Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2020; 12(12): 1381-1393
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i12.1381
Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i12.1381
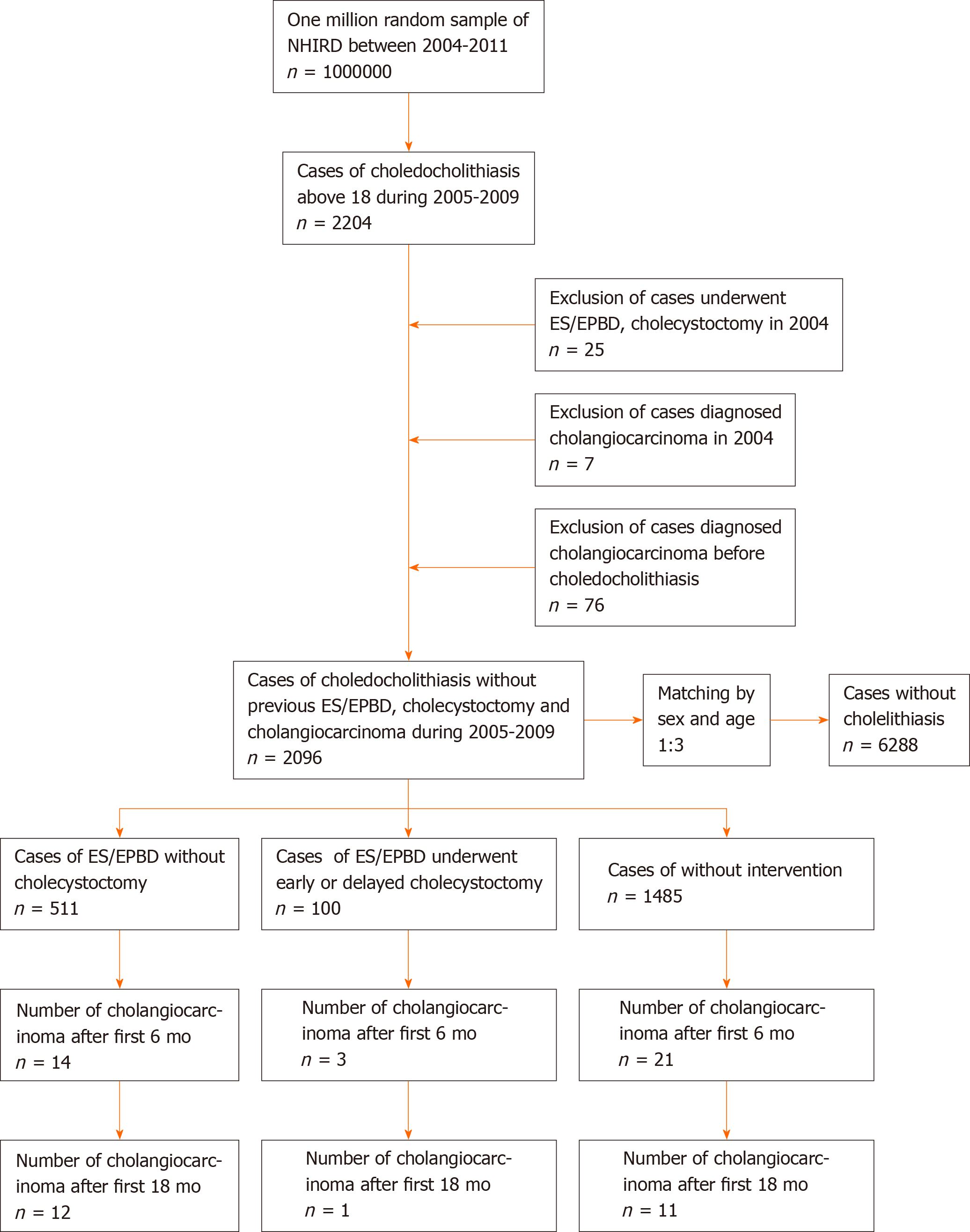
Figure 1 Case selection flow chart for the one million nationwide representative database.
ES: Endoscopic sphincterotomy; EPBD: Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation; NHIRD: National Health Insurance Research Database.
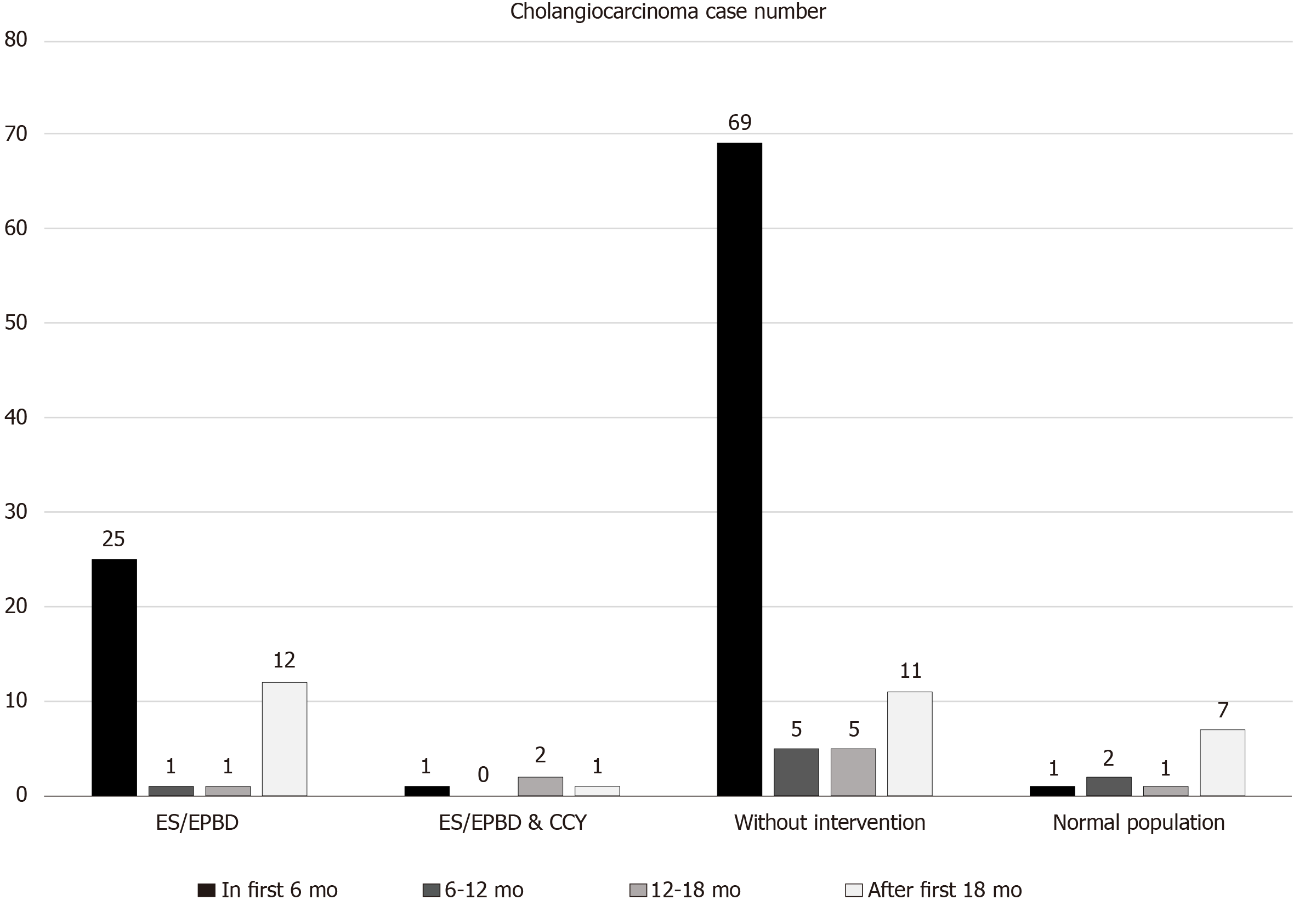
Figure 2 Cholangiocarcinoma cases diagnosed during different follow-up periods in the endoscopic sphincterotomy/endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation group, endoscopic sphincterotomy/endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation and cholecystectomy group, no intervention group, and normal population.
ES: Endoscopic sphincterotomy; EPBD: Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation; CCY: Cholecystectomy.
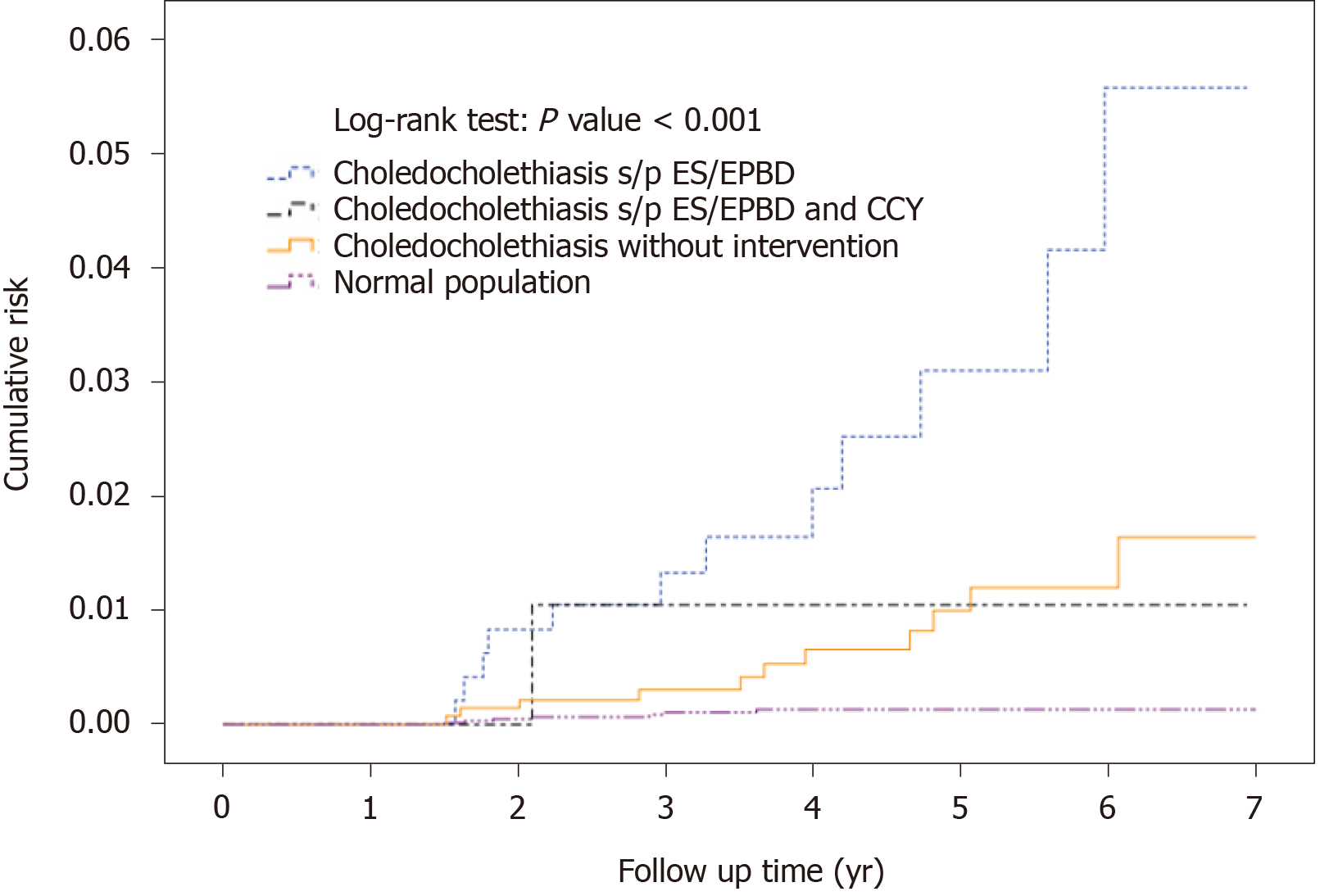
Figure 3 Cumulative subsequent cholangiocarcinoma risk in the endoscopic sphincterotomy/endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation group, endoscopic sphincterotomy/endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation and cholecystectomy group, no intervention group, and normal population (The cases of cholangiocarcinoma within 18 mo after index admission were excluded).
ES: Endoscopic sphincterotomy; EPBD: Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation; CCY: Cholecystectomy.
- Citation: Wang CC, Tseng MH, Wu SW, Yang TW, Chen HY, Sung WW, Su CC, Wang YT, Lin CC, Tsai MC. Cholecystectomy reduces subsequent cholangiocarcinoma risk in choledocholithiasis patients undergoing endoscopic intervention. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(12): 1381-1393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i12/1381.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i12.1381