Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2024; 16(4): 1479-1499
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1479
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1479
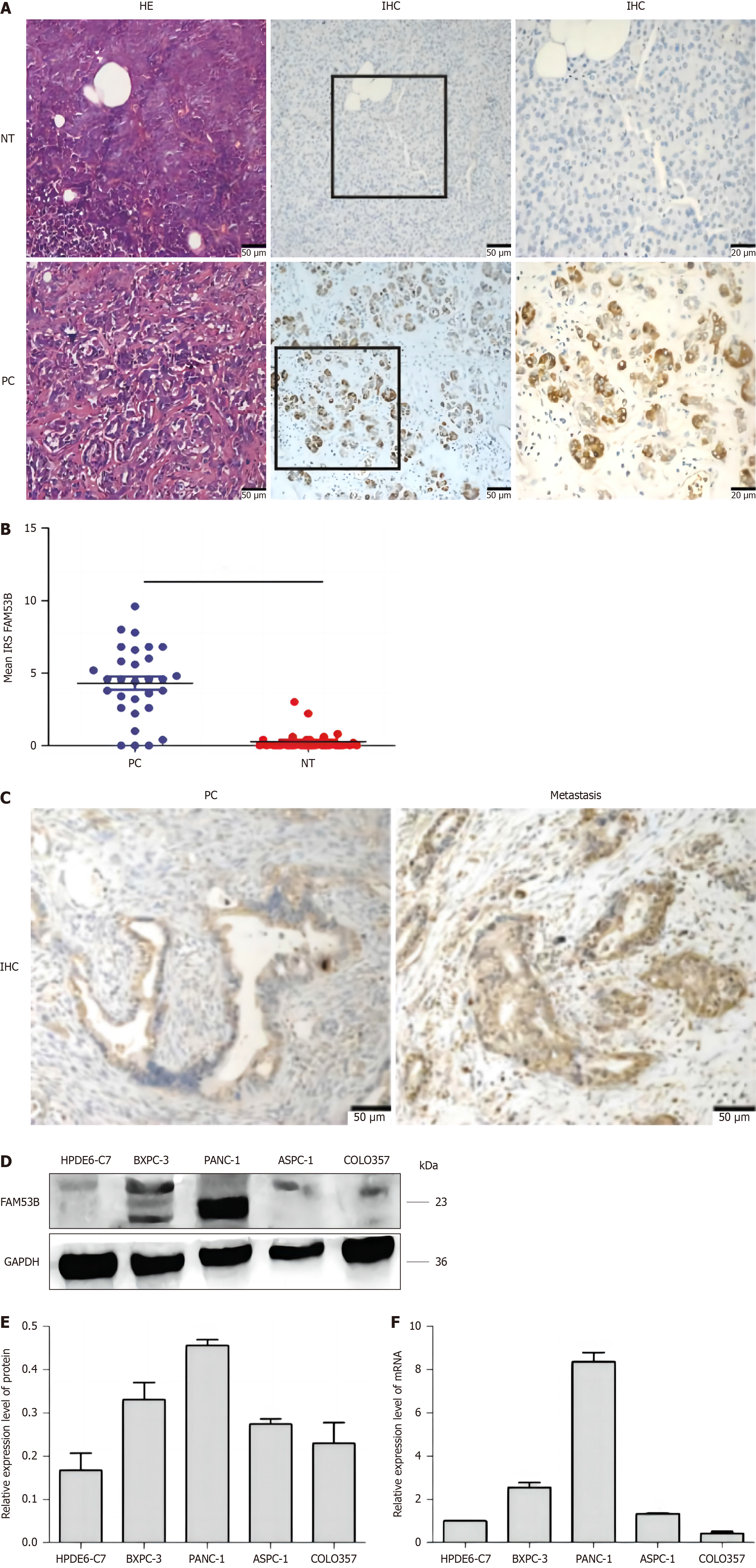
Figure 1 FAM53B expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissue.
A: Hepatic encephalopathy staining of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and para-carcinoma tissue (n = 30); B and C: Immunohistochemical staining for immune response score (NT for para-cancer non-tumor tissue, PC for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissue); D and E: Western blot analysis; F: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. HE: Hepatic encephalopathy.
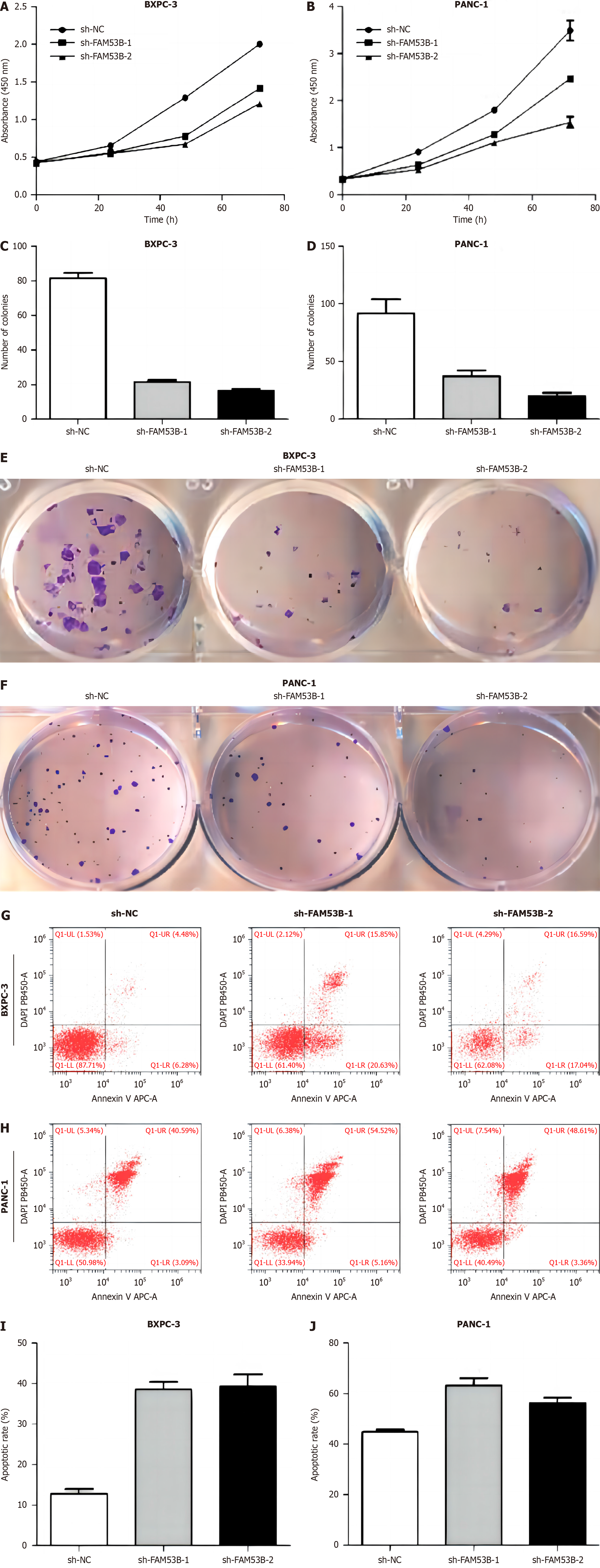
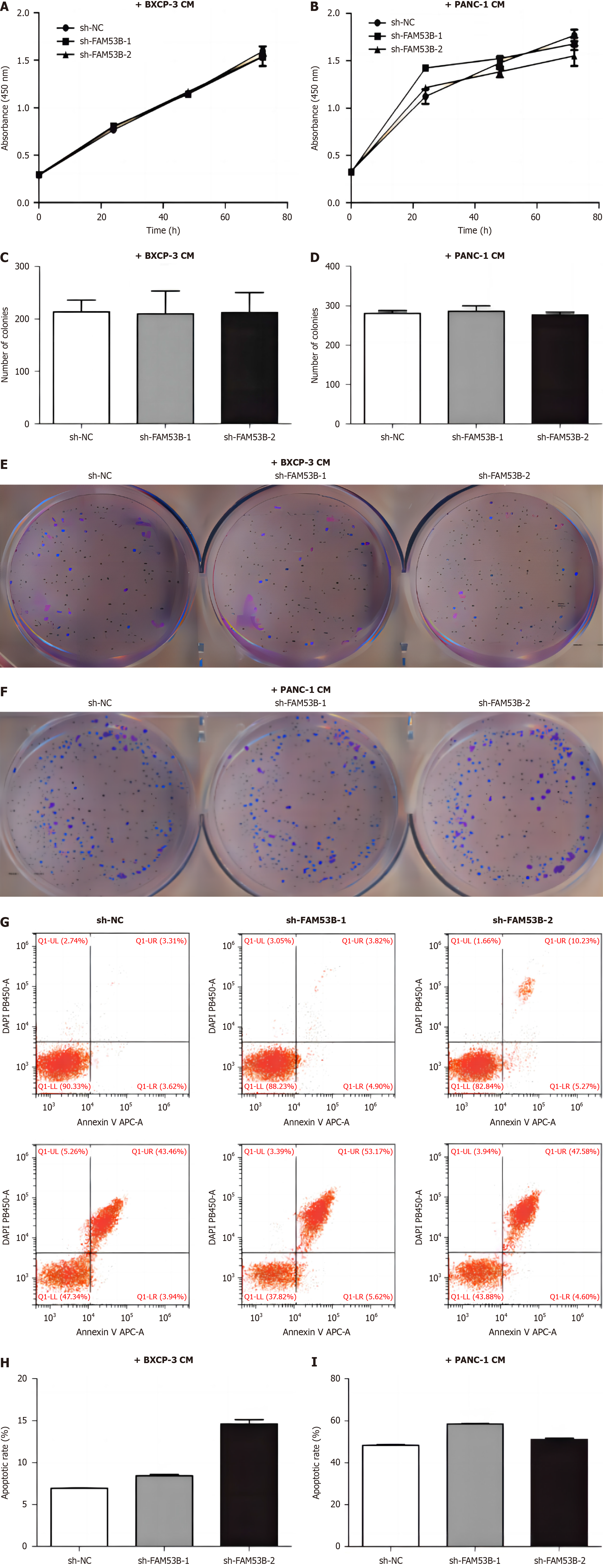
Figure 2 FAM53B knockout inhibited pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell proliferation.
A and B: Cell counting kit-8; C-F: Colony formation; G-J: Flow cytometry.
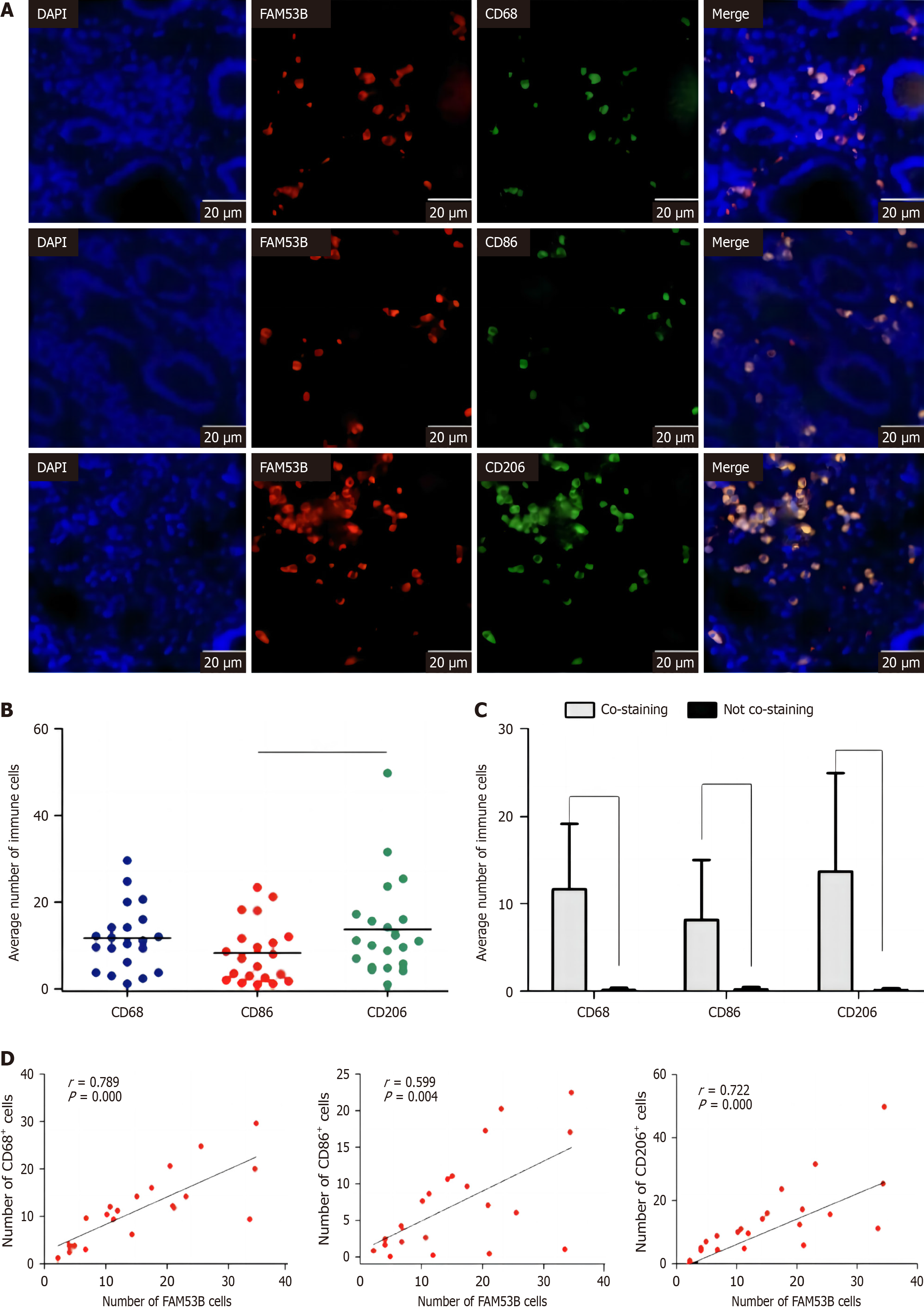
Figure 3 FAM53B expression associated with M2 polarization.
A-C: Tissue immunohistochemical test; D: FAM53B (+) associated with M2.
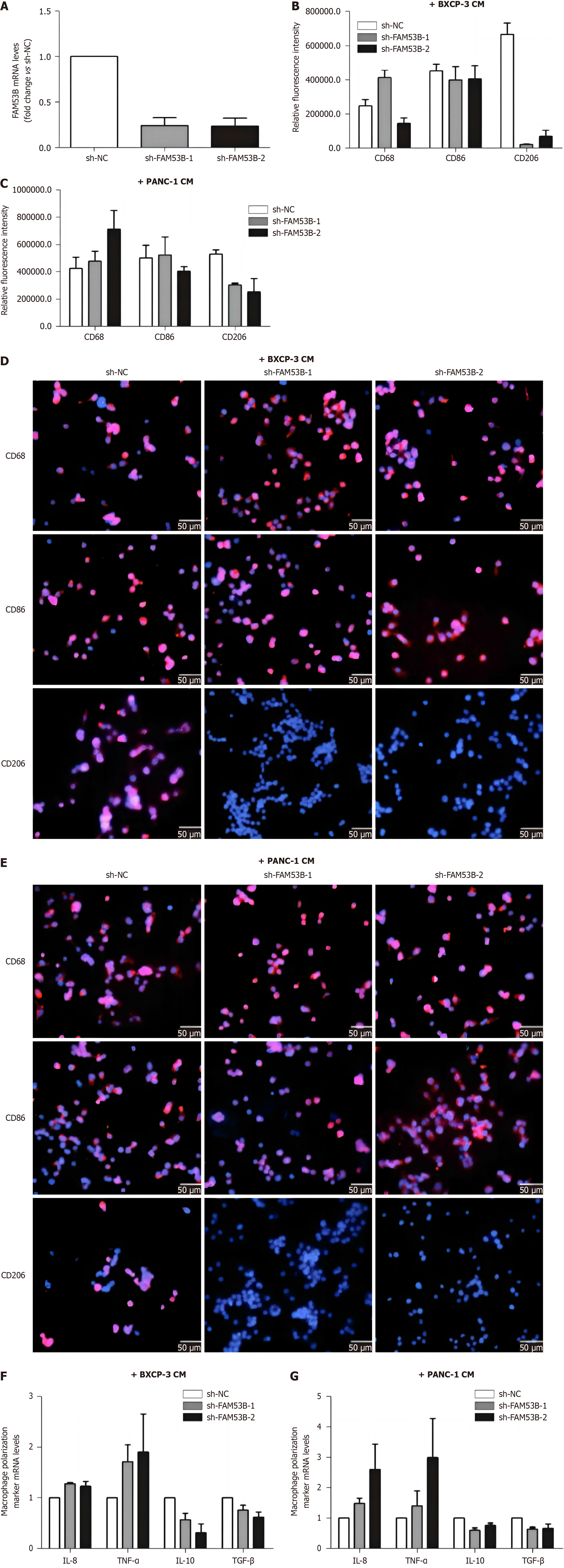
Figure 4 FAM53B induces the polarization of M2.
A-E: Tumor-associated macrophages induced; F and G: Expression of M1 macrophage markers.
Figure 5 M2 polarized macrophages have no effect on proliferation.
A and B: Cell counting kit-8 experiment; C-F: Single cell cloning experiment; G-I: Flow cytometry experiment.
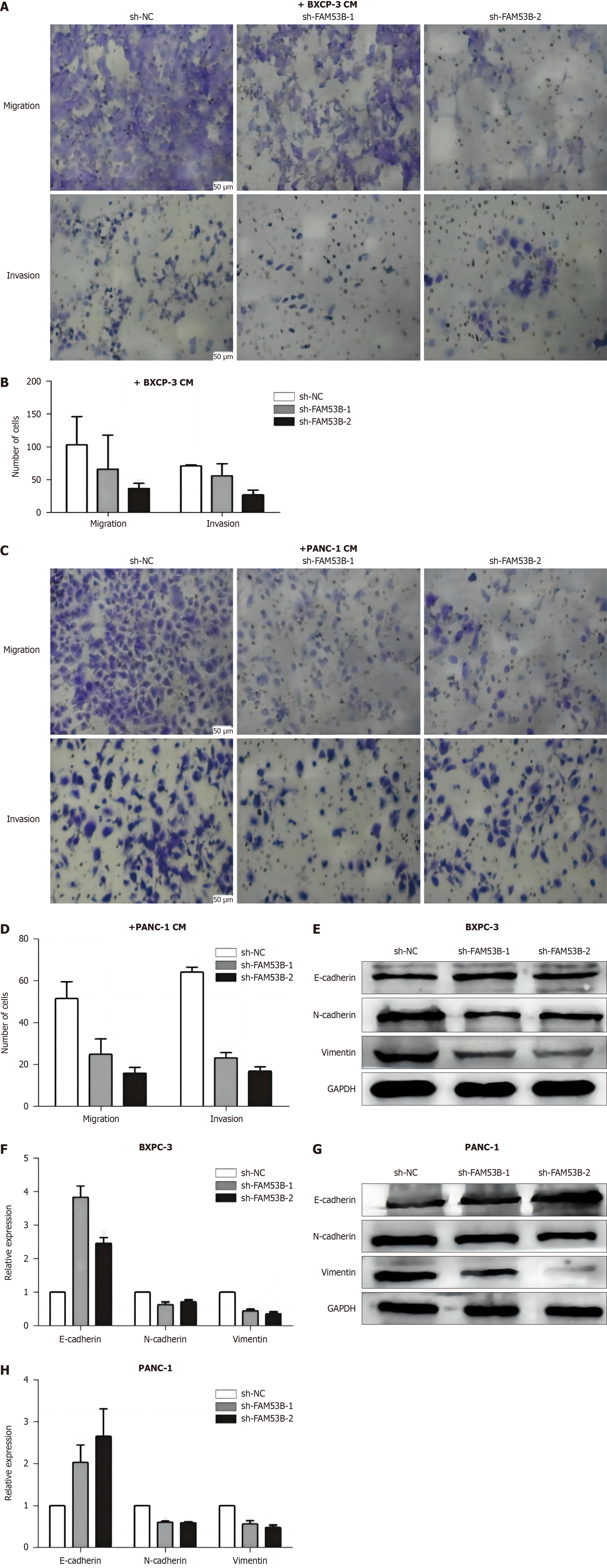
Figure 6 M2 polarized macrophages promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell development and invasion.
A-D: Transwell experiment; E-H: Western blotting experiment.
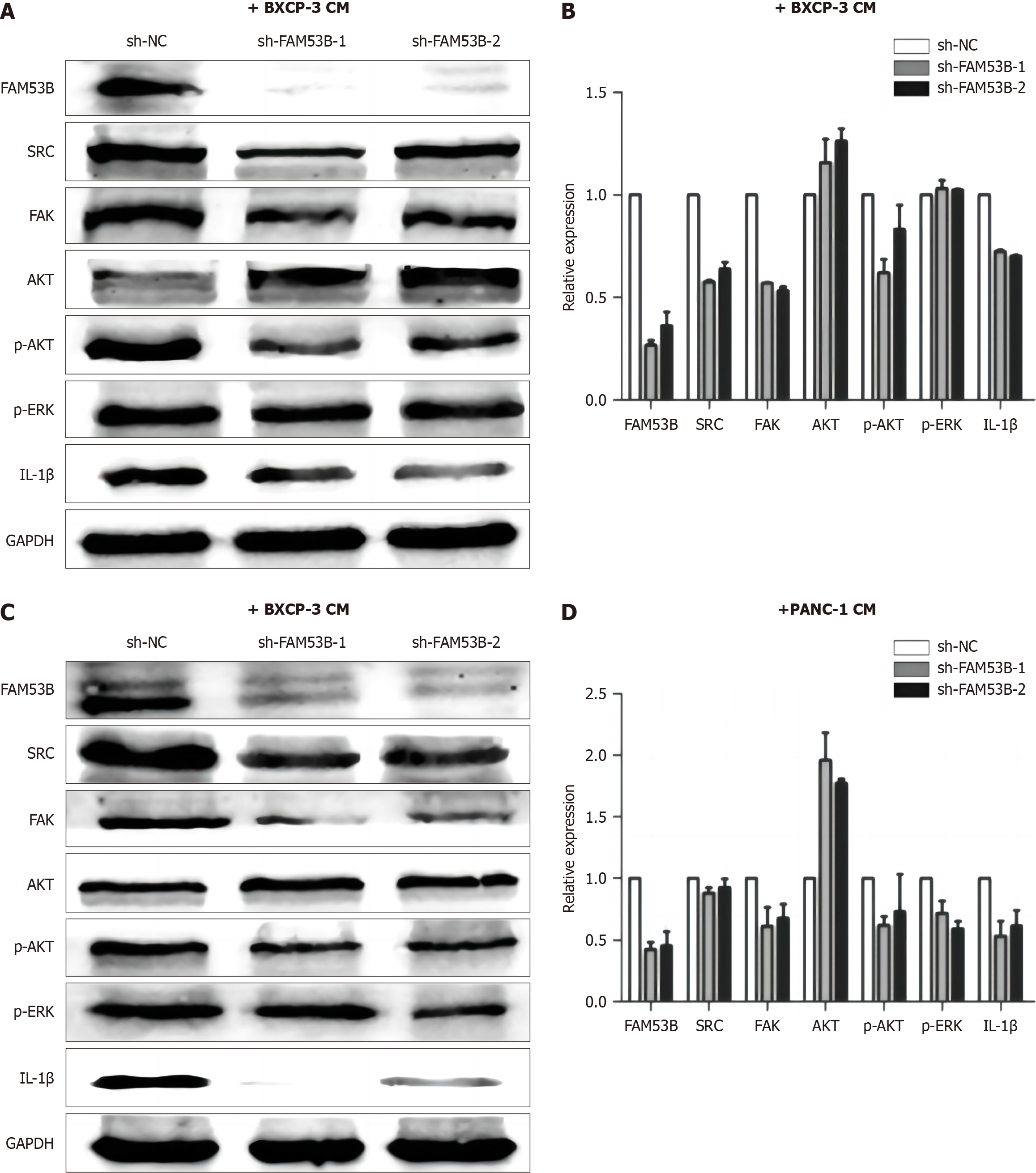
Figure 7 FAM53B induces M2 polarization by activating the Src/FAK/p-Akt/IL-1β signaling pathway.
A and B: FAM53B knockout in induced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs); C and D: FAM53B knockout in PANC-1-induced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma TAMs.
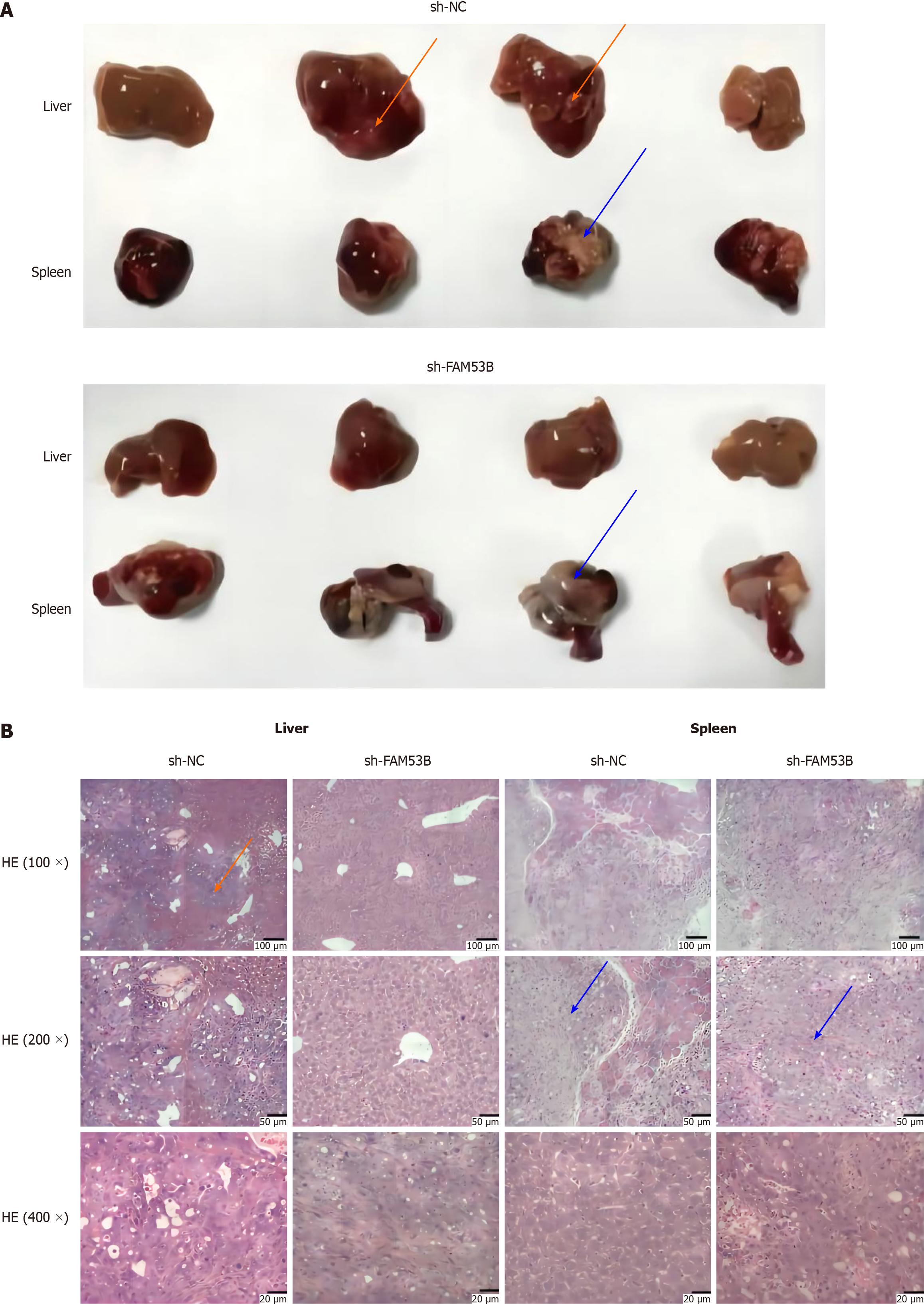
Figure 8 FAM53B induces pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis.
A: Metastasis model was established in the spleen of nude mice; B: Hepatic encephalopathy staining. HE: Hepatic encephalopathy.
- Citation: Pei XZ, Cai M, Jiang DW, Chen SH, Wang QQ, Lu HM, Lu YF. FAM53B promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis by regulating macrophage M2 polarization. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(4): 1479-1499
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i4/1479.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1479