Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 21, 2019; 10(3): 44-64
Published online Nov 21, 2019. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v10.i3.44
Published online Nov 21, 2019. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v10.i3.44
Figure 1 Bioinformatics analysis of hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 and serpin mRNA binding protein 1 amino acid sequences.
A: Alignment between hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 (HABP4) and serpin mRNA binding protein 1 (SERBP1) and their predicted secondary structure content obtained by Clustal Omega and PSIPRED 4.0, respectively; B: Predictable disorder of HABP4 and SERBP1 structure obtained by DISOPRED 3. Below amino acids: Asterisk: Identical amino acid residues; colon: Strong similar properties; period: Weak similar properties. HABP4: Hyaluronic acid binding protein 4; SERBP1: Serpin mRNA binding protein 1.
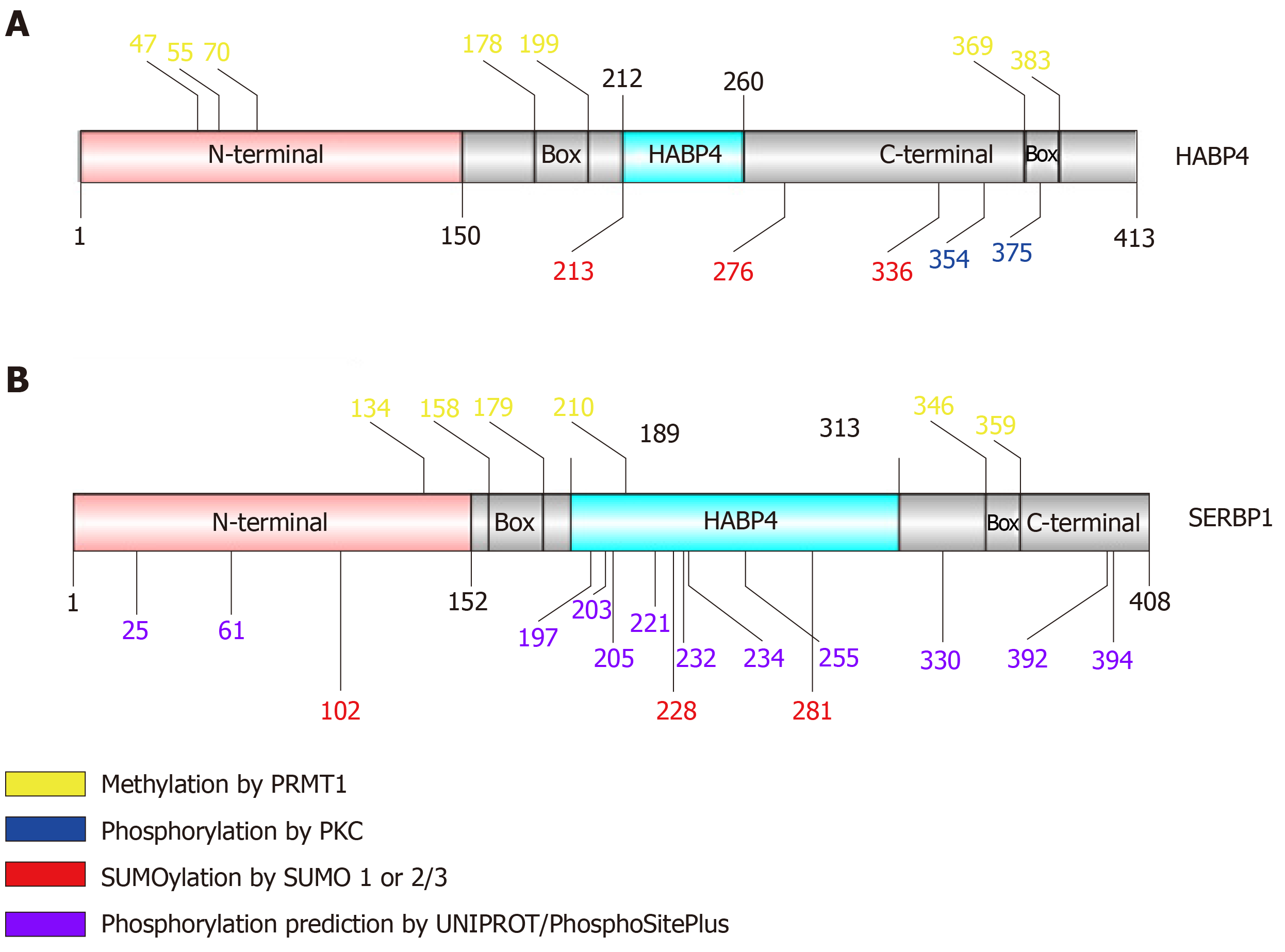
Figure 2 Schematic view of hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 and serpin mRNA binding protein 1 primary structure identifying residues that exhibit post-translational modification.
The pink region corresponds to the N-terminal domain; gray corresponds to the C-terminal; light blue corresponds to the HABP4 domain. “Box” indicates RGG/RXR boxes.
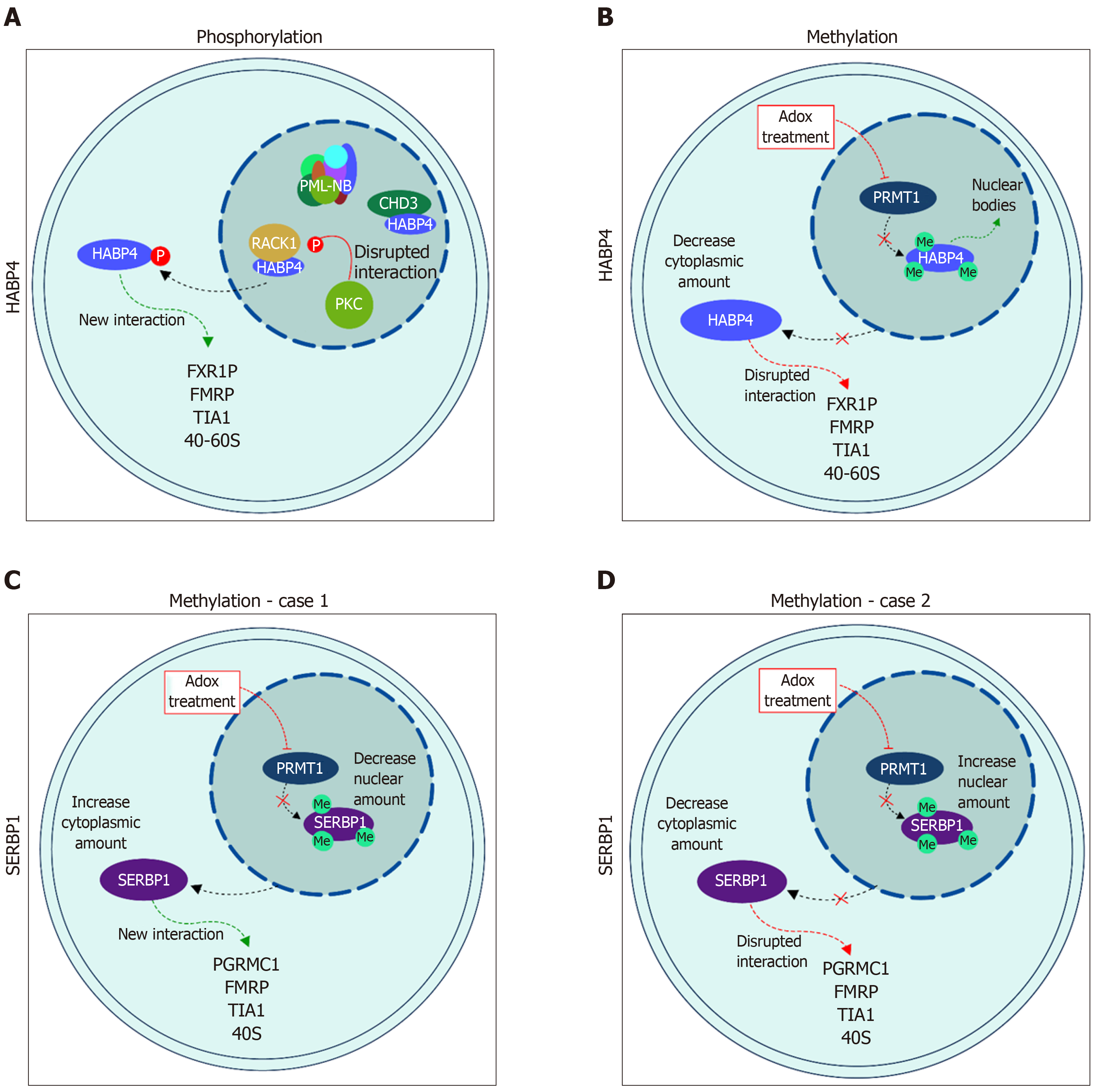
Figure 3 Cellular localization of hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 and serpin mRNA binding protein 1 in response to post-translational modification.
A: Localization of hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 (HABP4), in light blue, after phosphorylation; and B: after methylation; C and D: Localization of serpin mRNA binding protein 1 (SERBP1), in purple, after methylation. SERBP1 methylation is still controversial and both possibilities are presented as related in the literature: C[26] and D[28]. Please see text for details. HABP4: Hyaluronic acid binding protein 4; SERBP1: Serpin mRNA binding protein 1.
Figure 4 Global protein interaction network of hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 and serpin mRNA binding protein 1.
The published interactors of hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 (HABP4) (top) and serpin mRNA binding protein 1 (SERBP1) (below) were linked to the specific domains of interaction. Proteins that interact with both N- and C-terminal domains, or the site of interaction is unknown, were linked to the blue center. Common interactors between HABP4 and SERBP1 are connected to both proteins and are located between both proteins. Red dotted lines are published interactors of HABP4, and blue dotted lines are interactors of SERBP1. HABP4: Hyaluronic acid binding protein 4; SERBP1: Serpin mRNA binding protein 1.
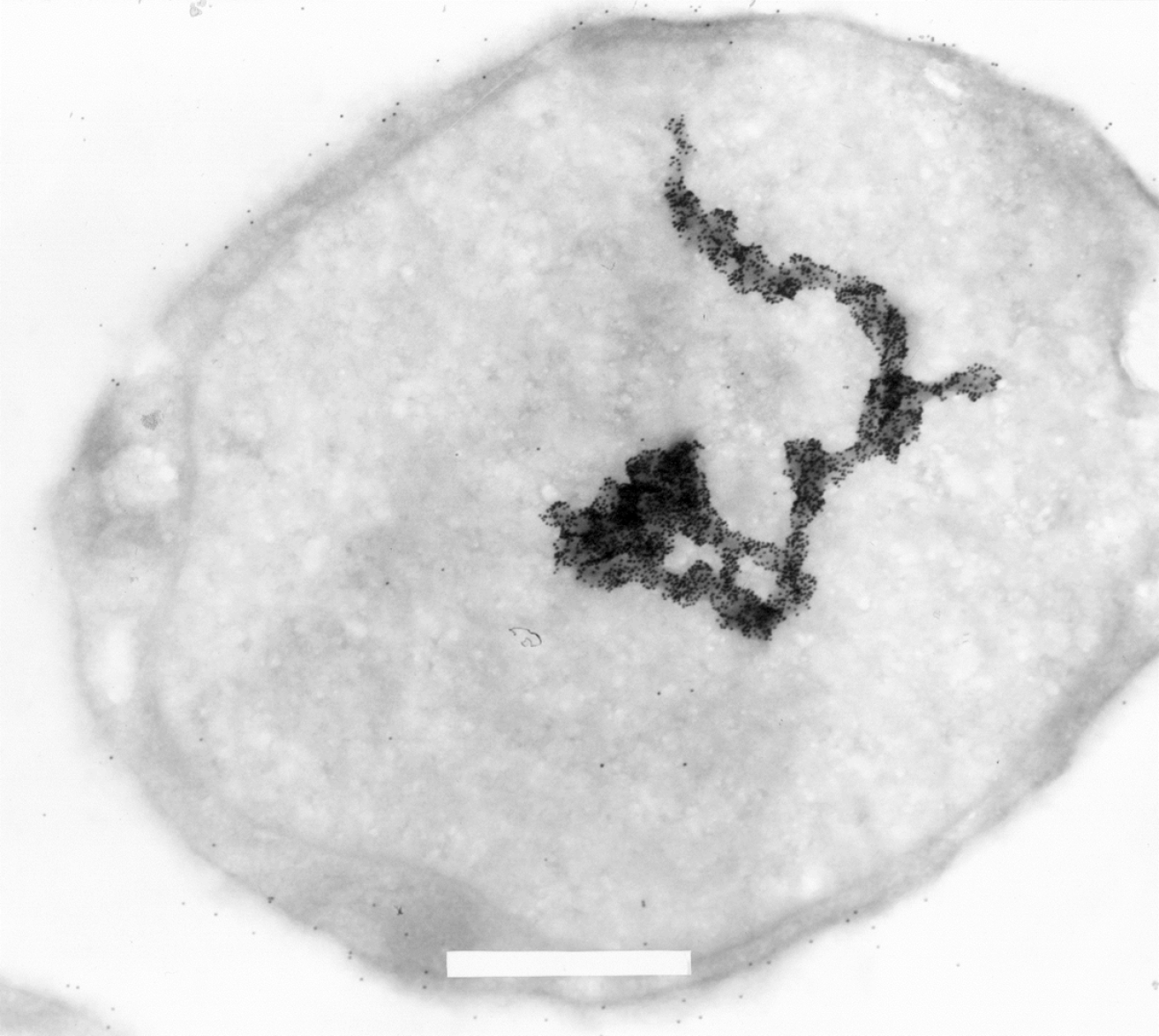
Figure 5 Electron microscopic image of a L540 Hodgkin-derived cell labeled with 15 nm gold-particle-coupled Ki-1 antibody (× 29.
000 fold magnification). Some labeling on the cell surface is due to Ki-1 binding to the CD30 cell surface receptor. Strong hyaluronic acid binding protein 4 (HABP4) labeling can be detected in the nucleus and the format of the large macrostructure seems to represent part of a chromosome or also (transcriptionally active?) chromatin. A part of the upper end of the macrostructure seems to follow a “corkscrew”-like pattern. Each small black dot is a single Ki-1 gold labeled antibody. Please see[3] for more experimental details. In brief, cells were pelleted by centrifugation. The cell pellet was solidified on ice and the solid cell block was prepared in slices of 2 mm that were dehydrated by incubation in a solution containing stepwise increasing sucrose concentration up to 70%. After fixation in frozen nitrogen, ultrathin cryosections were prepared with an ultracut E, FC-4D and collected on nickel grids. After incubation with Ki-1 antibody, washing, and incubation with secondary reagent Staphylococcal aureus protein A-gold labeled, and further washing, the sections were fixed and contrasted with 4% uranyl acetate to be subsequently analyzed in a Siemens Elmiskop 101, Electron Microscope. We would like to thank Prof. Dr. Hilmar Lemke (Kiel, Germany) for generously providing the electron micrography.
- Citation: Colleti C, Melo-Hanchuk TD, da Silva FRM, Saito Â, Kobarg J. Complex interactomes and post-translational modifications of the regulatory proteins HABP4 and SERBP1 suggest pleiotropic cellular functions. World J Biol Chem 2019; 10(3): 44-64
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v10/i3/44.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v10.i3.44