Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Hepatol. Oct 18, 2017; 9(29): 1158-1165
Published online Oct 18, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i29.1158
Published online Oct 18, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i29.1158
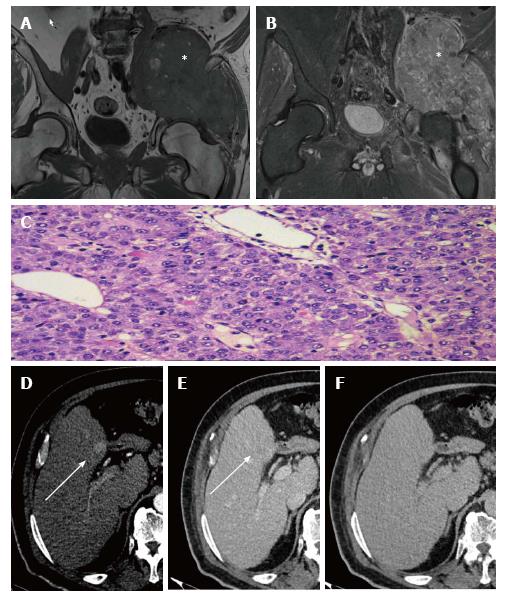
Figure 1 Clinical case 1.
A: Axial pelvic MRI T1-weighted imaging showing a large mass in the soft planes with lytic lesion on right iliac blade, markedly hypointense (asterisk); B: Coronal pelvic MRI T1-weighted imaging after administration of intravenous GD-DTPA contrast showing the mass with intense enhancement after administration of contrast (asterisk); C: Biopsy of pelvic mass (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 20 × magnification) showing broad metastatic presentation by well-differentiated HCC; D: Multiphasic liver MDCT showing hepatic focal lesion in segment IV (white arrow) with arterial phase enhancement; E: Multiphasic liver MDCT showing the lesion with slight washout in the portal phase (white arrow); F: Multiphasic liver MDCT showing the lesion as isodense with respect to the parenchyma in the equilibrium phase. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; MDCT: Multidetector computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
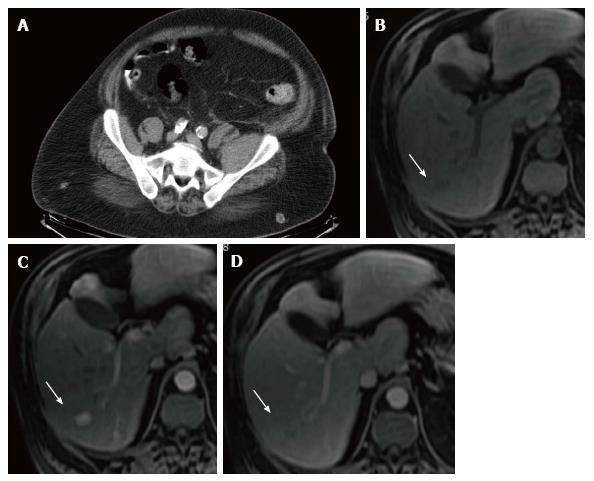
Figure 2 Clinical case 2.
A: MDCT showing asymmetry in the psoas-iliac muscles with enlargement of the left iliac muscle; B-D: Dynamic hepatic MRI performed after gadolinium administration. A focal liver lesion with wash in/wash out criteria of hepatocellular carcinoma was depicted in segment VI. MDCT: Multidetector computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
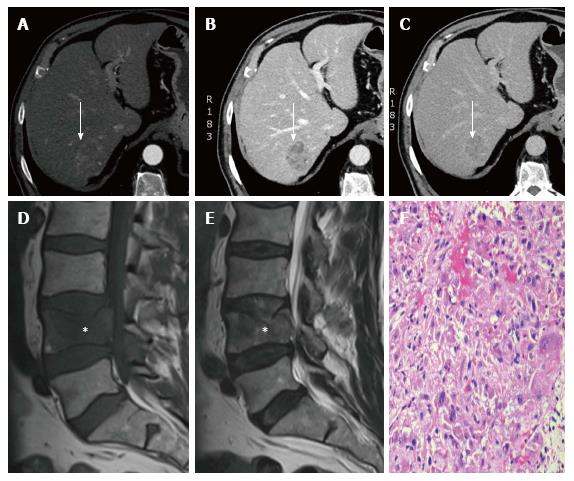
Figure 3 Clinical case 3.
A: Multiphasic liver MDCT showing a well-defined hepatic focal lesion in segment VII (white arrow) with heterogeneous enhancement in the arterial phase; B: Multiphasic liver MDCT showing the lesion with clear washout in the portal phase (white arrow); C: Multiphasic liver TCMD showing the lesion as markedly hypodense in the delayed phase; D, E: Lumbar MRI, sagittal T1-weighted and sagittal T2-weighted, showing pathological fracture of the fourth lumbar vertebrae with posterior wall displacement and vertebral channel invasion; F: Surgical specimen, a hemorrhagic biopsy, showing isolated metastatic groups constituted by hepatocytes after staining with hematoxylin-eosin (20 × magnification). MDCT: Multidetector computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Monteserin L, Mesa A, Fernandez-Garcia MS, Gadanon-Garcia A, Rodriguez M, Varela M. Bone metastases as initial presentation of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(29): 1158-1165
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i29/1158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i29.1158