Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2020; 12(9): 942-956
Published online Sep 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i9.942
Published online Sep 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i9.942
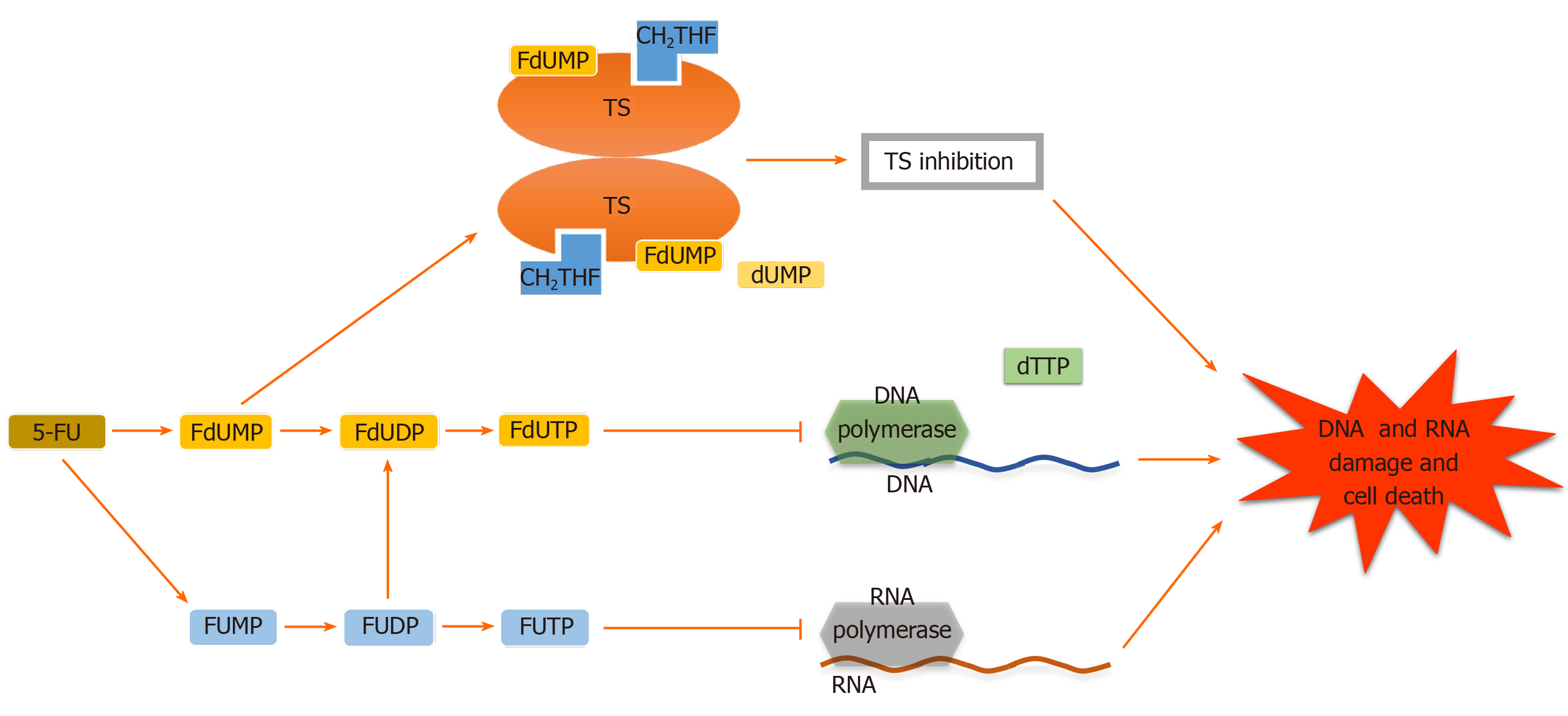
Figure 1 Different mechanisms of 5-fluorouracil action.
5-Fluorouracil (5_FU) and its derivative active metabolites exert their antitumor function at the levels of enzyme thymidylate synthase, DNA and RNA, leading to DNA and RNA damage and cell death. TS: Thymidylate synthase; FdUMP: Fluorodeoxyuridine’ monophosphate; FdUDP: Fluorodeoxyuridine diphosphate; FdUTP: Fluorodeoxyuridine triphosphate; FUMP: Fluorouridine monophosphate; FUDP: Fluorouridine diphosphate; FUTP: Fluorouridine triphosphate; CH2THF: 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; dTTP: Deoxythymidine triphosphate; dUMP: Deoxyuridine monophosphate.
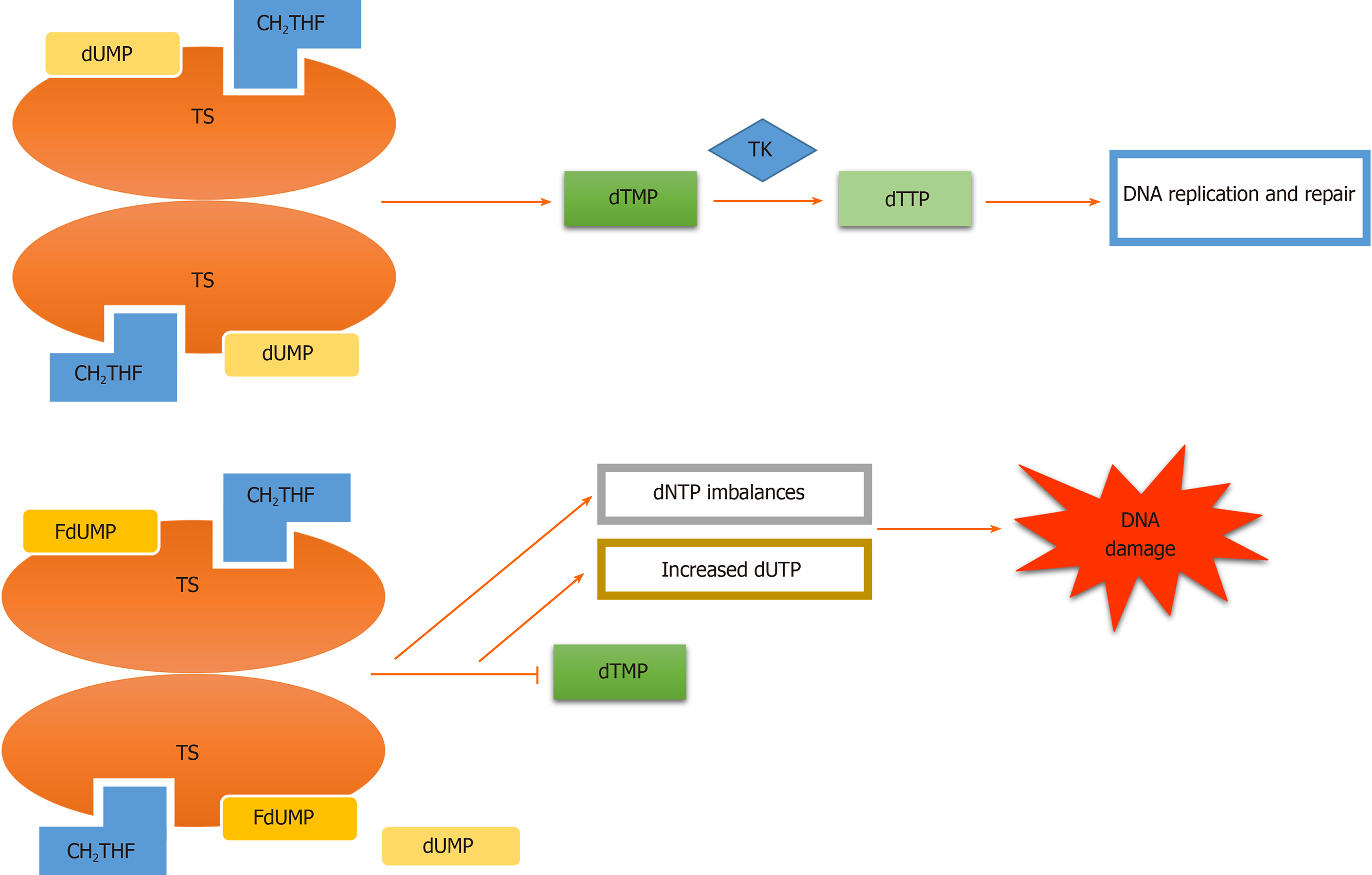
Figure 2 Thymidylate synthase inhibition.
Fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP) incorporation into thymidylate synthase in place of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) results in suppression of thymidylate synthase (TS). Consequently, the synthesis of thymidine monophosphate required for DNA replication and repair is diminished, which leads to deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) imbalances, increased dUTP, DNA damage and finally apoptosis of actively dividing cancerous cells[20]. TK: Thymidylate kinase; CH2THF: 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate; dTMP: Deoxythymidine monophosphate; dTTP: Deoxythymidine triphosphate; dNTP: Deoxynucleotide triphosphate.
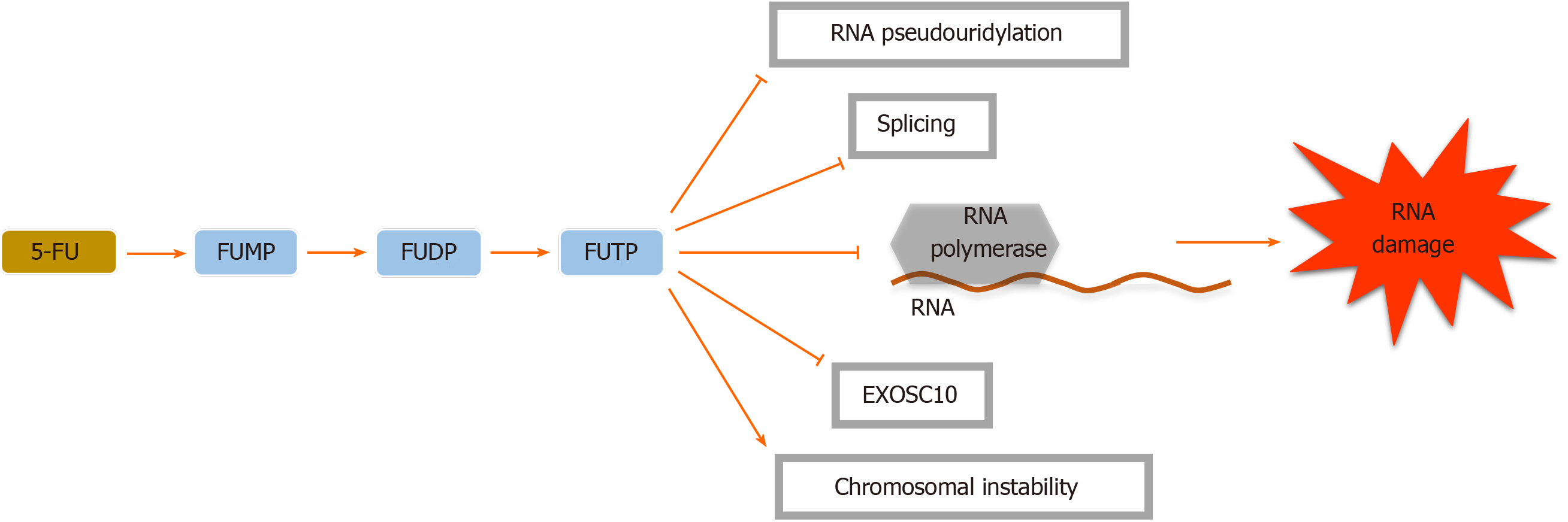
Figure 3 5-Fluorouracil inhibits ribonucleic acid pseudouridylation including the conversion of uridine to pseudouridine and formation of stable ribonucleoprotein complexes.
These actions will interrupt cellular tRNA, pre-mRNA and rRNA production and also post-transcriptional modification, leading to RNA biosynthesis cessation. Moreover, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) disrupts the assembly and activity of snRNA and protein complexes through its effect on the pseudouridylation of U2 snRNA, thereby inhibiting the splicing of pre-mRNA[21]. Because of the similarity between the 5-FU metabolite fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP) with uridine triphosphate, FUTP can be identified by RNA polymerases and incorporated into both nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA molecules, interrupting normal RNA processing and function[22]. RNA-based 5-FU toxicity decreases the cellular levels of the nuclear exosome Rrp6 or exosome component 10, a breakdown complex for RNA, banning the effectual turn-over of aberrant RNA transcripts[21]. FUMP: Fluorouridine monophosphate; FUDP: Fluorouridine diphosphate.
- Citation: Sabeti Aghabozorgi A, Moradi Sarabi M, Jafarzadeh-Esfehani R, Koochakkhani S, Hassanzadeh M, Kavousipour S, Eftekhar E. Molecular determinants of response to 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer: The undisputable role of micro-ribonucleic acids. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(9): 942-956
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i9/942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i9.942