Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Apr 16, 2019; 11(4): 262-270
Published online Apr 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i4.262
Published online Apr 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i4.262
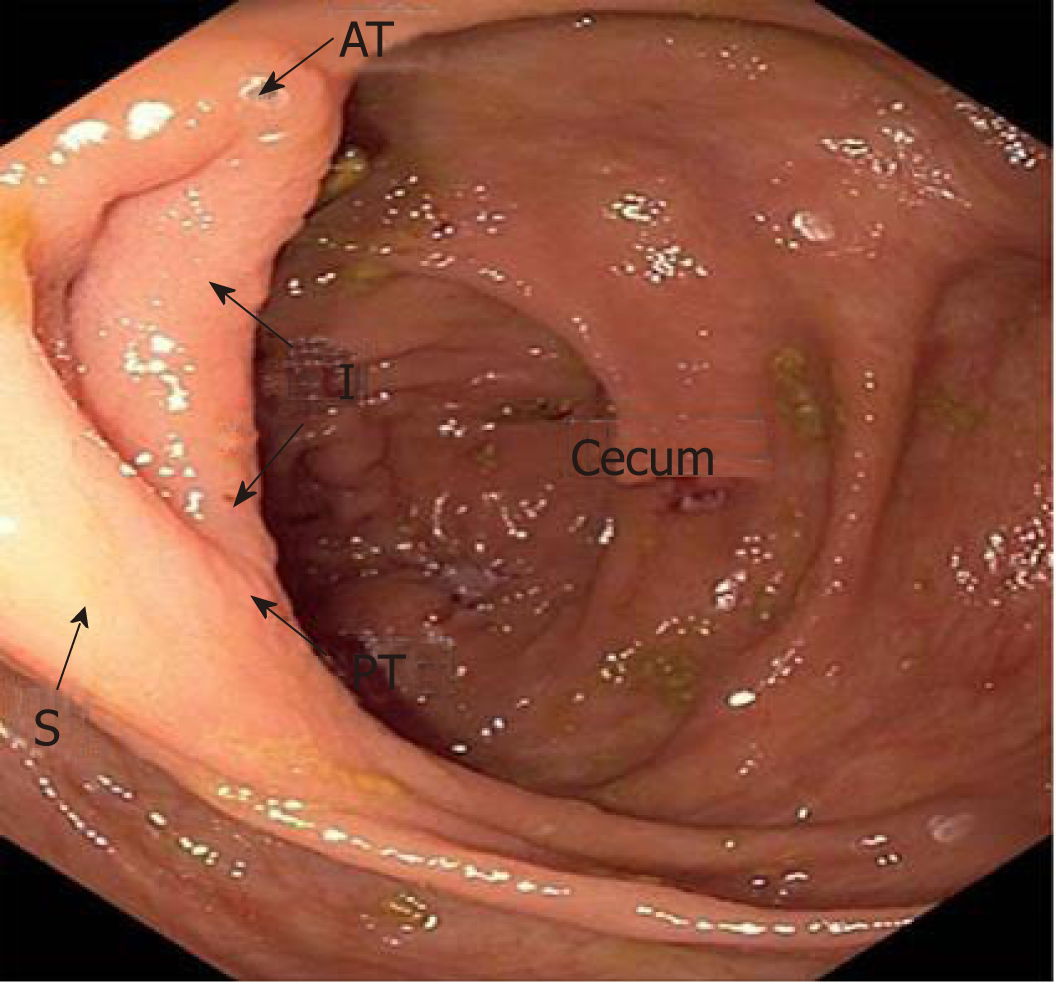
Figure 1 The ileocecal valve was divided into four sections: anterior angle, posterior angle, inferior lip, and superior lip.
A: Anterior angle; P: Posterior angle; I: Inferior lip; S: Superior lip.
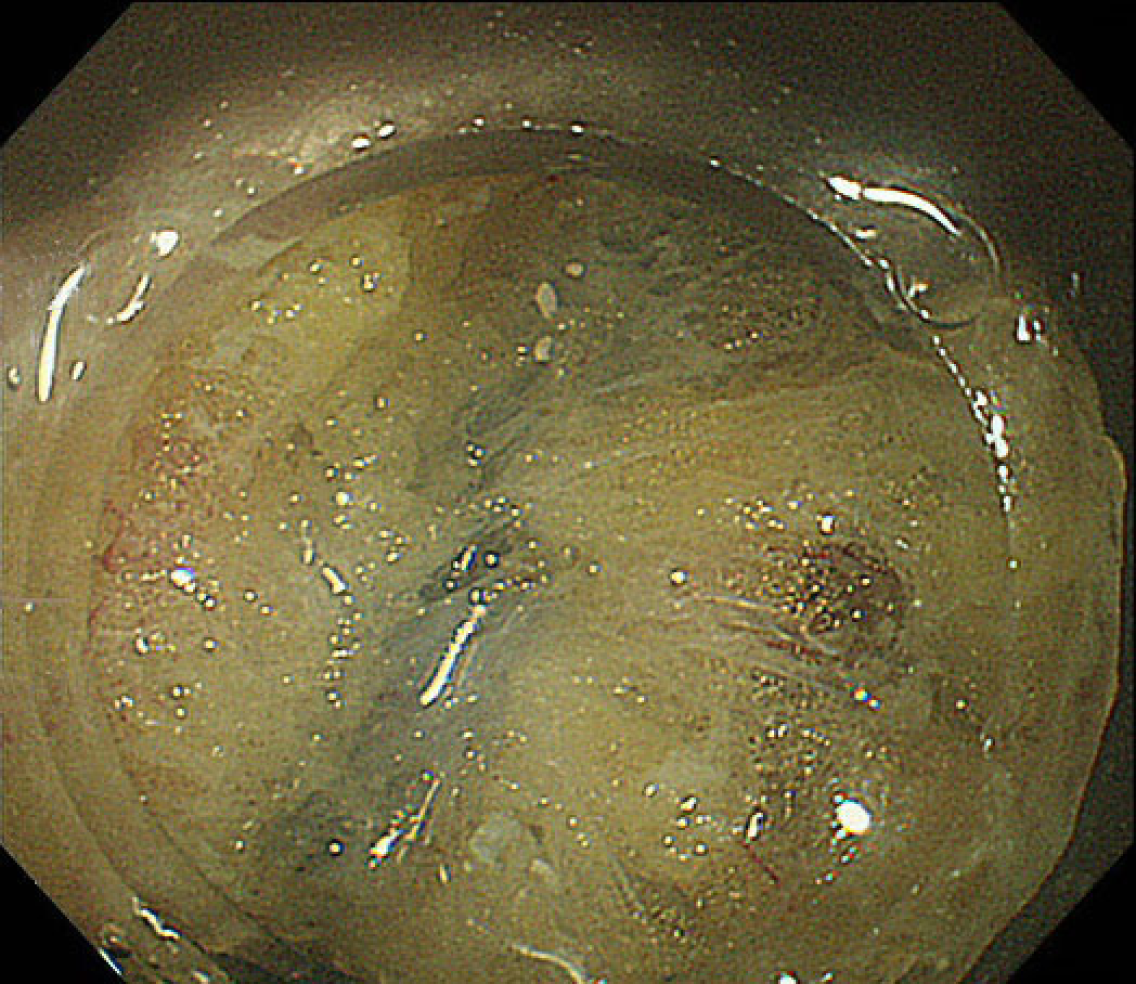
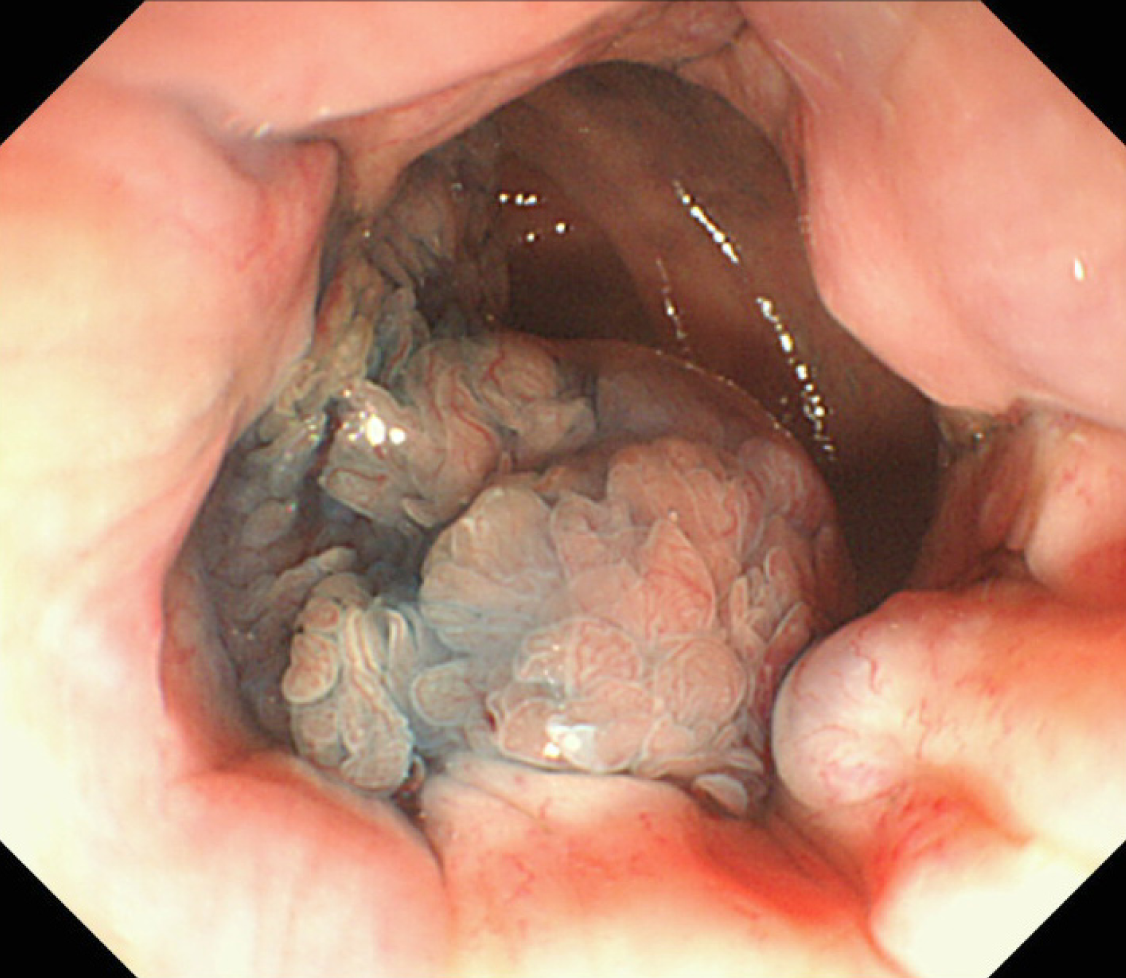
Figure 2 Submucosal fatty tissue around the ileocecal valve.
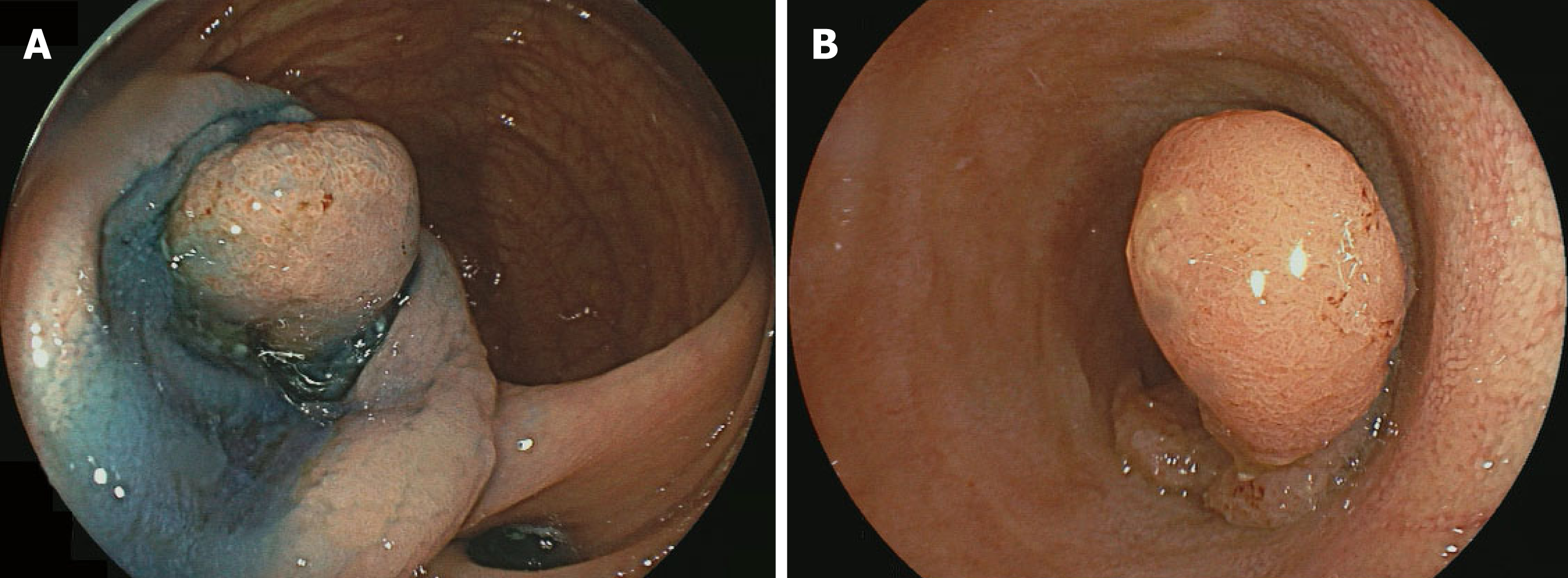
Figure 3 Endoscopic submucosal dissection in terminal ileal tumors.
A: Terminal ileal tumor; B: Mucosal incision.
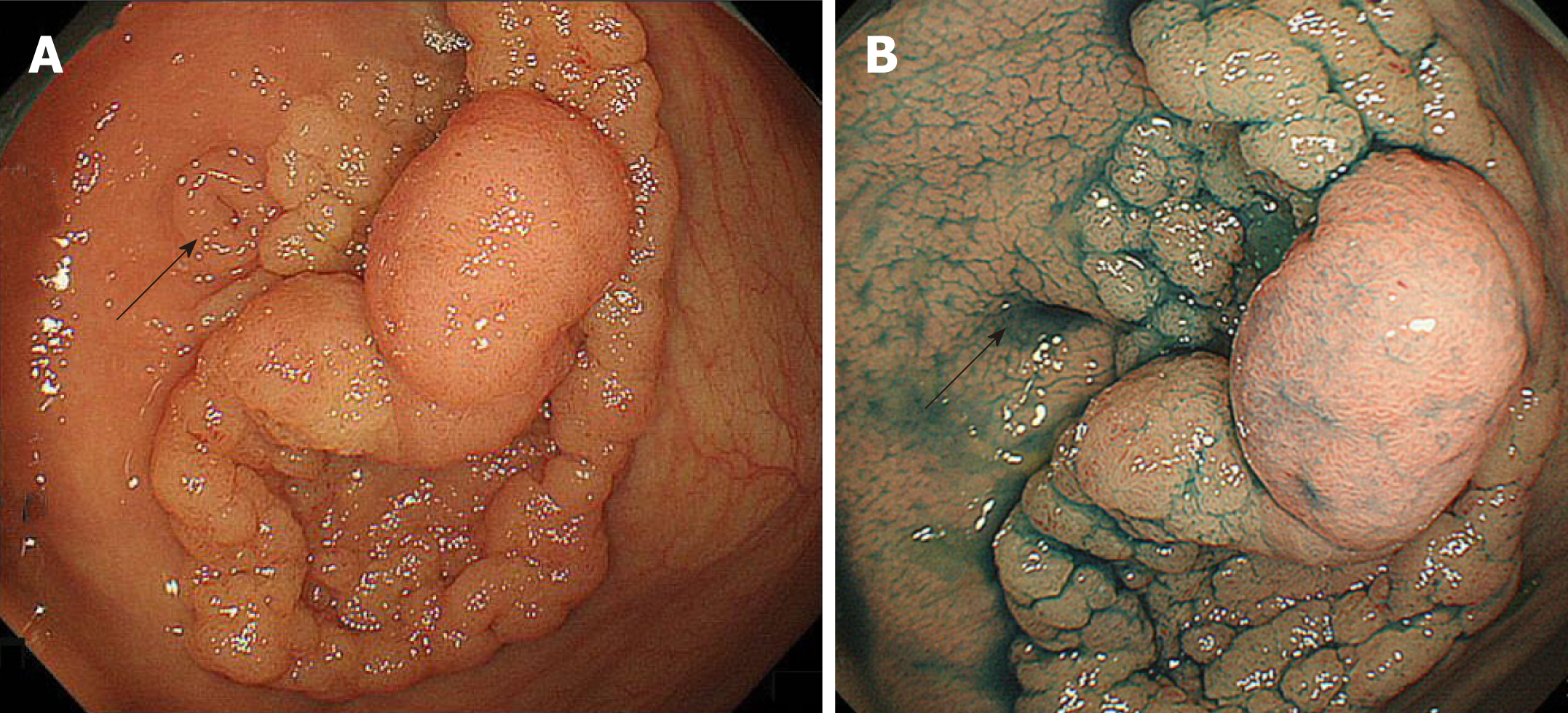
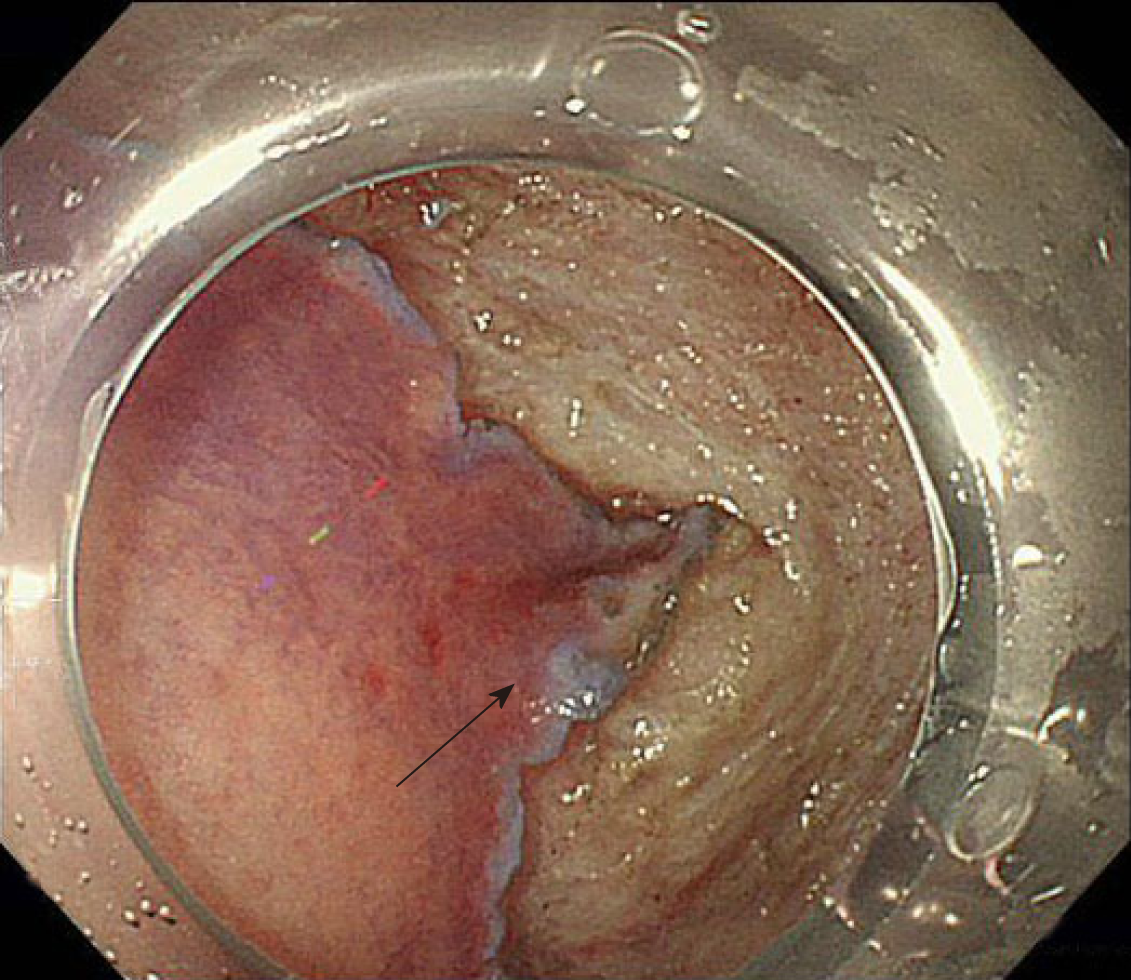
Figure 4 Laterally spreading tumor granular-nodular mix type involvement in the appendiceal orifice (arrow).
A: Conventional white light image; B: Chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine.
Figure 5 A transparent hood facilitates the endoscopic submucosal dissection of a lesion in close proximity to the appendix (arrow).
Figure 6 Rectal tumor involvement in the anal canal.
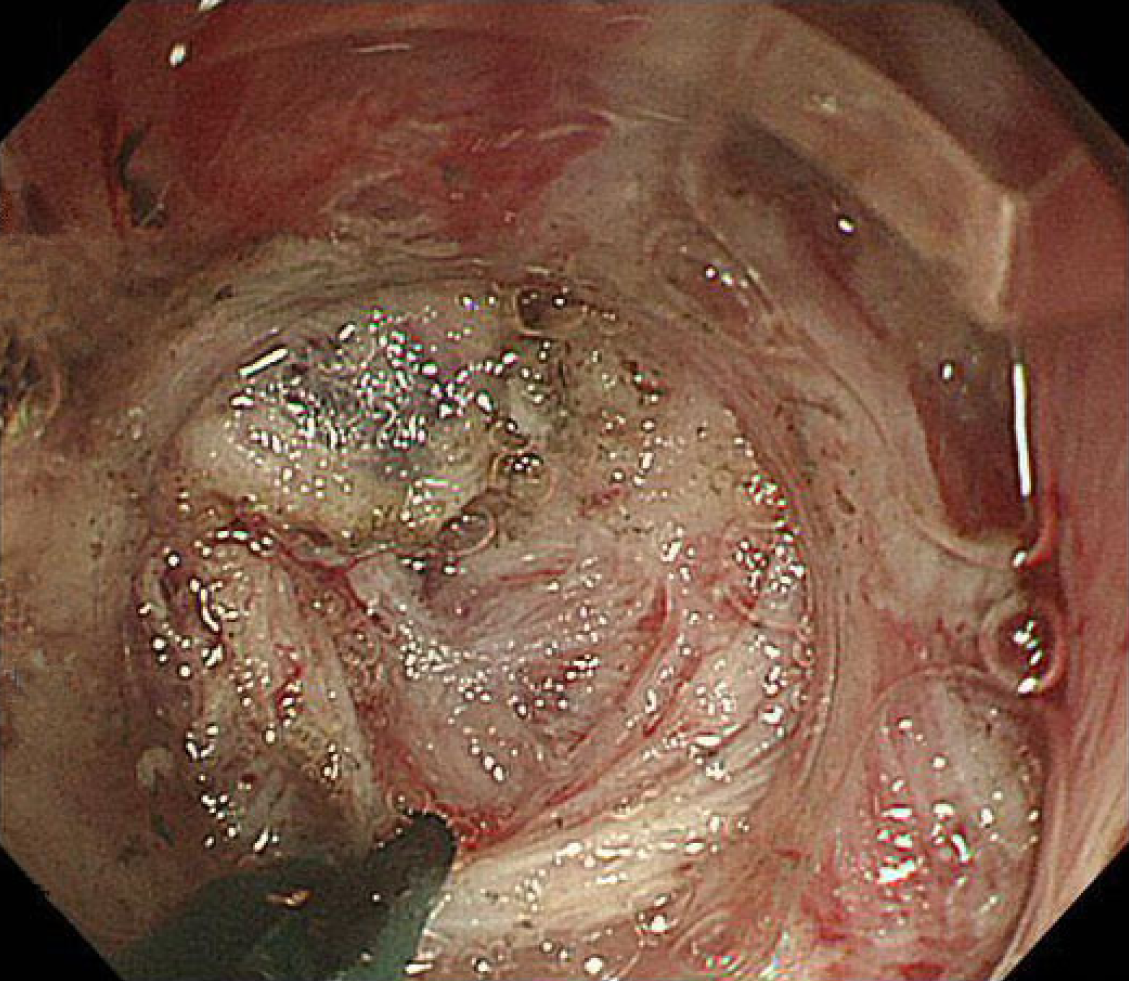
Figure 7 Severe submucosal fibrosis in the anal canal being managed with a scissor-type knife.
- Citation: Kaosombatwattana U, Yamamura T, Nakamura M, Hirooka Y, Goto H. Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection in special locations. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2019; 11(4): 262-270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v11/i4/262.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v11.i4.262