Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jul 16, 2010; 2(7): 252-256
Published online Jul 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i7.252
Published online Jul 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i7.252
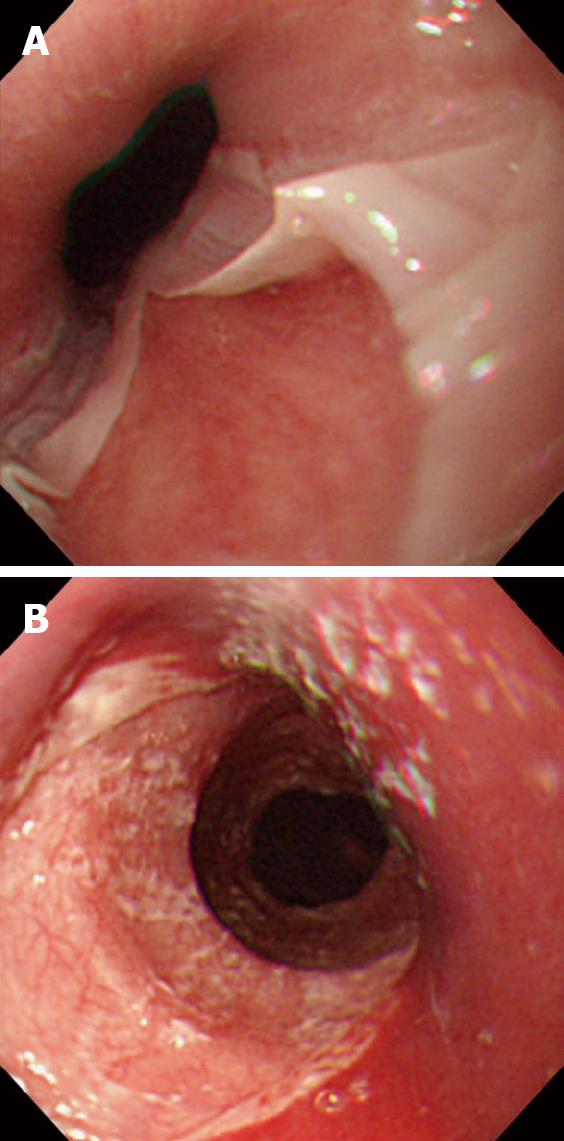
Figure 1 Endoscopic view of esophagitis dissecans superficialis.
A: With diffuse sloughing mucosa of the lower esophagus in a 76-year-old woman presenting hematemesis, and the cause was idiopathic; B: with longitudinal sloughing mucosa from upper to mid esophagus in a 67-year-old woman with mucocutaneous type pemphigus vulgaris, note fine whitish fragments of sloughed mucosa, and the index value for anti-desmoglein 3 antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was over 1280 (normal value < 7).
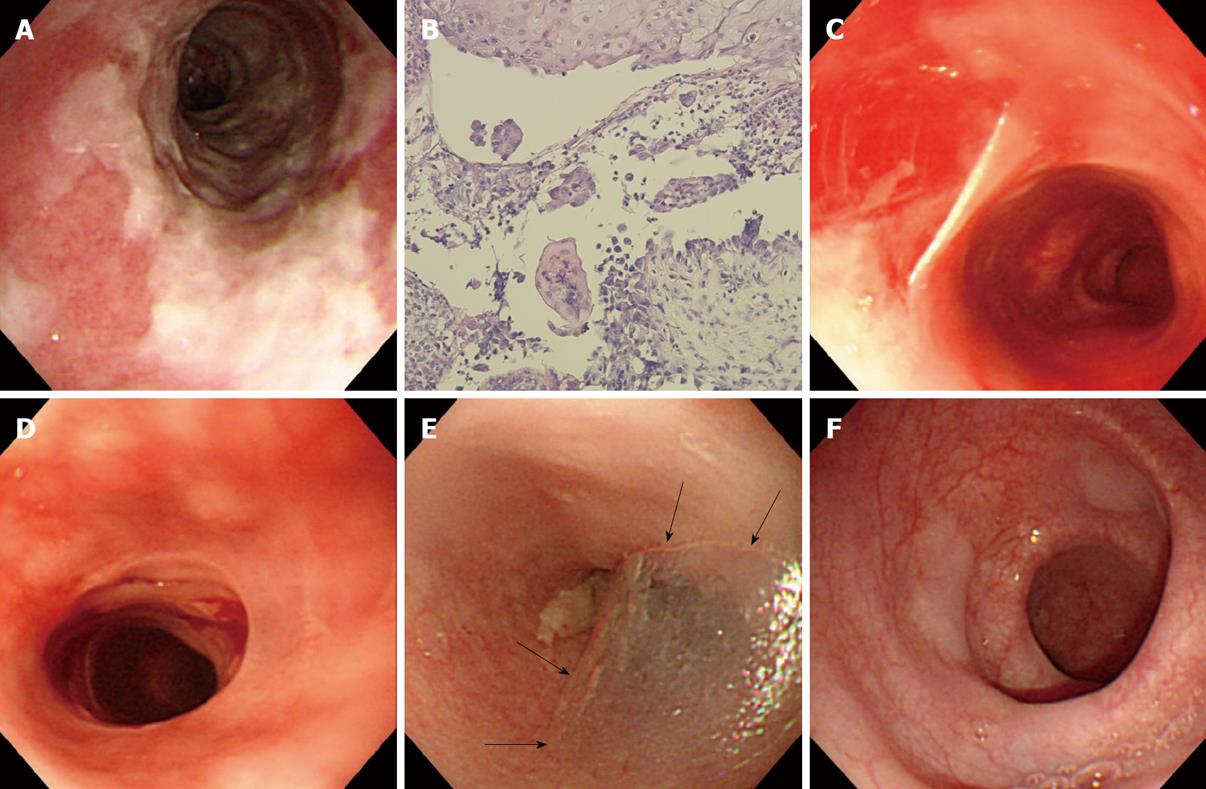
Figure 2 Endoscopic views of a variety of esophageal findings in a 71-year-old woman with mucosal-dominant pemphigus vulgaris.
A: Note esophagitis dissecans superficialis with extensive reddish erosion of the entire esophagus and whitish sheets of sloughed mucosa with the index value for anti-desmoglein 3 antibody of 1620; B: Histopathological examination of the esophageal mucosa, showing separation at the suprabasal level of epithelium. Note the formation of a row of tombstones-like basal cells that remain attached to the basement membrane (H&E, × 100); C: Esophagitis dissecans superficialis with sheets of sloughing mucosa in the mid esophagus with the index value for anti-desmoglein 3 antibody of 128; D: Sheets of sloughing mucosa presenting esophageal webs in the upper esophagus; E: A bulla (arrowheads) in the upper esophagus with the index value for anti-desmoglein 3 antibody of 145; F: Several slightly raised whitish blisters scattered in the lower esophagus.
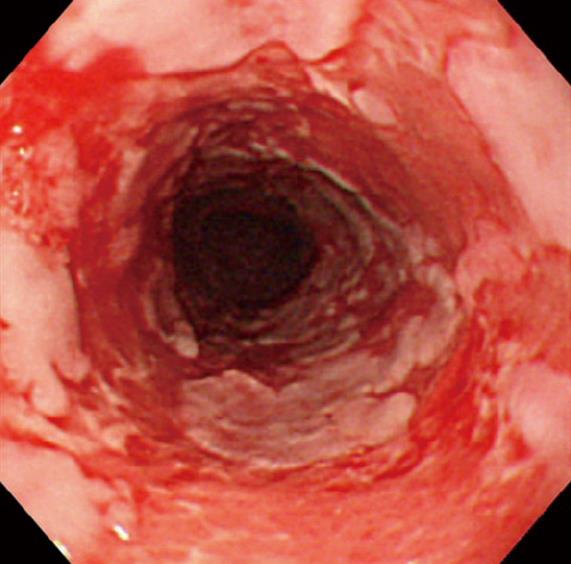
Figure 3 An endoscopic view of an 84-year-old man with mucous membrane pemphigoid.
Note esophagitis dissecans superficialis with extensive reddish erosion of the entire esophagus and whitish sheets and fragments of sloughed mucosa.
- Citation: Hokama A, Yamamoto YI, Taira K, Nakamura M, Kobashigawa C, Nakamoto M, Hirata T, Kinjo N, Kinjo F, Takahashi K, Fujita J. Esophagitis dissecans superficialis and autoimmune bullous dermatoses: A review. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(7): 252-256
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v2/i7/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v2.i7.252