic representation of the involvement of tyrosine kinase 2 in immune and inflammatory responses and its pathological significance.
IBD: Inflammatory bowel diseases; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; DTH: Delayed-type hypersensitivity; HIES: Hyper IgE syndrome; EAE: Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; MS: Multiple sclerosis.
- Citation: Muromoto R, Oritani K, Matsuda T. Current understanding of the role of tyrosine kinase 2 signaling in immune responses. World J Biol Chem 2022; 13(1): 1-14
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v13/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v13.i1.1