Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2022; 14(9): 1675-1688
Published online Sep 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1675
Published online Sep 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1675
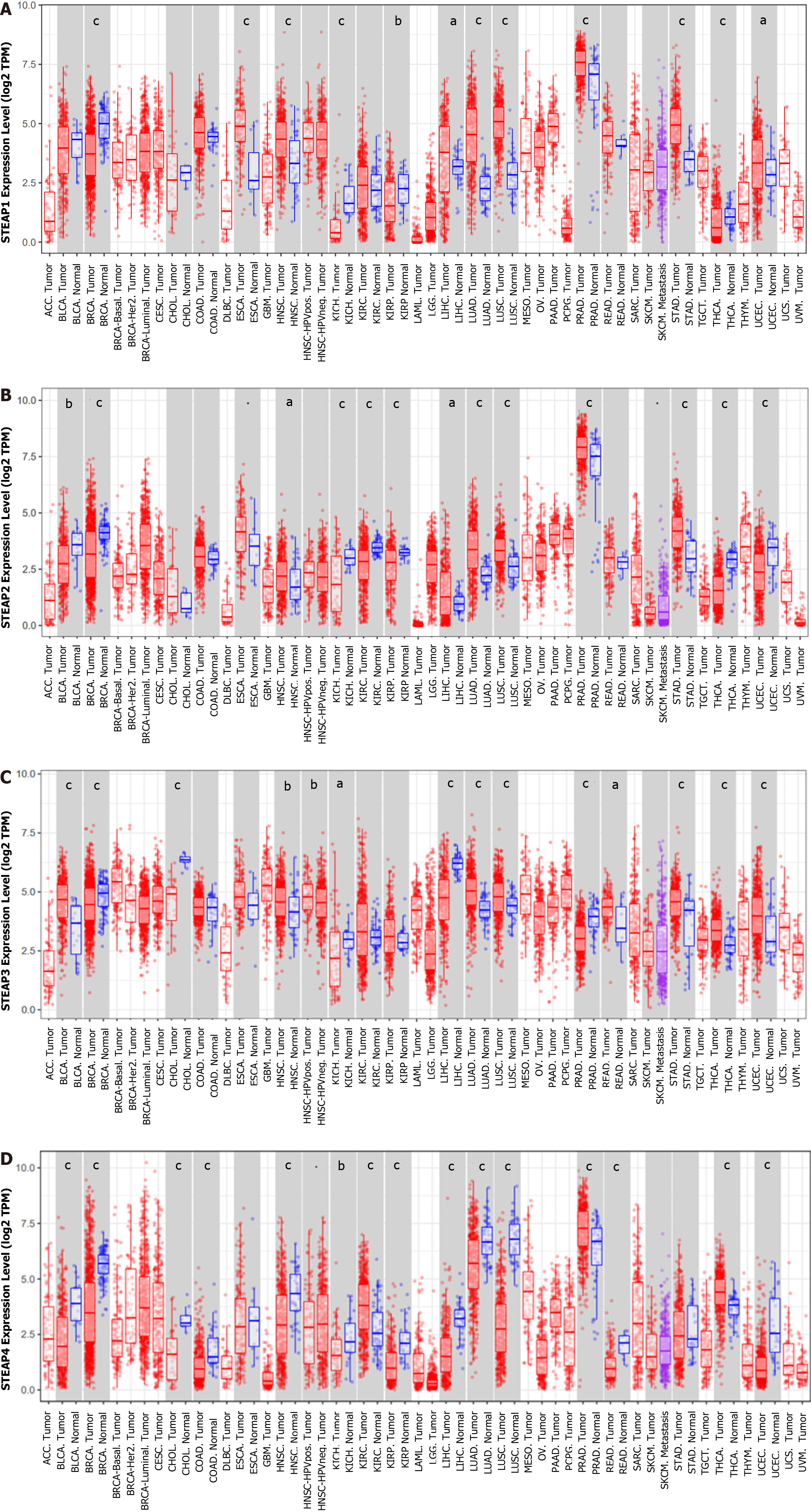
Figure 1 Expression of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate in different normal and cancerous tissues from the TIMER2.
0 database. A: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate (STEAP) 1; B: STEAP2; C: STEAP3; D: STEAP4. Student’s t-test was used to estimate the significance of the differences in gene expression levels between groups. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. STEAP: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate; ACC: Adrenocortical carcinoma; BLCA: Bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA: Breast invasive carcinoma; CESC: Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL: Cholangiocarcinoma; COAD: Colon adenocarcinoma; DLBC: Lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; ESCA: Esophageal carcinoma; GBM: Glioblastoma multiforme; HNSC: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH: Kidney chromophobe; KIRC: Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP: Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LAML: Acute myeloid leukemia; LGG: Brain lower grade glioma; LIHC: Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD: Lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC: Lung squamous cell carcinoma; MESO: Mesothelioma; OV: Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PCPG: Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PRAD: Prostate adenocarcinoma; READ: Rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC: Sarcoma; SKCM: Skin cutaneous melanoma; STAD: Stomach adenocarcinoma; TGCT: Testicular germ cell tumors; THCA: Thyroid carcinoma; THYM: Thymoma; UCEC: Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma; UCS: Uterine carcinosarcoma; UVM: Uveal melanoma.
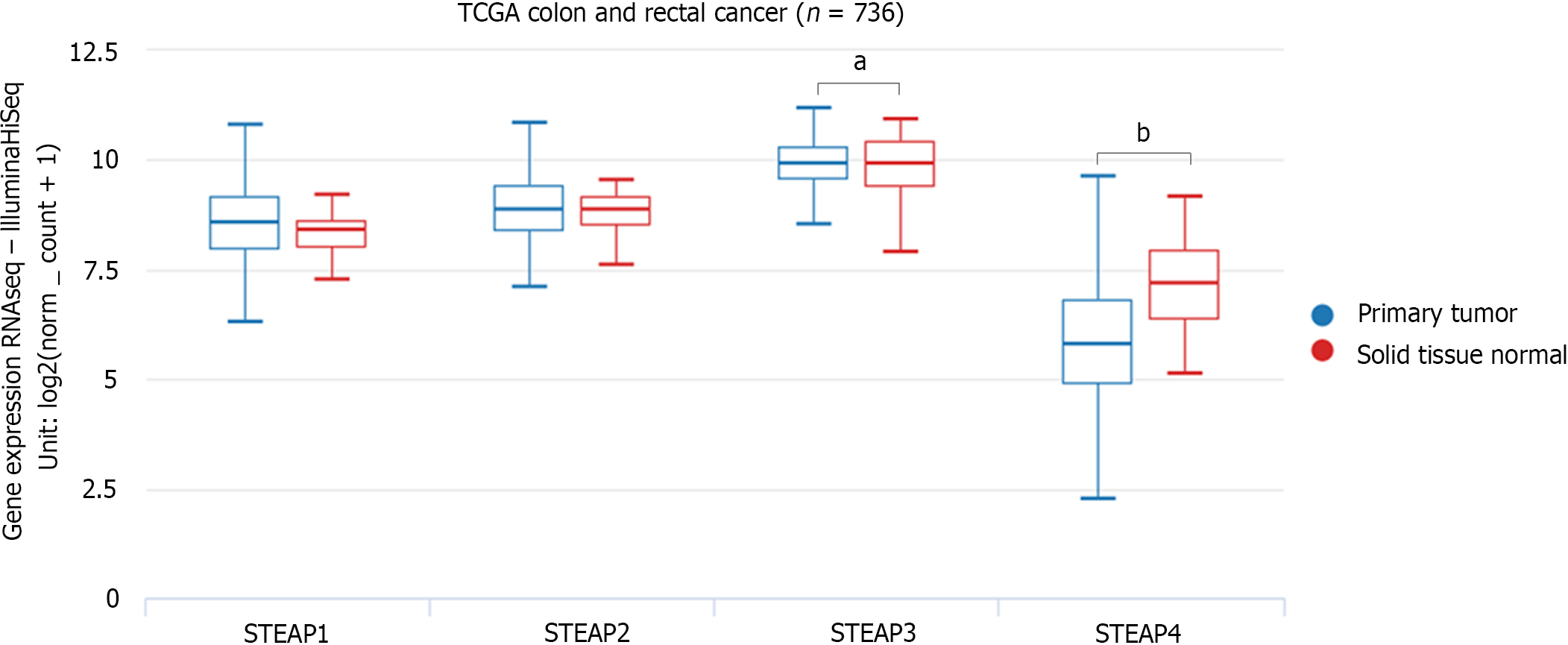
Figure 2 Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate mRNA expression in colon adenocarcinoma and rectal adenocarcinoma tissues in the UCSC Xena database.
Red represents normal tissue and blue is cancerous tissue. One-way ANOVA was utilized to estimate the significance of differences in six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate expression levels between groups. aP < 0.01, bP < 0.001. STEAP: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate.
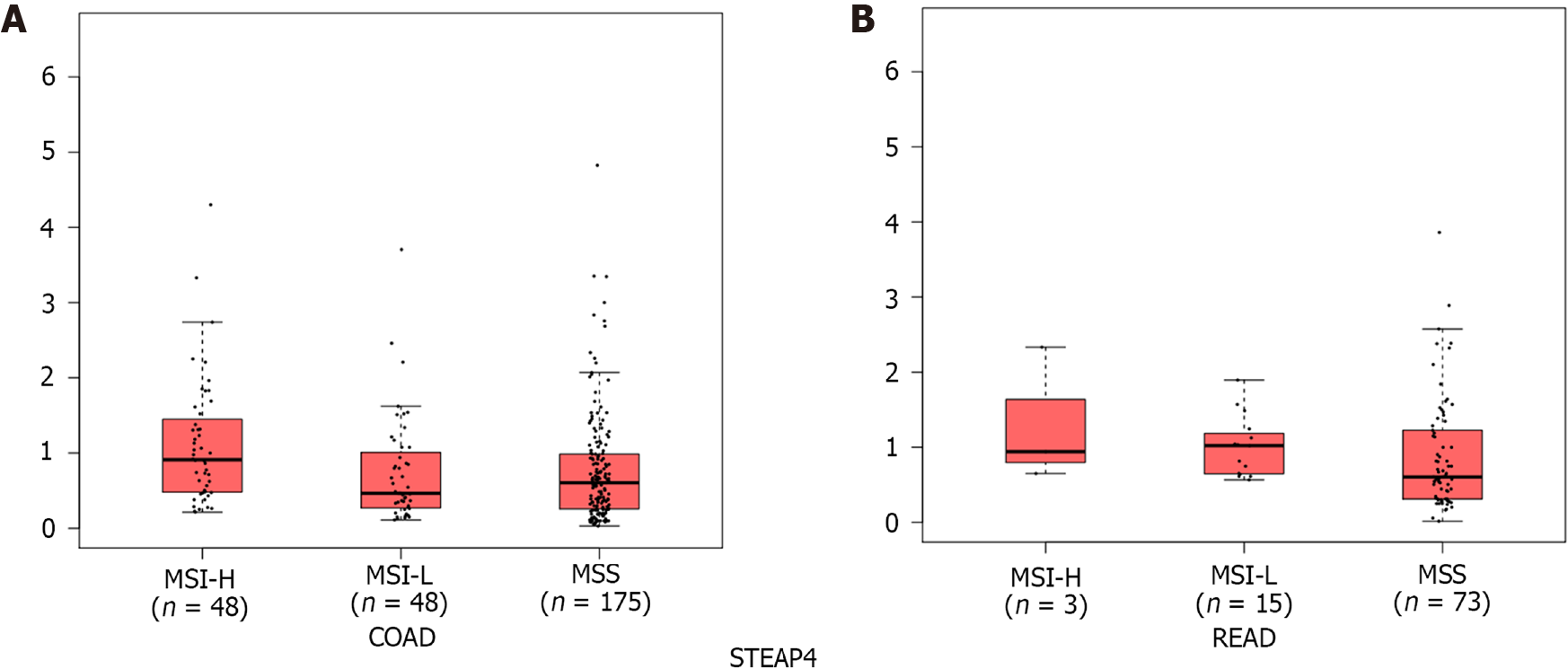
Figure 3 Expression patterns of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 in different subtypes of colorectal cancer.
A: Colon adenocarcinoma; B: Rectal adenocarcinoma. MSI-H: Microsatellite instability-high; MSI-L: Microsatellite instability-low; MSS: Microsatellite stable; STEAP4: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4; COAD: Colon adenocarcinoma; READ: Rectal adenocarcinoma.
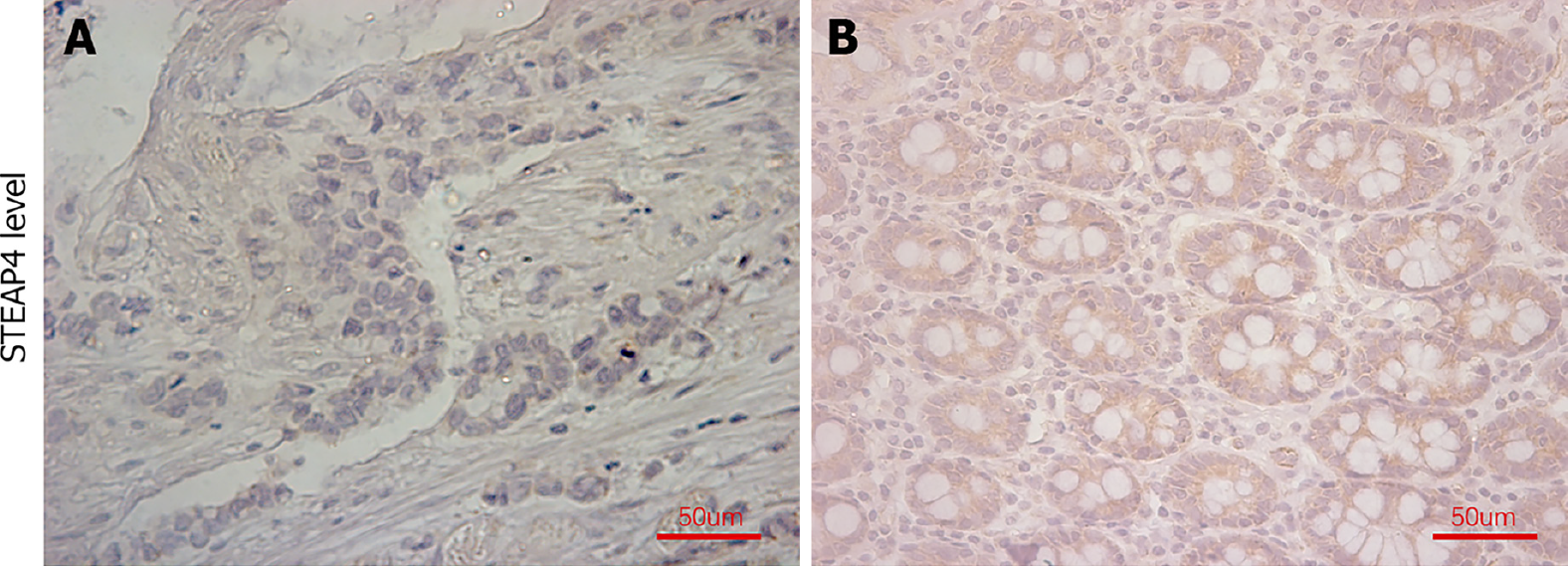
Figure 4 Representative images of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 expression in colorectal cancer and normal tissues.
A: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 (STEAP4) expression in colorectal cancer tissues; B: STEAP4 expression in adjacent normal tissues. Scale bar, 50 μm. STEAP4: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4.
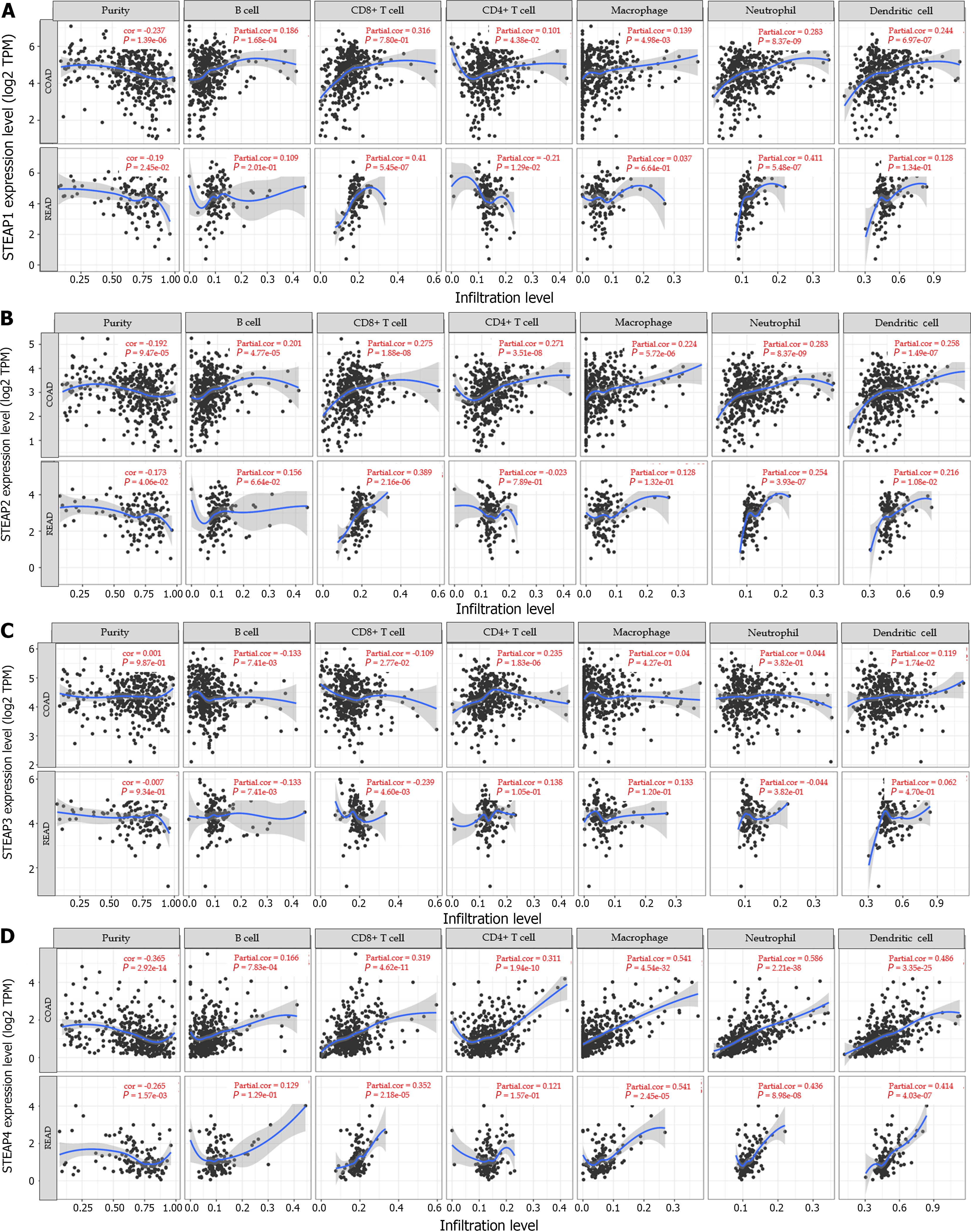
Figure 5 Relationship between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate family member expression levels and immune infiltrates validated by the TIMER database.
A: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate (STEAP1); B: STEAP2; C: STEAP3; D: STEAP4. STEAP: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate.
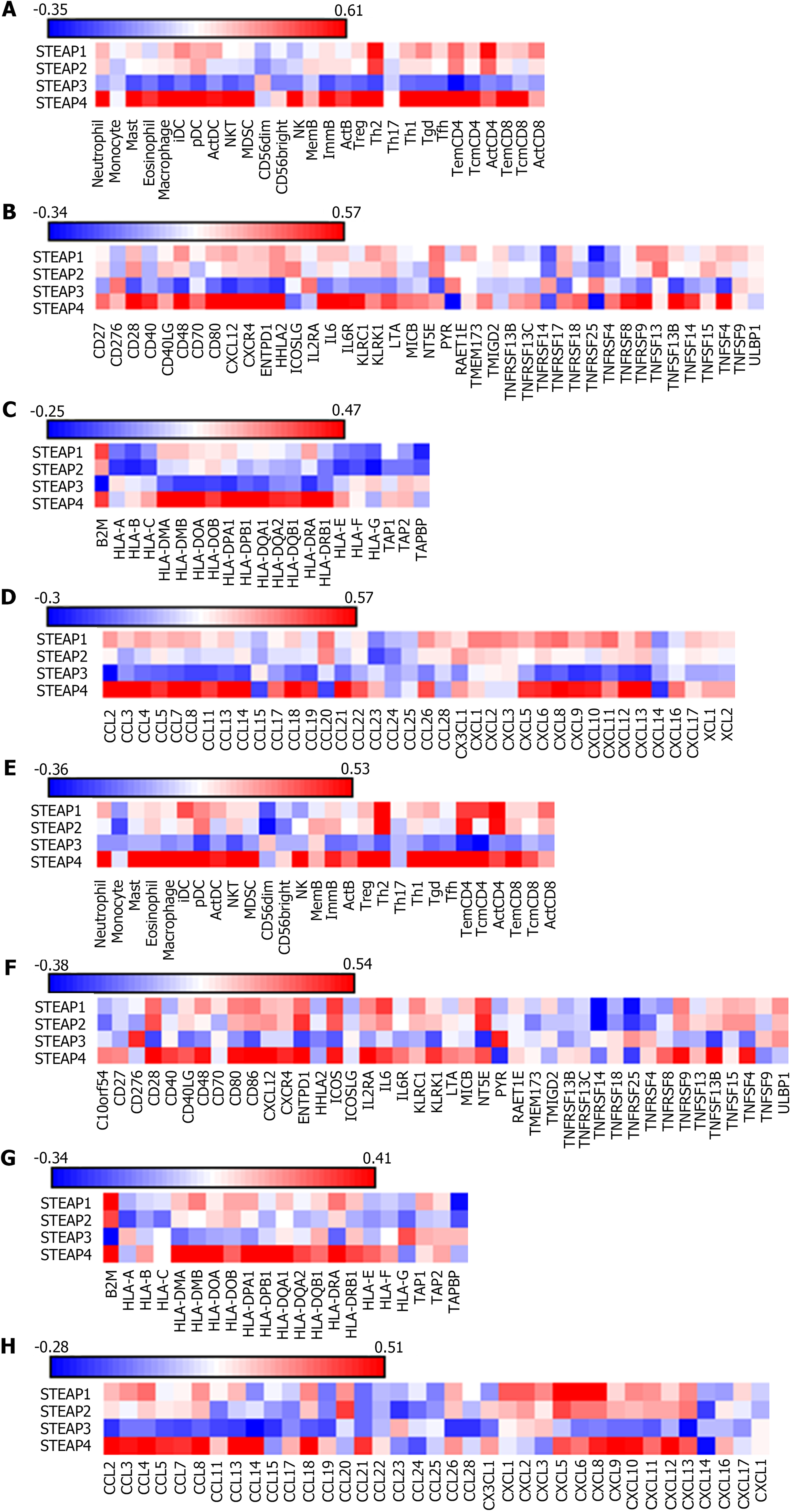
Figure 6 Spearman correlation between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate family member expression and immune factors in colon adenocarcinoma and rectal adenocarcinoma.
A-D: Colon adenocarcinoma; E-H: Rectal adenocarcinoma. STEAP: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate; iDC: Immature dendritic cell; pDC: Plasmacytoid dendritic cell; ActDC: Active dendritic cells; NKT: Natural killer T cell; MDSC: Myeloid derived suppressor cell; NK: Natural killer cell; Th: T helper cell; Tgd: Gamma delta T cell; Tfh: T follicular helper cell; B2M: Beta-2-microglobulin; HLA: Major histocompatibility complex; HLA-DOA: Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DO alpha; HLA-DOB: Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta; HLA-DPA1: Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1; HLA-DPB1: Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP beta 1; HLA-DQA1: Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1; HLA-DRA: Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha; TAP: Transporter; TAPBP: Transporter Binding Protein; CD: Cluster of differentiation; CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; ENTPD: Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase; HHLA: HERV-H LTR-associating; ICOS: Inducible T cell costimulator; ICOSLG: Inducible T cell costimulator ligand; IL2RA: Interleukin 2 receptor subunit alpha; IL: Interleukin; IL6R: Interleukin 6 receptor; KIRC1: KIR3DL3, Homo sapiens killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, three domains, long cytoplasmic tail, 3; KIRK1: Killer cell lectin like receptor subfamily K, member 1; LTA: Lymphotoxin alpha; MICB: MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence B; NT5E: 5’-nucleotidase ecto; PVR: Poliovirus receptor; RAET1E: Retinoic acid early transcript 1E; TMEM173: STING, stimulator of interferon response CGAMP interactor; TMIGD: Transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing; TNFRSF: TNF receptor superfamily member; ULBP: UL16 binding protein; CCL: C-C motif chemokine ligand; CX3CL: C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand; XCL: X-C motif chemokine ligand.
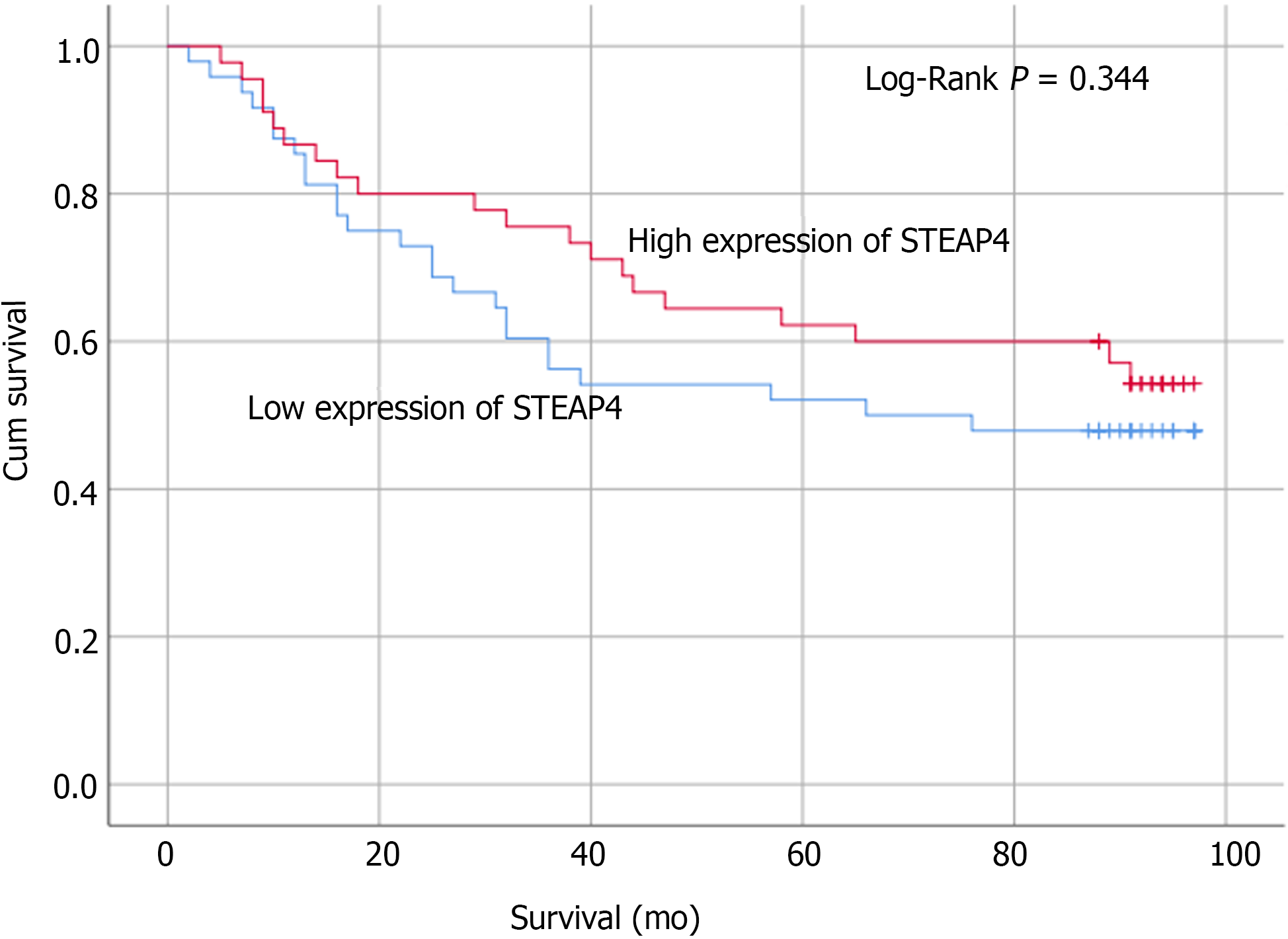
Figure 7 Low six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 protein level tends to predict a poor overall survival in colorectal cancer patients.
STEAP4: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4.
- Citation: Fang ZX, Li CL, Chen WJ, Wu HT, Liu J. Potential of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 as a prognostic marker for colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(9): 1675-1688
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i9/1675.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1675