Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2020; 12(11): 408-450
Published online Nov 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i11.408
Published online Nov 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i11.408
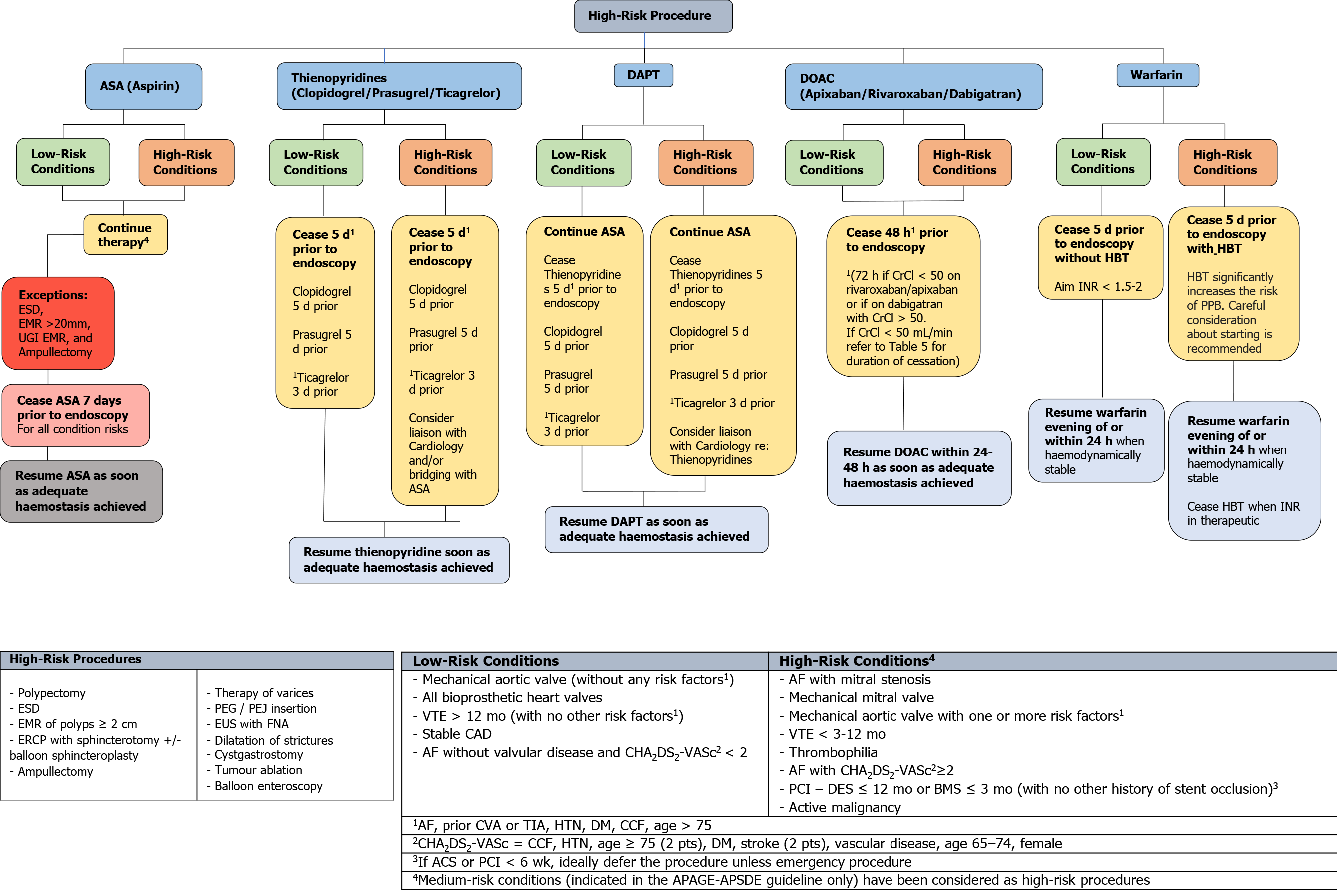
Figure 1 An evidence-based framework for safe clinical application of anticoagulant and antiplatelet management in the context of high-risk endoscopic procedures for all endoscopists.
ASA: Acetylsalicylic acid; DAPT: Dual antiplatelet therapy; DOAC: Direct oral anticoagulant; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection; UGI: Upper Gastrointestinal; CrCl: Creatinine clearance; HBT: Heparin bridging therapy; INR: International normalisation ratio; PPB: Post-procedural bleeding; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; PEG: Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy; PEJ: Percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; FNA: Fine needle aspiration; VTE: Venous thromboembolism; CAD: Coronary artery disease; AF: Atrial fibrillation; PCI: Percutaneous coronary intervention; DES: Drug eluding stent; BMS: Bare metal stent; CVA: Cerebrovascular accident; TIA: Transient ischaemic attack; HTN: Hypertension; DM: Diabetes mellitus; CCF: Congestive cardiac failure; ACS: Acute coronary syndrome.
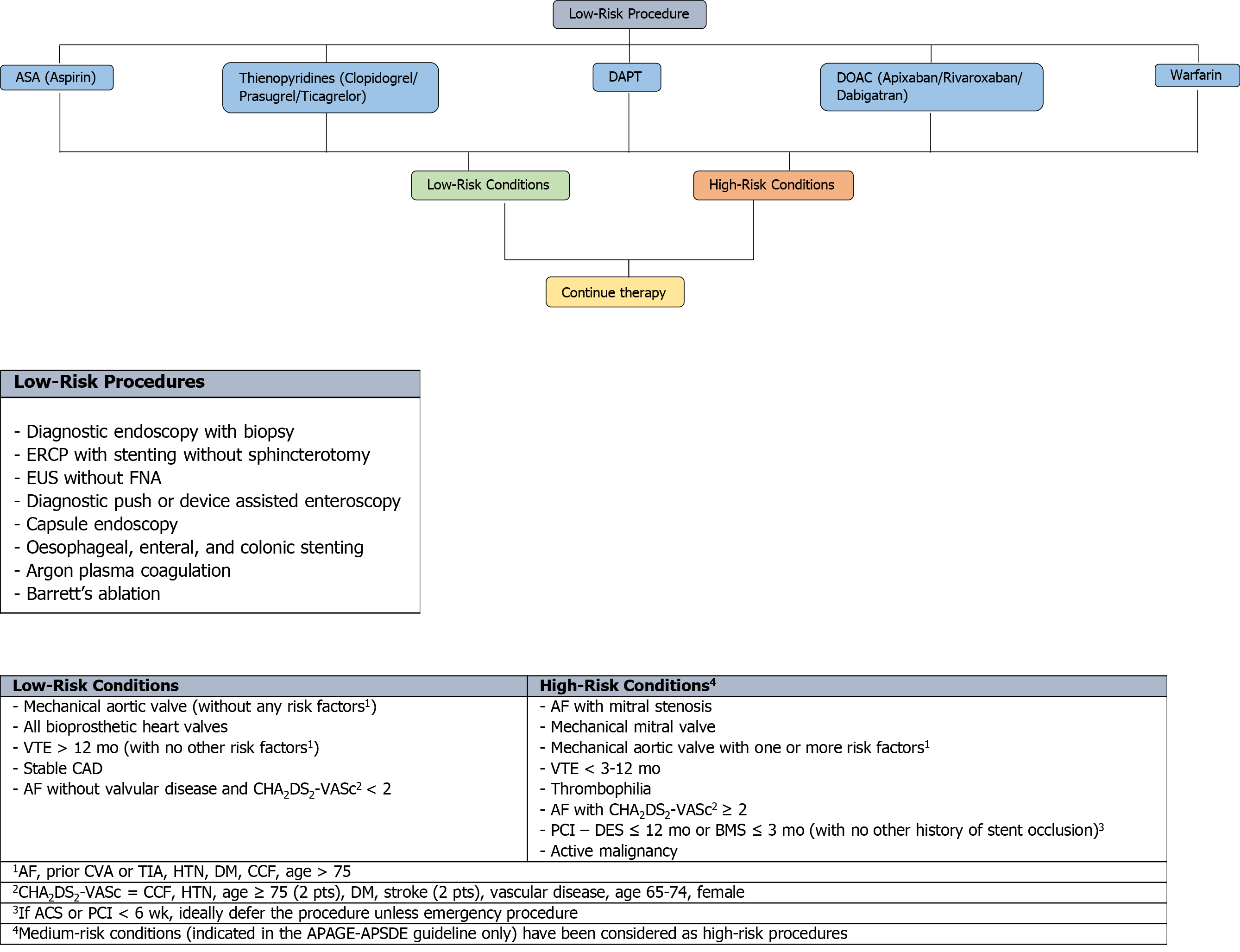
Figure 2 An evidence-based framework for safe clinical application of anticoagulant and antiplatelet management in the context of low-risk endoscopic procedures for all endoscopists.
ASA: Acetylsalicylic acid; DAPT: Dual antiplatelet therapy; DOAC: Direct oral anticoagulant; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; FNA: Fine needle aspiration; VTE: Venous thromboembolism; CAD: Coronary artery disease; AF: Atrial fibrillation; PCI: Percutaneous coronary intervention; DES: Drug eluding stent; BMS: Bare metal stent; CVA: Cerebrovascular accident; TIA: Transient ischaemic attack; HTN: Hypertension; DM: Diabetes mellitus; CCF: Congestive cardiac failure; ACS: Acute coronary syndrome.
- Citation: Chan A, Philpott H, Lim AH, Au M, Tee D, Harding D, Chinnaratha MA, George B, Singh R. Anticoagulation and antiplatelet management in gastrointestinal endoscopy: A review of current evidence. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2020; 12(11): 408-450
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v12/i11/408.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v12.i11.408