Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2019; 11(4): 335-347
Published online Apr 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.335
Published online Apr 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.335
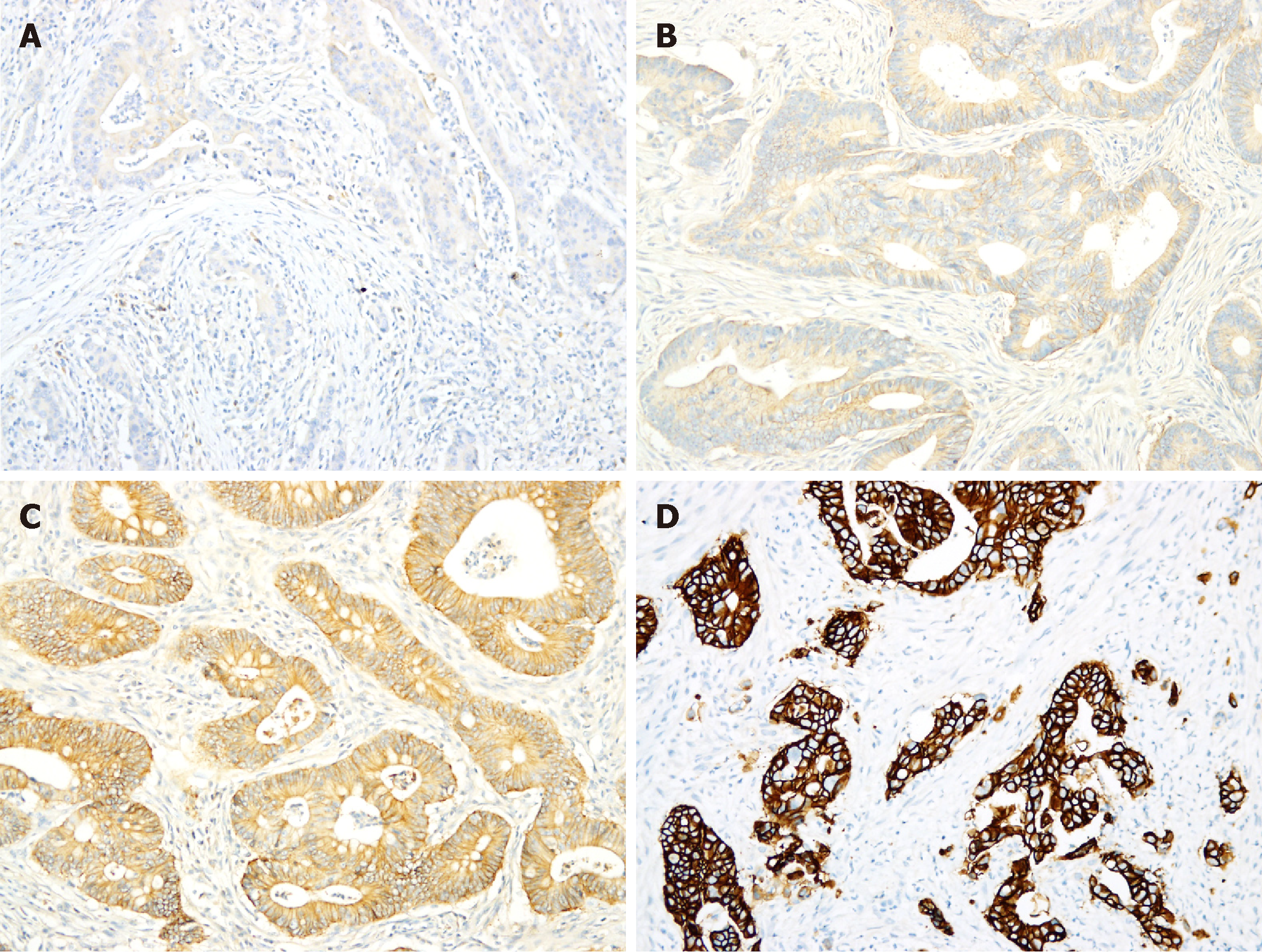
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2.
A,B: Immunohistochemical staining of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in most colorectal adenocarcinomas (CRCs) was scored as either 0 (A) or 1+ (B); C: Approximately 9% of CRCs exhibited 2+ staining; D: Only 2.6% of CRCs exhibited 3+ staining.
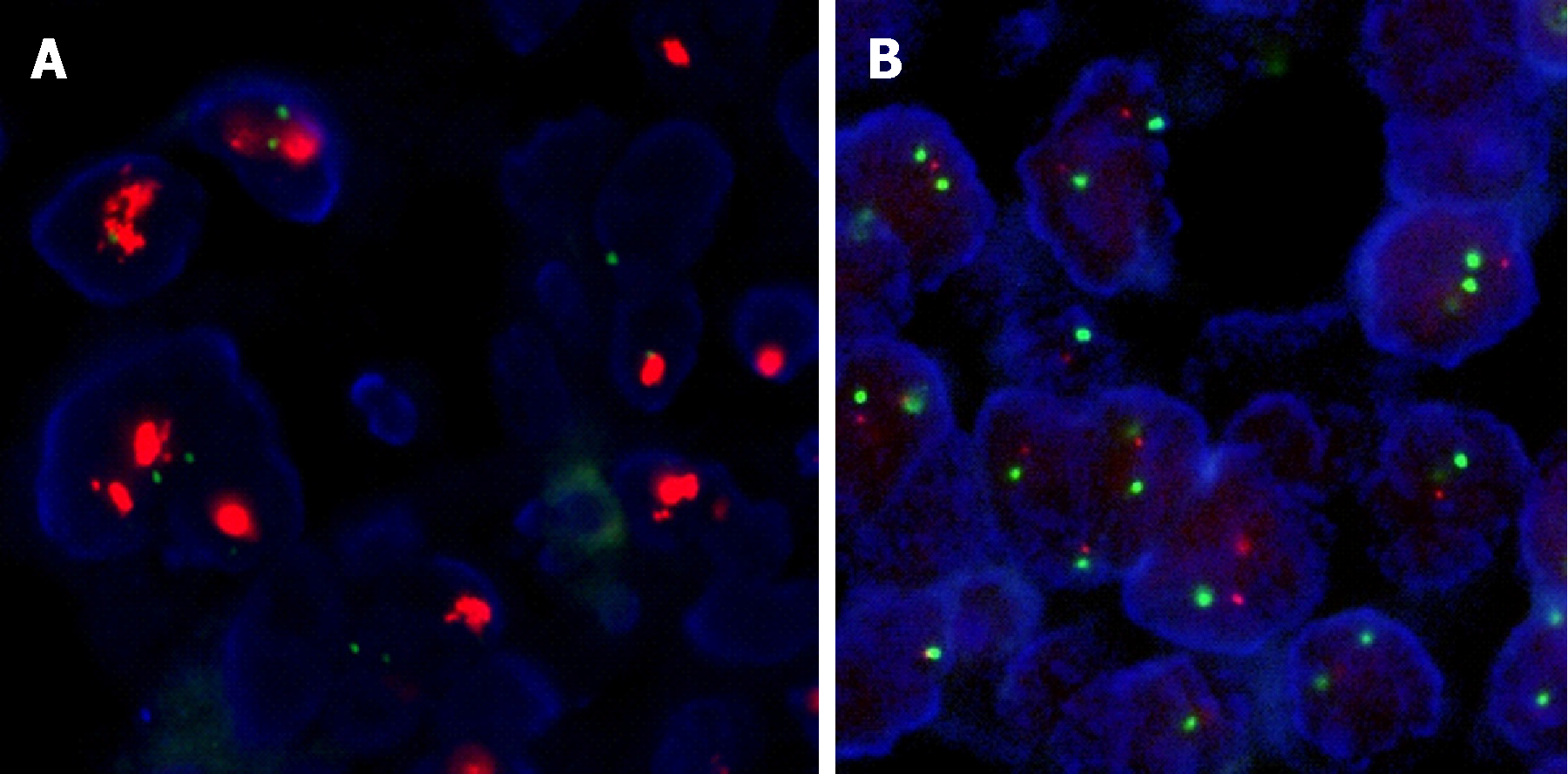
Figure 2 Fluorescence in situ hybridization results.
By fluorescence in situ hybridization, all tested tumors with 1+ human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) staining and 80% of tumors with 2+ staining showed no evidence of HER2 gene amplification (A) whereas 83% of tumors with 3+ HER2 staining harbored HER2 gene amplifications (B).
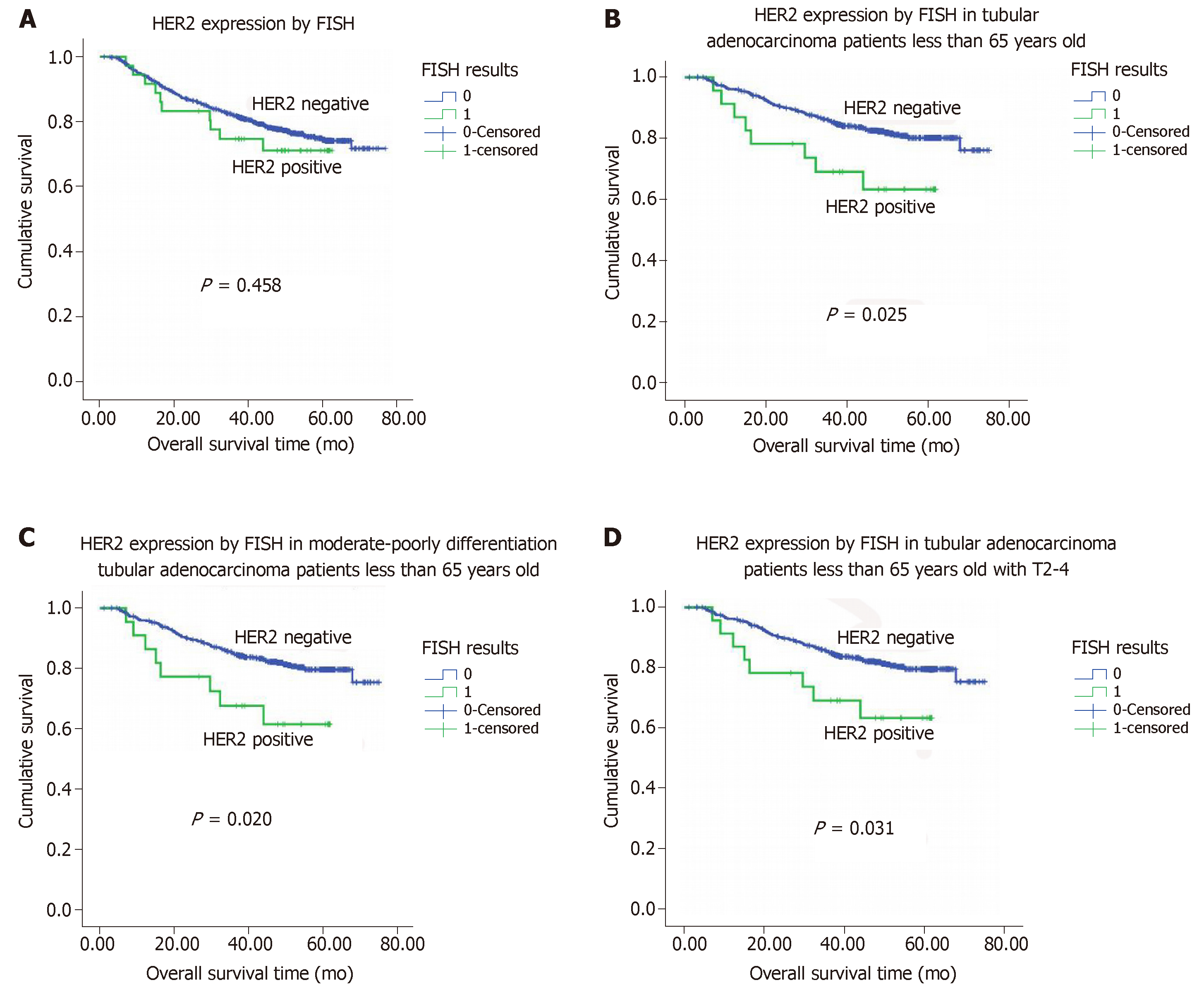
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier overall survival analysis.
A: Kaplan-Meier overall survival (OS) analysis of colorectal adenocarcinoma patients based on human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression status (as determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization); B: Kaplan-Meier OS analysis of tubular adenocarcinoma patients age ≤ 65 based on HER2 expression status; C: Kaplan-Meier OS analysis of tubular adenocarcinoma patients with moderate-poor differentiation and age ≤ 65 based on HER2 expression status; D: Kaplan-Meier overall survival analysis of tubular adenocarcinoma patients with stage T2-4 tumors and age ≤ 65 based on HER2 expression status. HER2: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; FISH: Fluorescence in situ hybridization.
- Citation: Wang XY, Zheng ZX, Sun Y, Bai YH, Shi YF, Zhou LX, Yao YF, Wu AW, Cao DF. Significance of HER2 protein expression and HER2 gene amplification in colorectal adenocarcinomas. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(4): 335-347
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i4/335.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.335