Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Mar 18, 2016; 8(8): 401-410
Published online Mar 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i8.401
Published online Mar 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i8.401
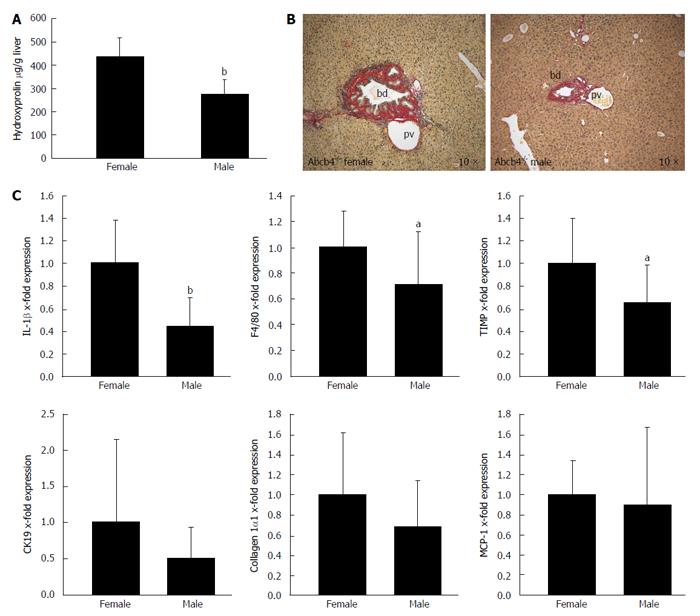
Figure 1 Gender differences in liver disease in ATP-binding cassette transporter b4-/- mice.
Gender differences in liver fibrosis and liver inflammation were assessed with hydroxyproline measurement, Sirius red staining and quantitative real-time PCR in male and female Abcb4-/- mice between 6 and 13 mo of age. A: The hepatic hydroxyproline content of liver homogenates (μg/g liver) was lower in male animals than in female animals ( = 13-15; bP < 0.001; Mann-Whitney U-test); B: Sirius-red staining illustrates the gender differences regarding fibrosis in Abcb4-/- mice. Images were taken from 9- to 10-mo-old animals (original magnification, 10 ×; bd: bile duct; pv: portal vein); C: Gene expression was assessed via quantitative real-time PCR and was normalised for 18 s as a housekeeping gene. Expressions were normalised against the means of female mice. The hepatic IL-1β and F4/80 mRNA expression levels as markers for hepatic inflammation were significantly lower in male Abcb4-/- mice than in female animals (n = 12-15; bP < 0.001; aP < 0.05; Mann-Whitney U-test). The mRNA expression levels of the profibrotic gene TIMP-1 were also significantly lower in male Abcb4-/- mice than in female Abcb4-/- mice (n = 13-15; aP < 0.05; Mann-Whitney U-test). PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; TIMP-1: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1; Abcb4-/-: ATP-binding cassette transporter b4-/-; IL-1: Interleukin-1; CK19: Cytokeratin 19; MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1.
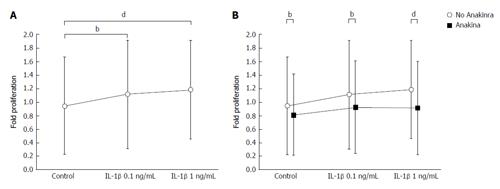
Figure 2 Interleukin-1β exerts proliferative effects in primary murine hepatic stellate cells, while Anakinra reduces hepatic stellate cell proliferation in vitro.
The effects of IL-1β± the IL-1 receptor antagonist Anakinra on the proliferation of murine HSCs were tested in vitro. A and B: The effects on HSC proliferation were examined using the BrdU assay after stimulation of cells with vehicle, and IL-1β at 0.1 and 1 ng/mL in the presence and absence of Anakinra (2.5 μg/mL), respectively (samples from n = 6 donor animals, bP < 0.01; dP < 0.001; ANOVA). HSC: Hepatic stellate cells; IL-1: Interleukin-1; ANOVA: Analyses of variance.
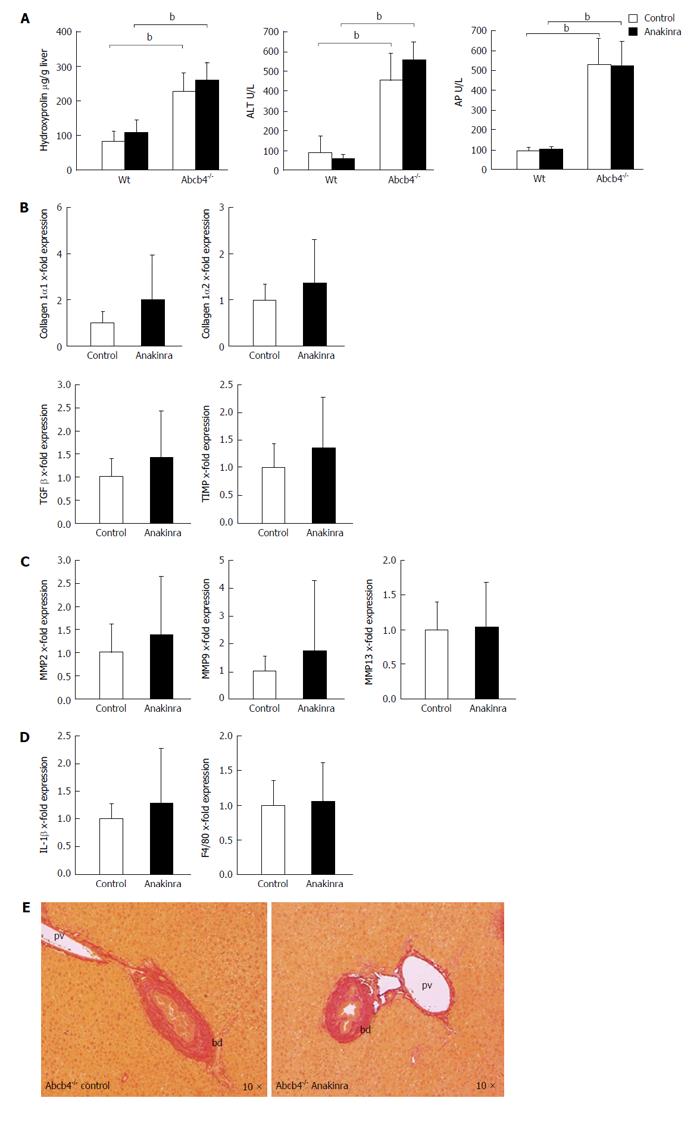
Figure 3 Anakinra does not reveal therapeutic effects on liver injury in ATP-binding cassette transporter b4-/- mice.
Eight-week-old female Abcb4-/- animals were treated with daily intraperitoneal injections of saline (control) as vehicle or Anakinra (1 mg/kg body-weight) for 4 wk. A: The levels of hepatic hydroxyproline, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and alkaline phosphatase (AP) were determined as described previously (n = 8-11, bP < 0.01; Mann-Whitney U-test). Gene expression was assessed via quantitative real-time PCR using glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as the housekeeping gene. Data were normalised against the means of the controls (saline); B: No alterations in the profibrotic genes were found [n = 10-11; not significant (n.s.); Mann-Whitney U-test]; C: No alterations in the antifibrotic genes were found (n = 10-11; n.s.; Mann-Whitney U-test); D: Anakinra treatment did not result in a significant change in the mRNA expression of the pro-inflammatory gene IL-1β or F4/80 (n = 10-11, n.s., Mann-Whitney U-test); E: The Sirius-red staining illustrates the absence of antifibrotic effects (original magnification 10 ×). bd: Bile duct; pv: Portal-vein; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; Abcb4-/-: ATP-binding cassette transporter b4-/-; IL: Interleukin; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
- Citation: Reiter FP, Wimmer R, Wottke L, Artmann R, Nagel JM, Carranza MO, Mayr D, Rust C, Fickert P, Trauner M, Gerbes AL, Hohenester S, Denk GU. Role of interleukin-1 and its antagonism of hepatic stellate cell proliferation and liver fibrosis in the Abcb4-/- mouse model. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(8): 401-410
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i8/401.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i8.401