Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2010; 2(11): 399-406
Published online Nov 15, 2010. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v2.i11.399
Published online Nov 15, 2010. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v2.i11.399
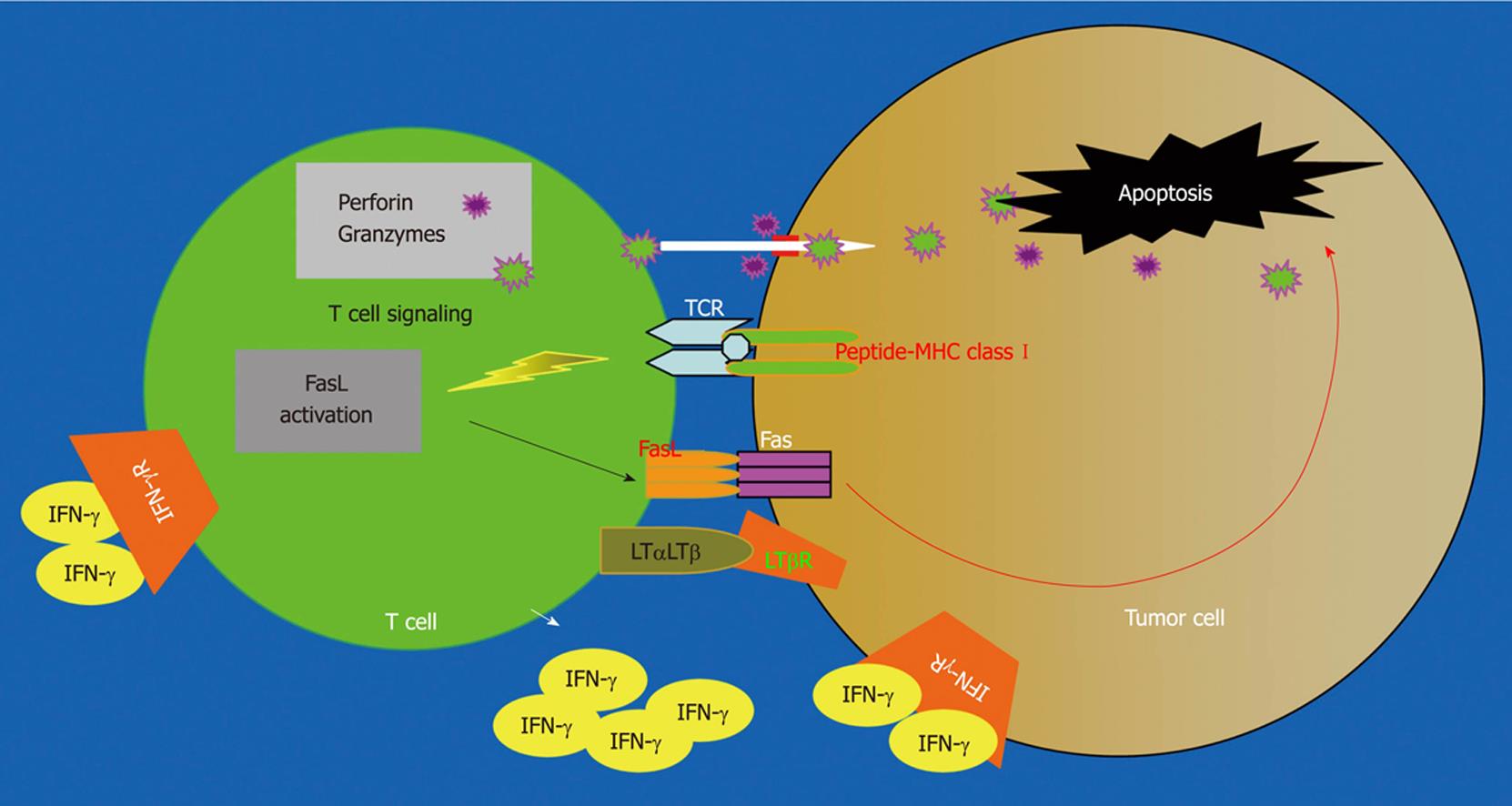
Figure 1 Anti-tumor cytotoxicity pathways.
Tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) recognize tumor cells through TCR and Ag-bound MHC class I. Interactions between the CTL and the tumor cell involve direct cell-cell physical contact and release of modulator molecules (i.e. IFN-γ and other molecules). CTLs primarily use the perforin exocytosis pathway and the Fas-mediated apoptosis pathways to destruct the tumor cells. However, other effector mechanisms, such as the LTβR-mediated apoptosis pathway, also play a role in tumor cell destruction.
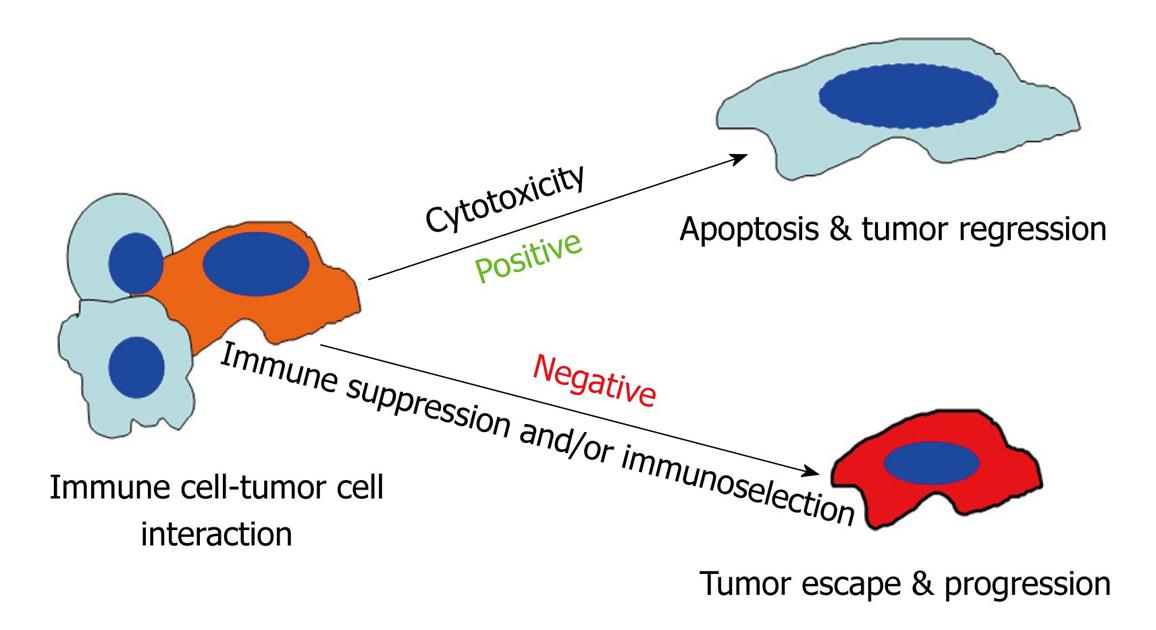
Figure 2 Model of immune cell-tumor cell interaction.
Interactions between immune cells and tumor cells involve direct cell-cell physical contact and release of modulator molecules, primarily cytokines and chemokines. In this survival and death battle, on the one hand, the immune cells may prevail and eradicate the tumor cells. On the other hand, tumor cells can counterattack the immune cells by producing inhibitory molecules, activating the immune suppressive cells or acquiring apoptosis-resistant mechanisms to avoid destruction by the immune system. Thus, the anti-tumor immune response can be a two-edged sword and can result in both positive and negative consequences.
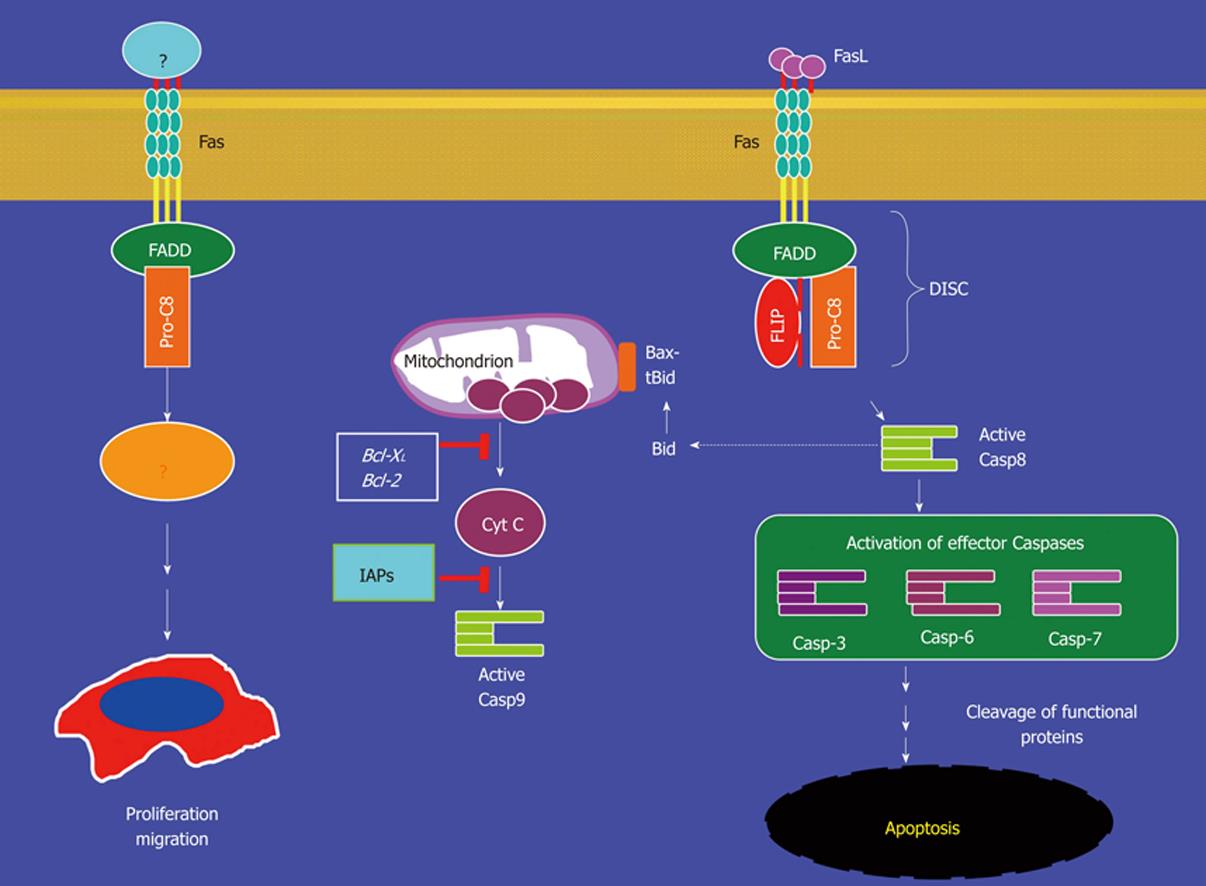
Figure 3 Fas-mediated signaling pathways.
Engagement of the Fas receptor induces DISC formation and subsequently caspase 8 activation. The active caspase 8 can either directly activate caspase 3 to initiate apoptosis, or active caspase 8 may cleave and activate Bid (tBid). tBid interacts with Bax to activate the caspase 9 cascade to induce apoptosis. On the other hand, Fas signaling may also lead to activation of cellular proliferation. Therefore, Fas engagement may leads to two conflicting cellular processes: apoptosis and survival. The molecular mediators controlling the switcher between these two opposing pathways remain to be determined.
- Citation: Liu K. Role of apoptosis resistance in immune evasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2010; 2(11): 399-406
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v2/i11/399.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v2.i11.399