Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2023; 15(10): 1756-1770
Published online Oct 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i10.1756
Published online Oct 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i10.1756
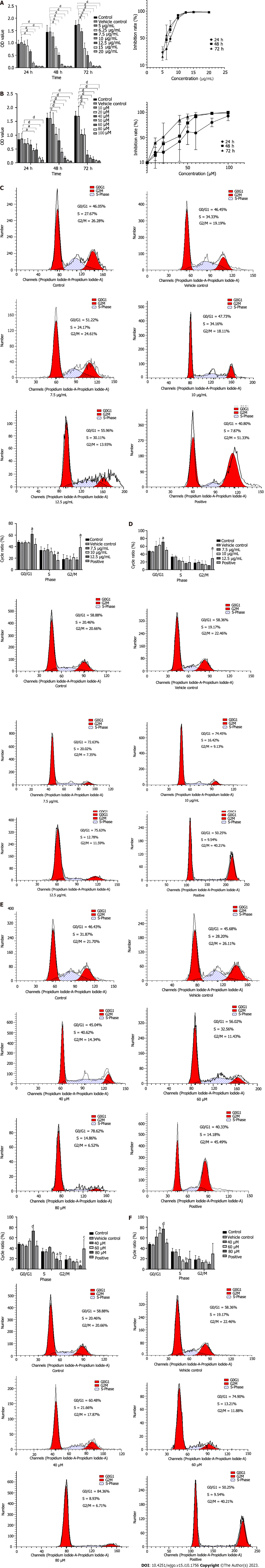
Figure 1 The effects of pomolic acid and pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester on proliferation of colon cancer cells.
A: The proliferation of HT-29 cells after treatment with different concentrations of pomolic acid (PA) for 24, 48, and 72 h; B: The proliferation of HT-29 cells after treatment with different concentrations of pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (PAO) for 24, 48, and 72 h; C: The cell cycle distribution of HT-29 cells after treatment with different concentrations of PA for 24 h; D: The cell cycle distribution of HT-29 cells after treatment with different concentrations of PA for 48 h; E: The cell cycle distribution of HT-29 cells after treatment with different concentrations of PAO for 24 h; F: The cell cycle distribution of HT-29 cells after treatment with different concentrations of PAO for 48 h. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001.
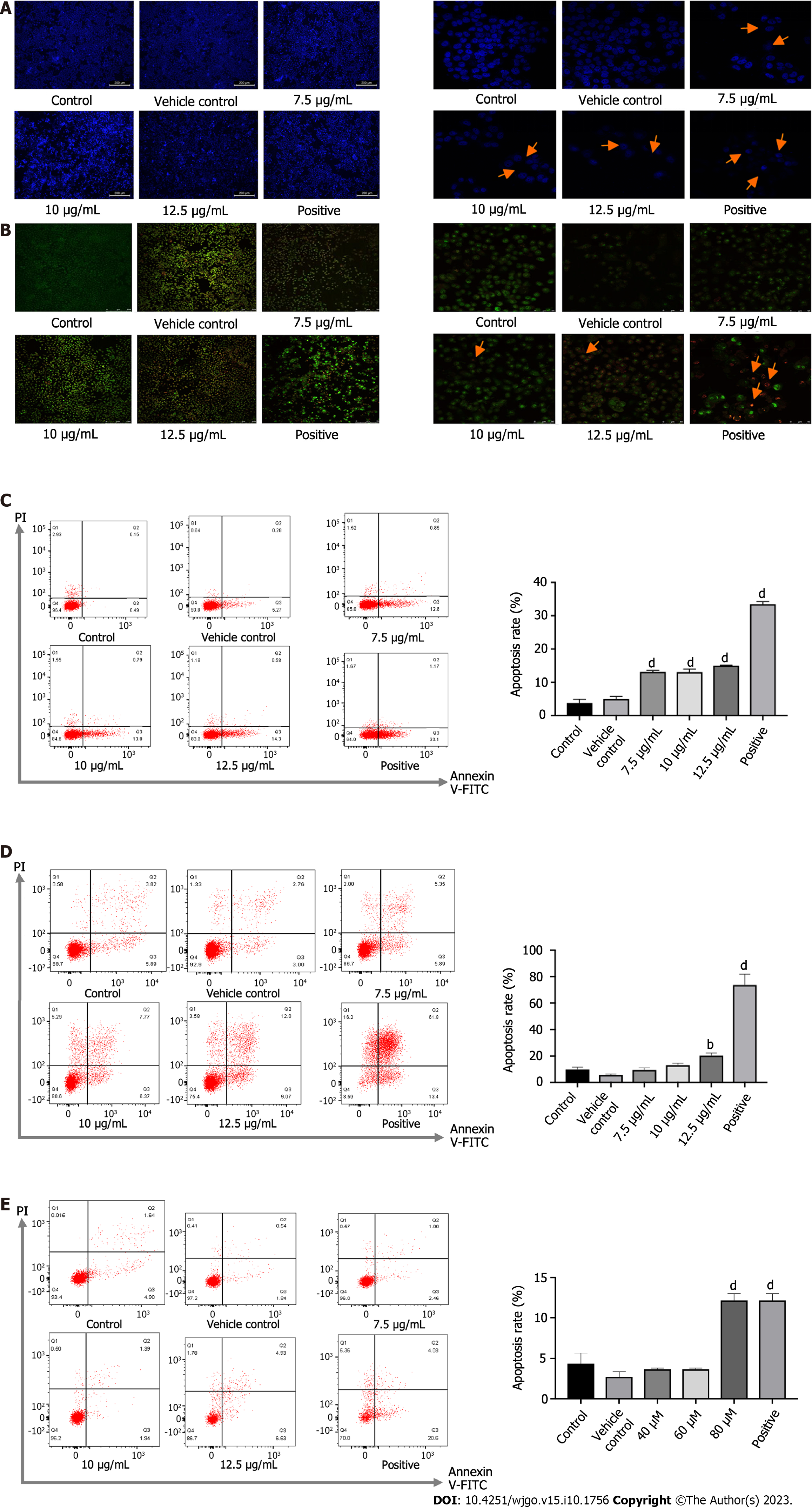
Figure 2 Apoptosis of HT-29 cells after drug administration.
A: HT-29 cells were stained with Hoechst 33342 and observed under an inverted fluorescence microscope (40 ×); B: HT-29 cells were stained with Hoechst 33342 and observed under an inverted fluorescence microscope (400 ×); C: Apoptosis of cells after treated with pomolic acid (PA) for 24 h; D: Apoptosis of cells after treated with PA for 48 h; E: Apoptosis of cells after treated with pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester for 48 h. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001.
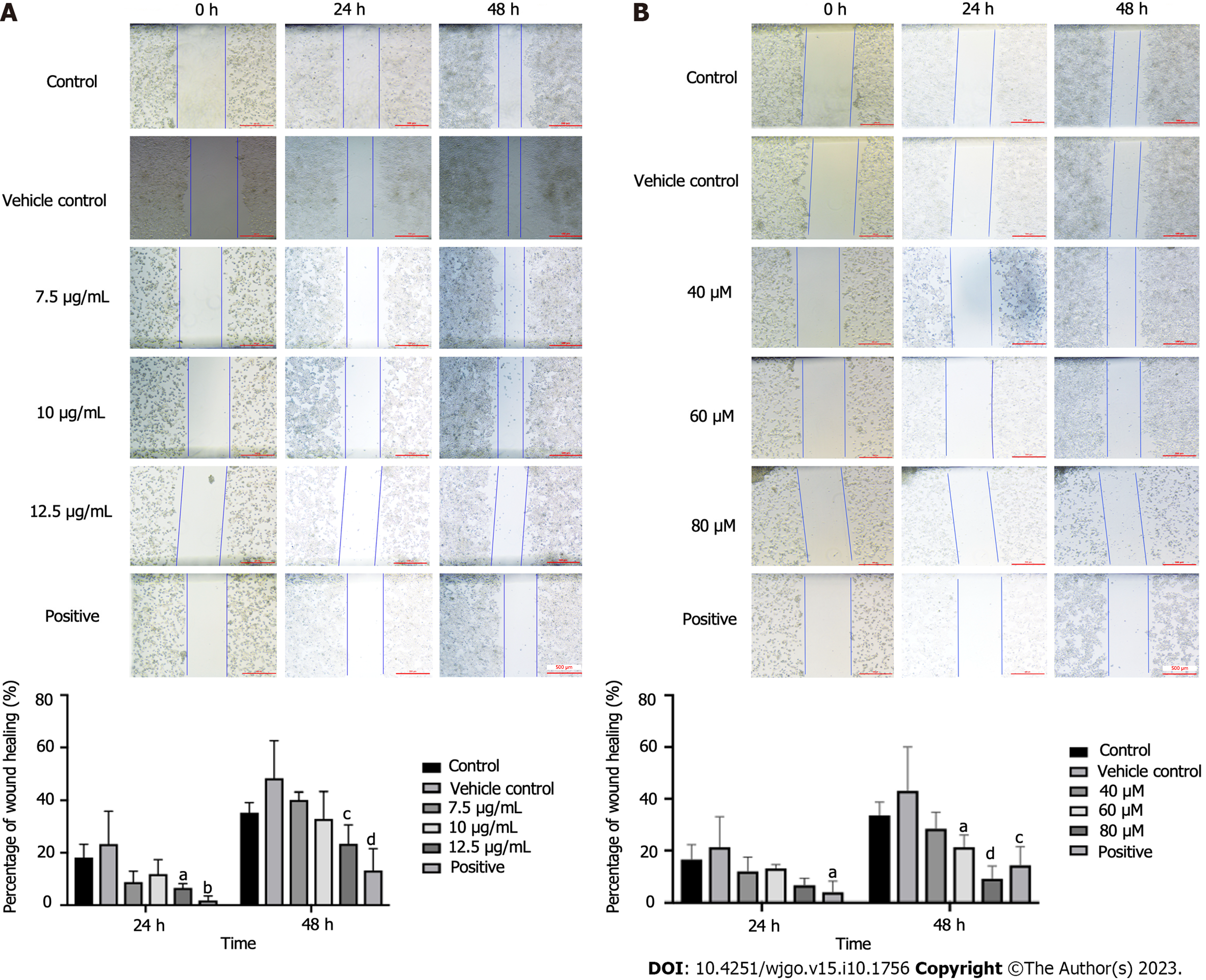
Figure 3 Effects of pomolic acid and pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester on scratch assay in HT-29 cells.
A: The speed and extent of scratch healing of cells after treated with different concentration of pomolic acid; B: The speed and extent of scratch healing of cells after treated with different concentration of pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001.
Figure 4 Effects of pomolic acid and pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester on the relative expression of proteins.
A and B: The expression of apoptosis related protein in HT-29 cells treated with pomolic acid (PA) for 24 h and 48 h; C and D: The expression of autophagy related protein in HT-29 cells treated with PA for 24 h and 48 h; E and F: The expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and janus kinase (JAK) protein in HT-29 cells treated with PA for 24 h and 48 h; G and H: The expression of apoptosis related protein in HT-29 cells treated with pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (PAO) for 24 h and 48 h; I and J: The expression of p62 protein in HT-29 cells treated with PAO for 24 h and 48 h; K: The expression of STAT3 and JAK1 protein in HT-29 cells treated with PAO for 24h; L: The expression of STAT3 protein in HT-29 cells treated with PAO for 48 h. Caspase: Cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase; LC3: Light chain 3; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; JAK: Janus kinase.
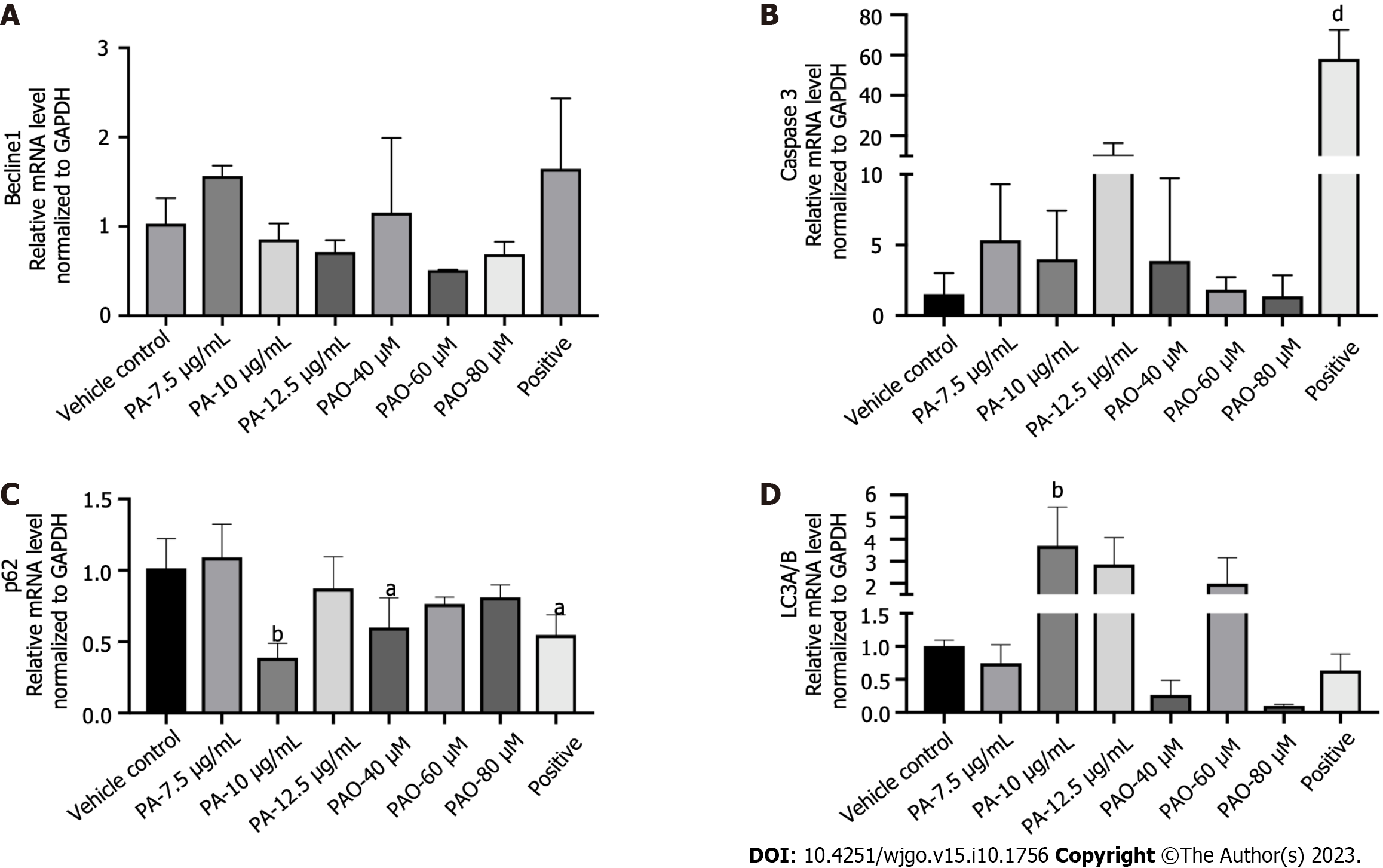
Figure 5 Effects of pomolic acid and pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester on the mRNA expression of Beclin1, cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3, p62, and light chain 3A/B.
A: mRNA expression of Beclin1; B: mRNA expression of cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3; C: mRNA expression of light chain 3A/B; D: mRNA expression of p62. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001. PA: Pomolic acid; PAO: Pomolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester; Caspase 3: Cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3; LC3: Light chain 3.
- Citation: Liu LY, Yu TH, Liao TS, Xu P, Wang Y, Shi M, Li B. Pomolic acid and its glucopyranose ester promote apoptosis through autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(10): 1756-1770
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i10/1756.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i10.1756