Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Biol Chem. May 27, 2021; 12(3): 38-51
Published online May 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i3.38
Published online May 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i3.38
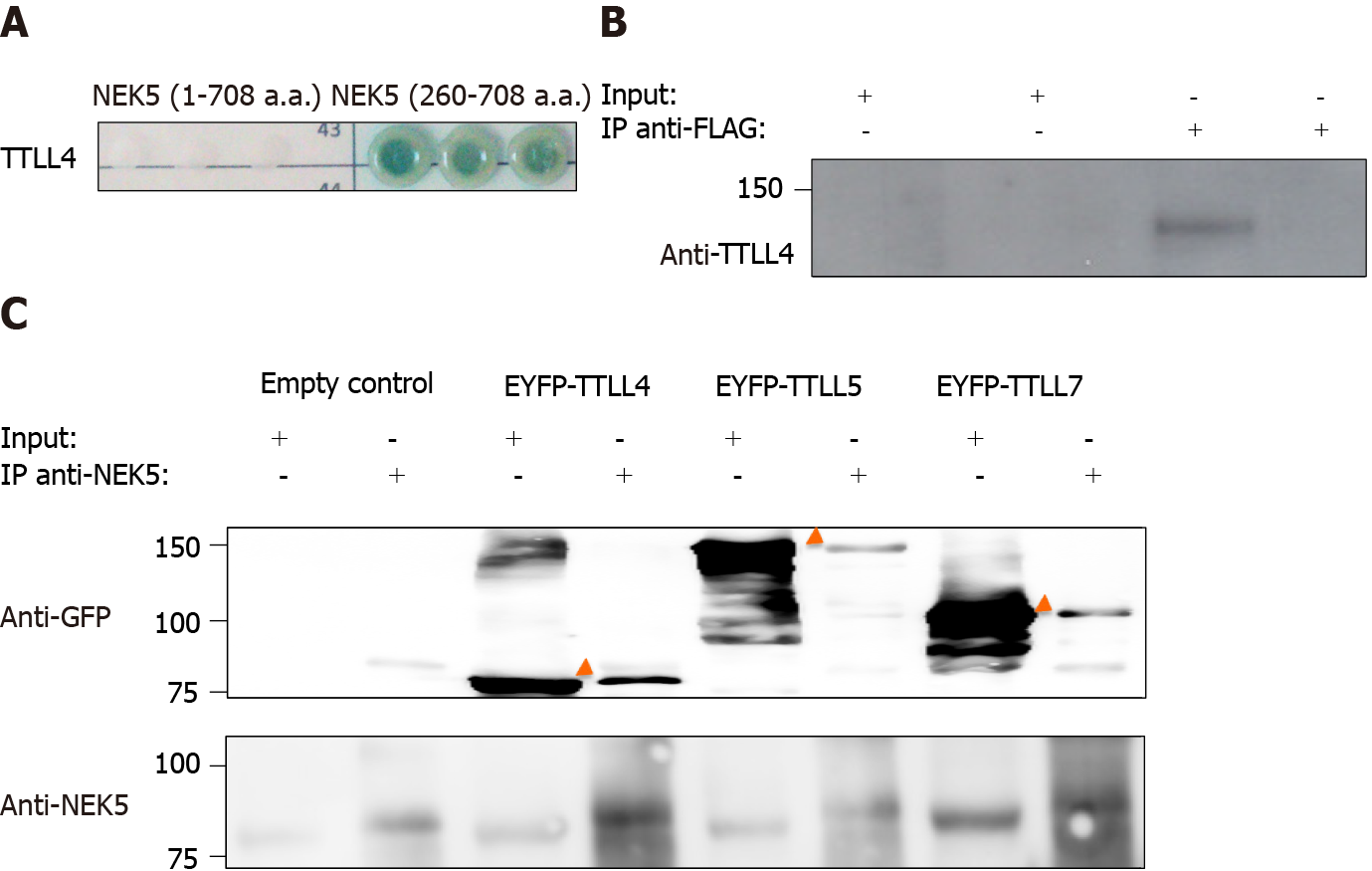
Figure 1 Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 interacts with tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4.
A: Yeast colonies grew in selective medium SD-WLAH with aureobasidin and X-α-Gal. In addition to the reporter gene Auri-C we also activated the genes MEL1, ADE2 and His3 as indicators of interaction between the proteins. Controls of the yeast two-hybrid assay are presented in Supplementary Figure 3; B: Stable cells expressing never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 (NEK5)-FLAG were induced with 2 μg/mL of tetracycline and fractionated in cytoplasm and mitochondria. 1 µg of protein was used to immunoprecipitate NEK5 using an anti-FLAG resin, after elution the proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane. Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) 4 was co-immunoprecipitated with NEK5 as assessed with anti-TTLL4 antibody. Controls of cell fractioning are presented in Supplementary Figure 5; and C: NEK5 interacts with TTLL4, TTLL5 and TTLL7 by immunoprecipitation. HEK293T were transfected with EYFP-TTLL4, EYFP, TTLL5 and EYFP-TTLL7. Endogenous NEK5 was immunoprecipitated using anti-NEK5 antibody. Immunoprecipitated proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The identification of TTLLs was assessed by an anti-green fluorescent protein antibody to confirm interaction between the proteins. NEK5: Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5; GFP: Green fluorescent proteins; EYFP: Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; TTLL: Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like.
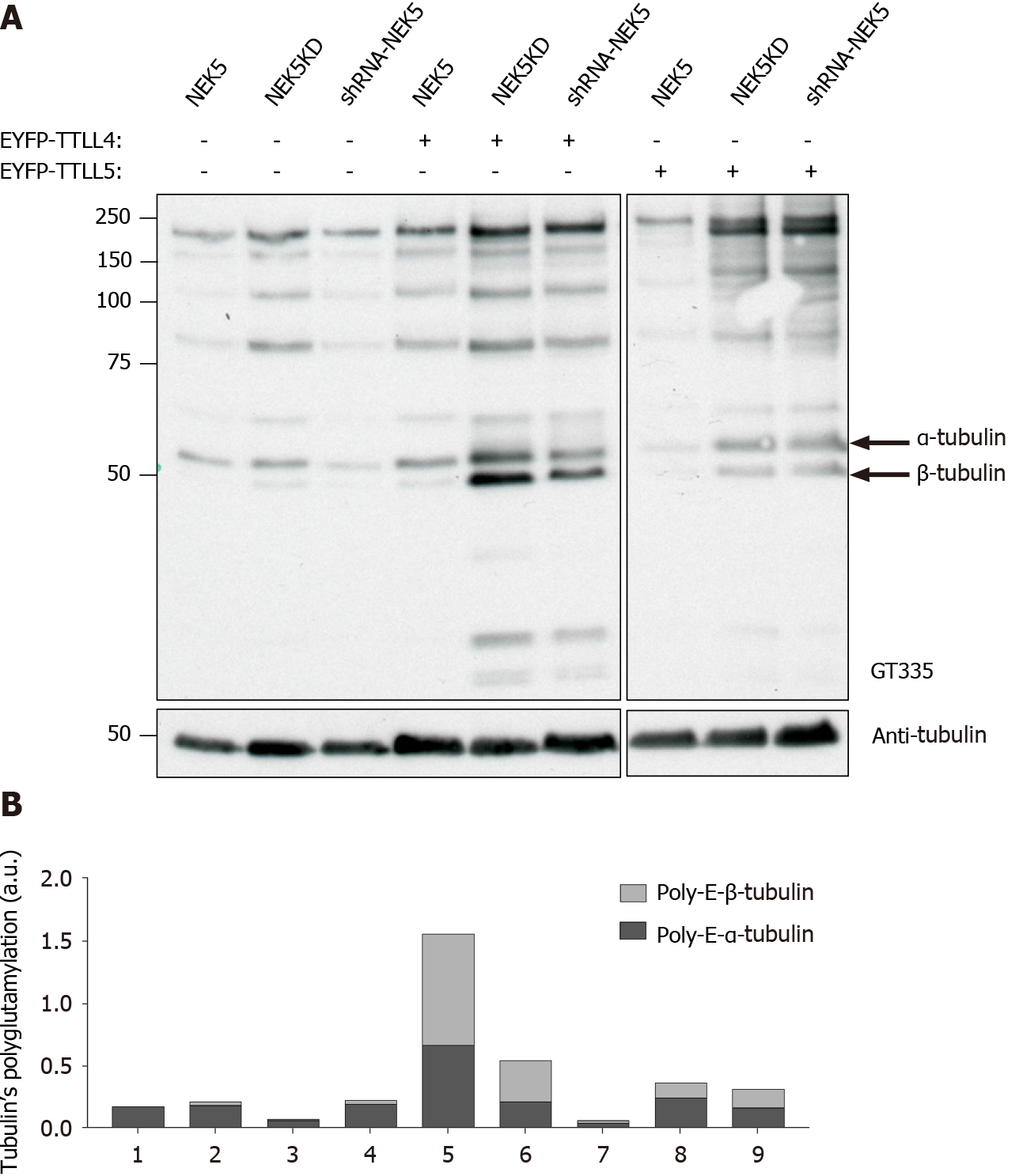
Figure 2 Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 changes the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4 and tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 5-mediated polyglutamylation.
A: Analysis by Western blot of tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4 and 5 in polyglutamylation in cells that stably express either never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 (NEK5) or NEK5-kinase-dead (catalytically inactive) or cells silenced for NEK5 expression. The graph next to the Western blot corresponds to the intensity of polyglutamylated α- and β-tubulins selected among the bands labeled by GT335 antibody which were measured and normalized to total α-tubulin. The arrows indicate α- and β-tubulins polyglutamylated used in this graph; and B: The intensity (area of the bands) of Western blot of the figure presented in “c” was measured using ImageJ software. NEK5: Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5; EYFP: Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; TTLL: Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like.
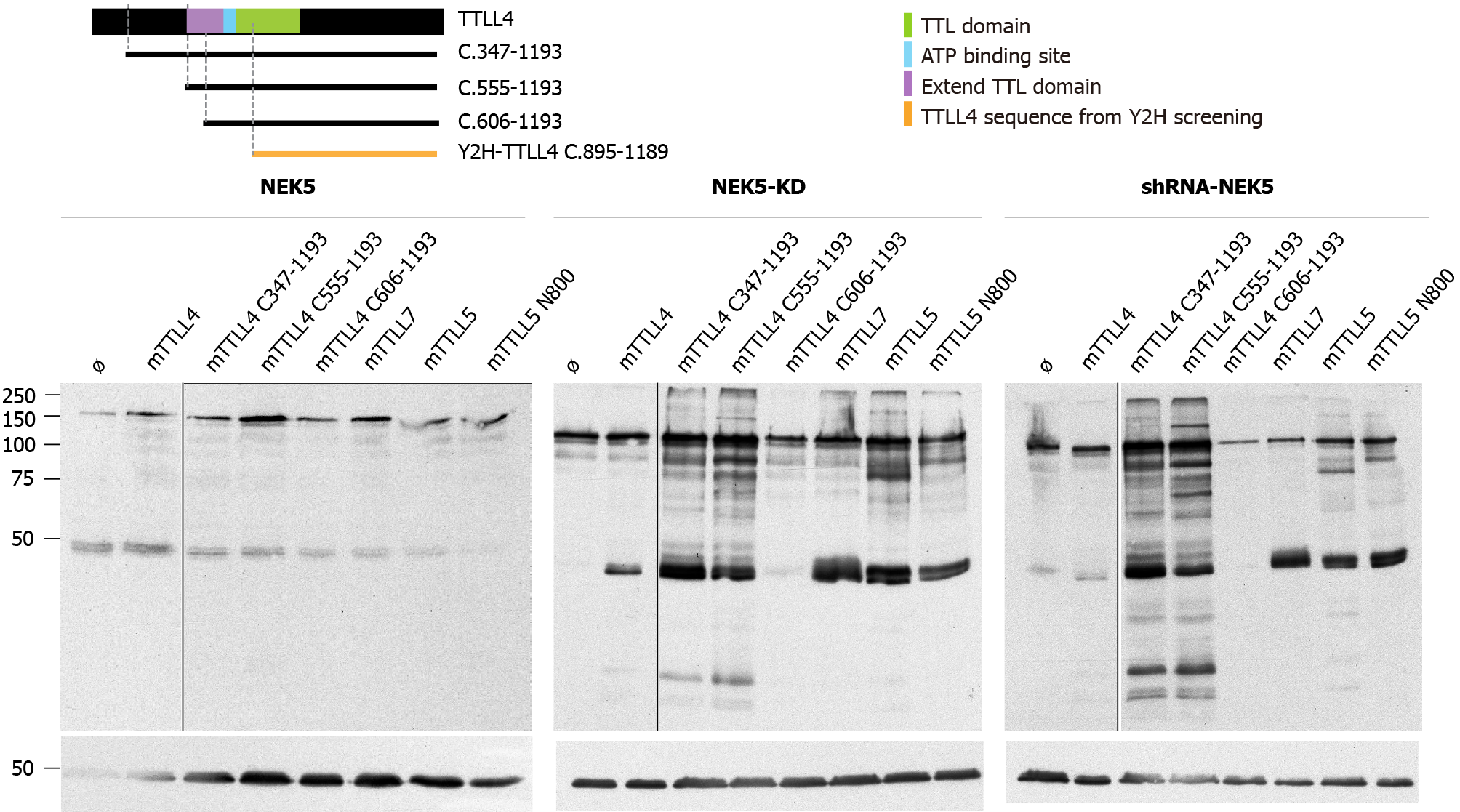
Figure 3 The effect of never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 on the activity of different truncations of the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4.
A: Schematic representation of the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) 4 constructs used. The sequences expressed for each truncated version used in this work are depicted as black bars underneath the pictograms of the full-length TTLL proteins. Domains unnecessary or required for autonomous activities are shown. Green area corresponds to tubulin tyrosine ligase domain (599-942 a.a.), the purple area is extended tubulin tyrosine ligase domain, the blue area is the ATP binding site and the orange construction is the TTLL4 sequence identified by yeast two-hybrid screening. See text for more details; and B-D Analysis by Western blot of truncations of TTLL4 and TTLL5 promoting polyglutamylation in (b) control, (c) cells stably expressing never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5-kinase-dead or (d) cells silenced for expression of never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5. NEK5: Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5; KD: Kinase-dead; shRNA: Short hairpin ribonucleic acid; EYFP: Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; TTLL: Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like.
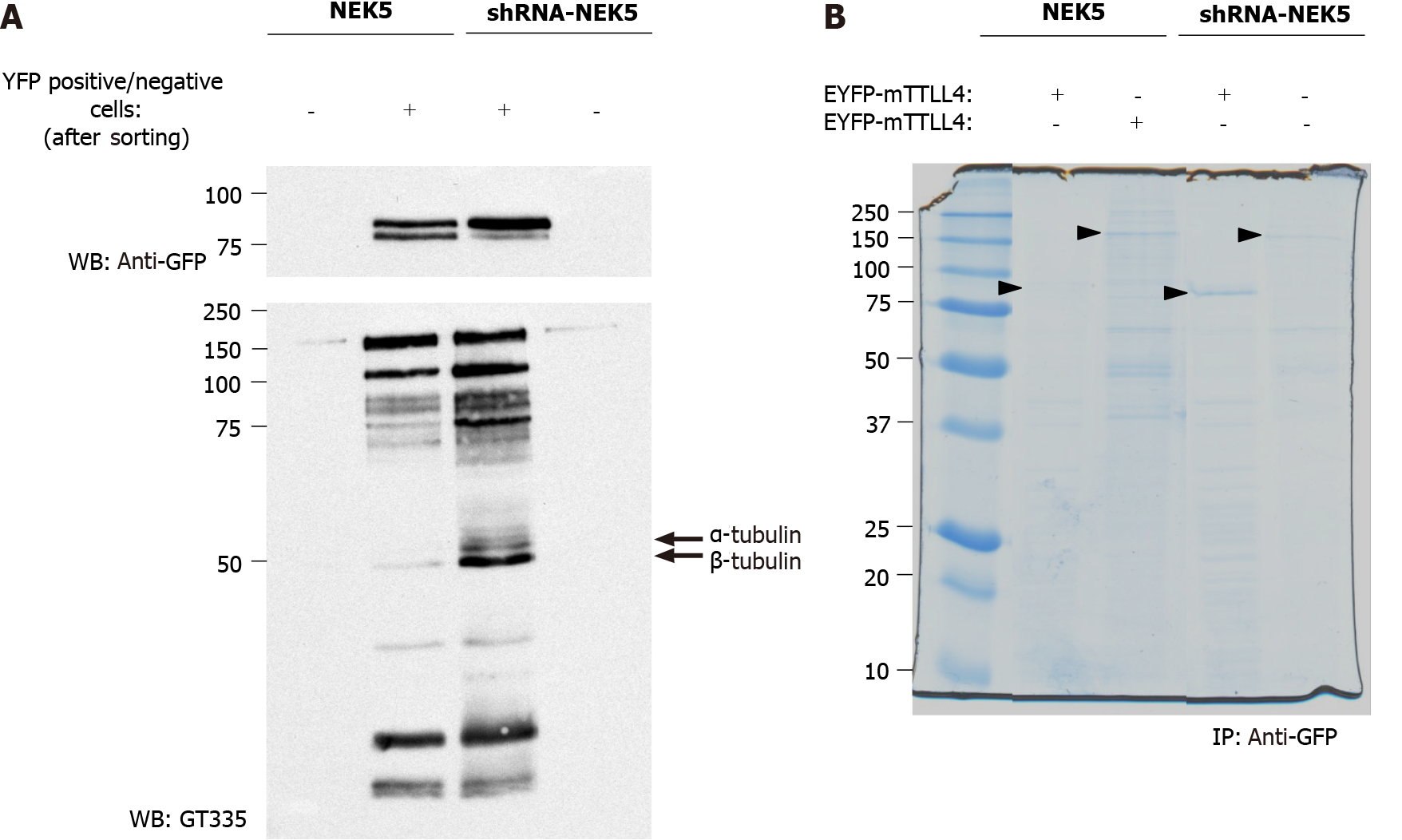
Figure 4 Presence of never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 decreases tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4 activity in a phosphorylation dependent manner.
Short hairpin ribonucleic acid-never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 and control cells transfected with enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP)-tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) 4 or EYFP-TTLL5 were sorted in TTLL5/TTLL4+ and TTLL5/TTLL4- cells by flow cytometry. A: Sorted EYFP-TTLL4 transfected cells were lysed and analyzed by Western-blot. Stable cells expressing never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5 were used as controls; and B: The protein extracts from EYFP-mTTLL-4 or -5 positive cells were immunoprecipitated by anti-green fluorescent protein-beads for TTLL4 or TTLL5 enrichment. The bands indicated by the black arrow correspond to TTLL4 and TTLL5, respectively, and were cut, digested and submitted to mass spectrometry. NEK5: Never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 5; GFP: Green fluorescent proteins; shRNA: Short hairpin ribonucleic acid; EYFP: Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; TTLL: Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like.
Figure 5 Tyrosine 815 is important for tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4 activity.
Based on the residues identified by mass spectrometry, phosphomimetic or inactivating point mutants (Ser/Thr/Tyr to Alanine, Phenylalanine) were generated. A: Schematic representation of the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4 and sites of target amino acids for point mutations. The green region corresponds to the tubulin tyrosine ligase domain; and B: HEK293T proteins of cells transfected with enhanced yellow fluorescent protein-tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4 containing different mutations were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes and stained with GT335, anti-green fluorescent proteins and anti-tubulin antibodies. GFP: Green fluorescent proteins; shRNA: Short hairpin ribonucleic acid; EYFP: Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; TTLL: Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like; TTL: Tubulin tyrosine ligase.
- Citation: Melo-Hanchuk TD, Kobarg J. Polyglutamylase activity of tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 4 is negatively regulated by the never in mitosis gene A family kinase never in mitosis gene A -related kinase 5. World J Biol Chem 2021; 12(3): 38-51
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v12/i3/38.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v12.i3.38