Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2020; 12(7): 332-349
Published online Jul 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.332
Published online Jul 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.332
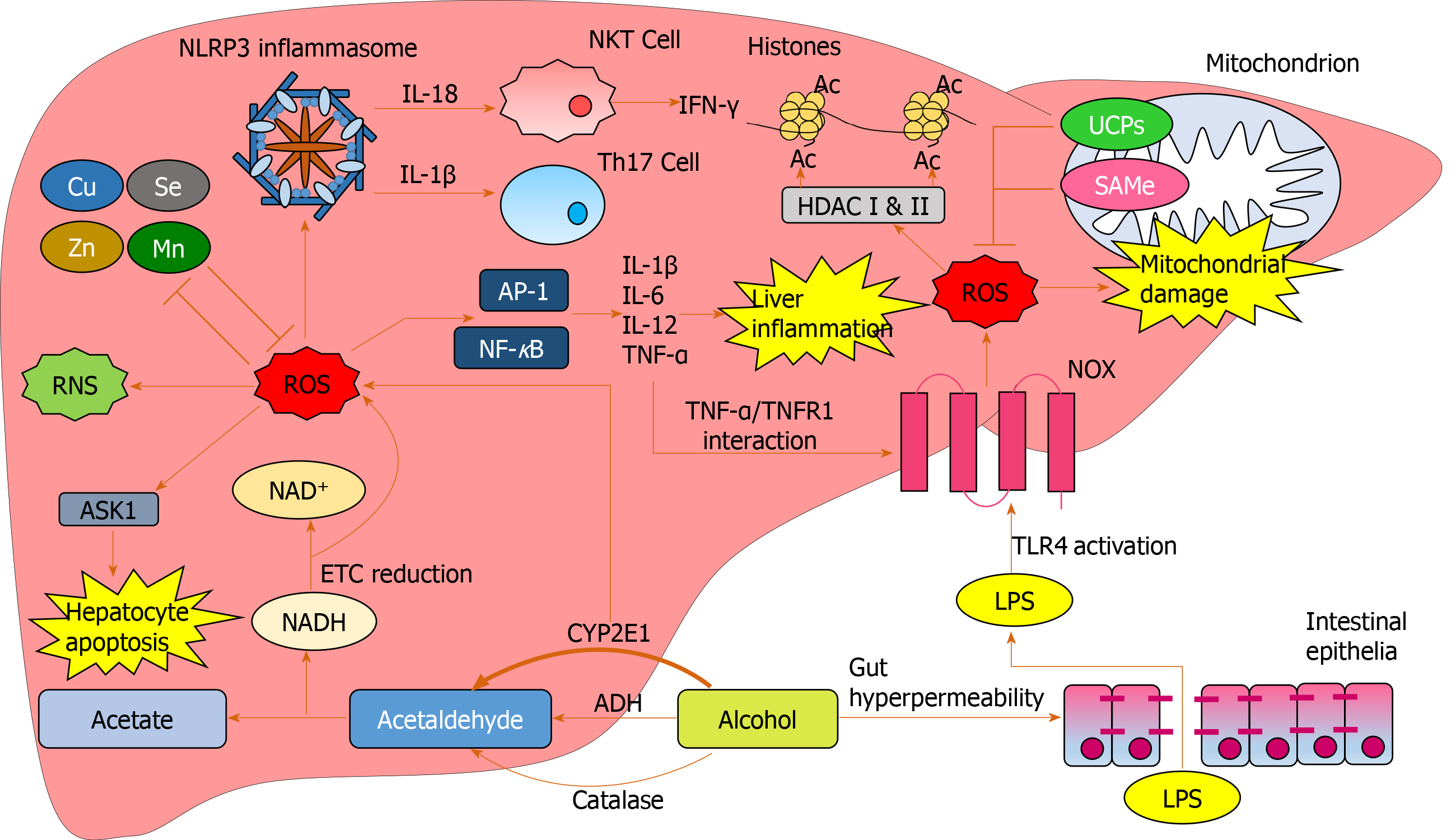
Figure 5 Reactive oxygen species-mediated oxidative damage in the liver.
Increased cytochrome p450 2E1-mediated alcohol breakdown and electron transport chain reduction results in overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Excess alcohol causes gut hyperpermeability resulting in tight junction disruption and an excess of lipopolysaccharide translocation from the gut to the liver. Lipopolysaccharide activates NADPH oxidase via toll-like receptor 4 activation resulting in further ROS production. Excess ROS produce RNS and reduce antioxidant cofactors such as Mn and Zn. ROS induce hepatocyte damage through activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3 inflammasomes are activated by ROS, inducing T-helper 17 generation and natural killer T cell-mediated interferon-γ production through interleukin expression. ROS upregulate transcription factors activator protein 1 and nuclear factor κB resulting in pro-inflammatory cytokine expression causing downstream liver inflammation. Tumour necrosis factor alpha further upregulates ROS through activating NADPH oxidase via tumour necrosis factor alpha receptor 1. ROS cause an array of functional and structural mitochondrial damage, which is initially impeded by uncoupling proteins and SAMe expression. ROS mediates epigenetic alterations through interacting with HDACs which mediate histone acetylation. Ac: Acetylation; ADH: Alcohol dehydrogenase; AP-1: Activator protein 1; ASK1: Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; Cu: Copper; CYP2E1: Cytochrome p450 2E1; ETC: Electron transport chain; HDAC: Histone deacetylases; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; Mn: Manganese; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB; NKT: Natural killer T-cell; NOX: NADPH oxidase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SAMe: S-adenosylmethionine; Se: Selenium; Th17: T-helper 17 cells; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; TNFR1: Tumour necrosis factor alpha receptor 1; UCP: Uncoupling protein; Zn: Zinc.
- Citation: Tan HK, Yates E, Lilly K, Dhanda AD. Oxidative stress in alcohol-related liver disease. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(7): 332-349
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i7/332.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.332