Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Mar 16, 2013; 5(3): 111-116
Published online Mar 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i3.111
Published online Mar 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i3.111
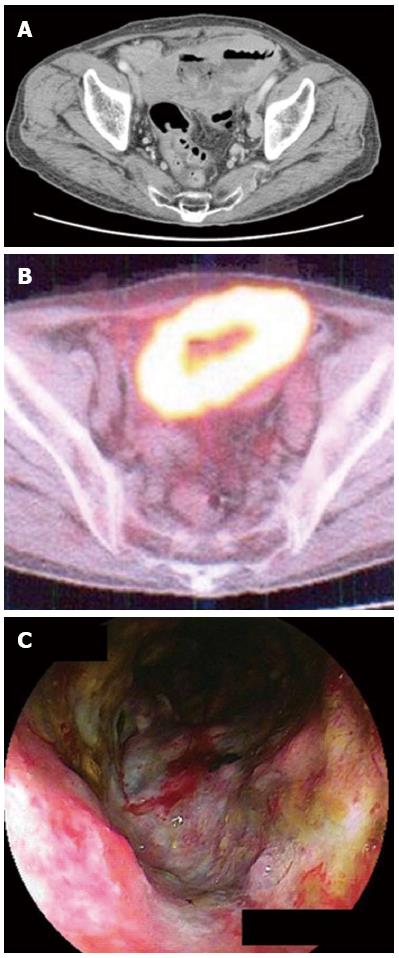
Figure 1 In the 10 cases that showed accumulation of fluorodeoxyglucose, 4 tumor was classified as ulcerative type.
A: The isolated dilation and wall thickening of the small intestine was recognized by computed tomography in a 78-year-old man with anemia and abdominal tumor; B: At the same site, fluorodeoxyglucose accumulated; C: The ulcerative tumor was observed by double-balloon endoscopy. The histopathological diagnosis was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
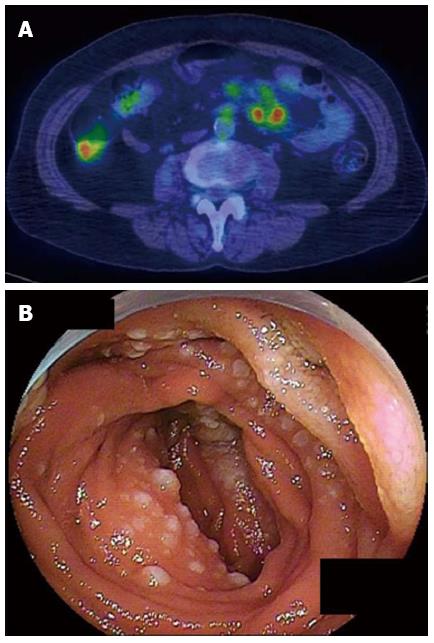
Figure 2 In the 10 cases that showed accumulation of fluorodeoxyglucose, 1 as elevated type.
A: Multiple foci of abnormally increased fluorodeoxyglucose uptake were recognized in a 64-year-old female case of follicular lymphoma; B: Small intestinal involvement was confirmed by double-balloon endoscopy.
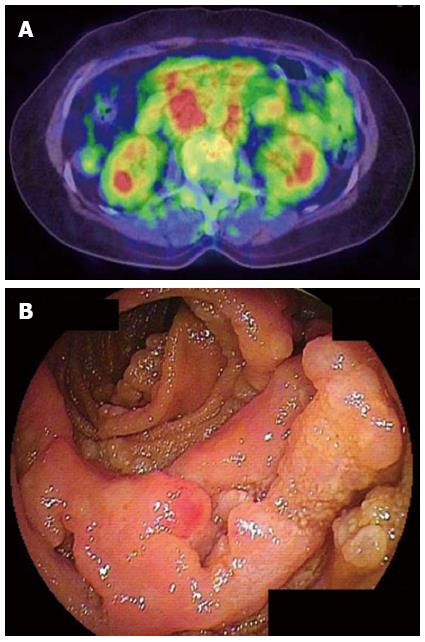
Figure 3 In other 10 cases that did not show accumulation of fluorodeoxyglucose, 4 tumors were classified as elevated type.
A: In a 64-year-old female with follicular lymphoma, we identified abnormally increased fluorodeoxyglucose uptake only in the intraabdominal lymph nodes, but not in the small intestine; B: However, small intestinal involvement was confirmed by double-balloon endoscopy.
- Citation: Ibuka T, Araki H, Sugiyama T, Nakanishi T, Onogi F, Shimizu M, Hara T, Takami T, Tsurumi H, Moriwaki H. Diagnosis of the jejunoileal lymphoma by double-balloon endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2013; 5(3): 111-116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v5/i3/111.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v5.i3.111