Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Aug 16, 2017; 9(8): 389-395
Published online Aug 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i8.389
Published online Aug 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i8.389
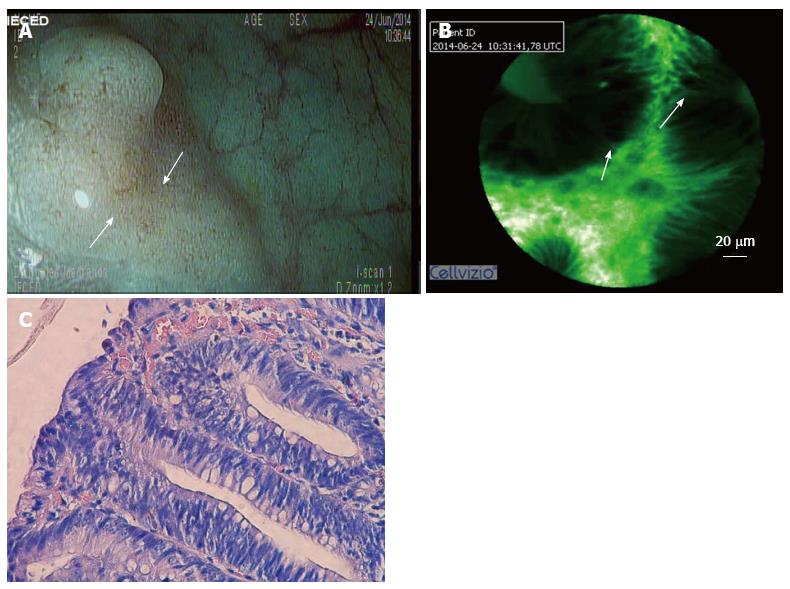
Figure 1 Colonic polyp.
A: A sigmoid flat polyp was viewed using digital chromoendoscopy with high definition by i-scan, which revealed a pit pattern suggestive of a hyperplastic lesion in a patient with cirrhosis and important coagulation disorders; B: CLE showing dysplasia (image optimized by using a green-white image color palette in Cellvizio® viewer software); C: A histological analysis of the specimen confirmed the dysplasia. CLE: Confocal laser endomicroscopy.
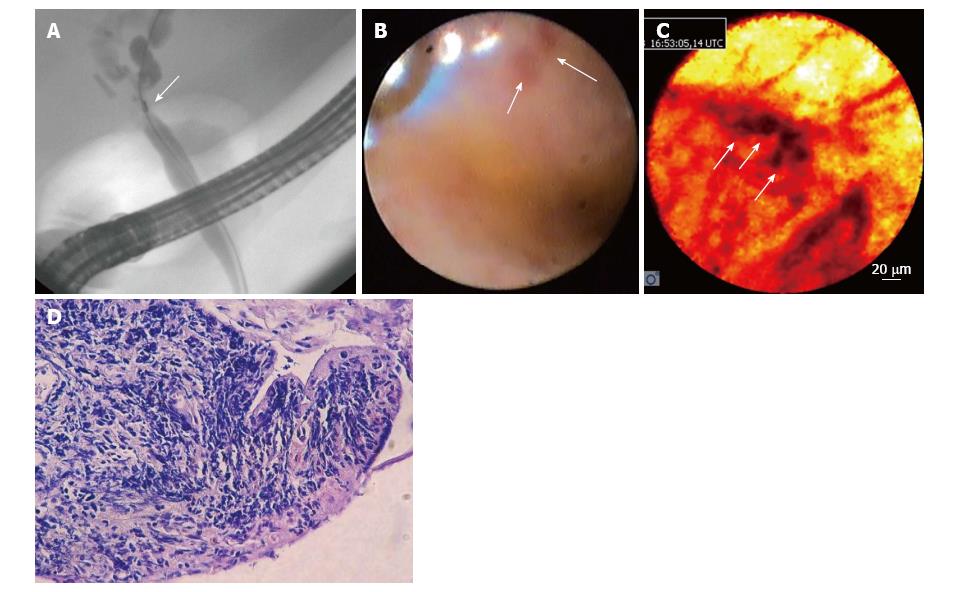
Figure 2 Undetermined stenosis of the biliary tract.
A: ERCP was performed in a patient with undetermined stenosis who was cytobrush-negative for malignancy; B: Spyglass cholangioscopy showing a reddish area that was not suspected of malignancy; C: CLE showing dark clumps that were suspected of malignancy (image optimized using the “black-red-yellow” image color palette in Cellvizio® viewer software); D: The histological results of a target biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma. CLE: Confocal laser endomicroscopy; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
- Citation: Robles-Medranda C, Vargas M, Ospina J, Puga-Tejada M, Valero M, Soria M, Bravo G, Robles-Jara C, Lukashok HP. Clinical impact of confocal laser endomicroscopy in the management of gastrointestinal lesions with an uncertain diagnosis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(8): 389-395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v9/i8/389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v9.i8.389