Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2013; 5(4): 189-195
Published online Apr 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i4.189
Published online Apr 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i4.189
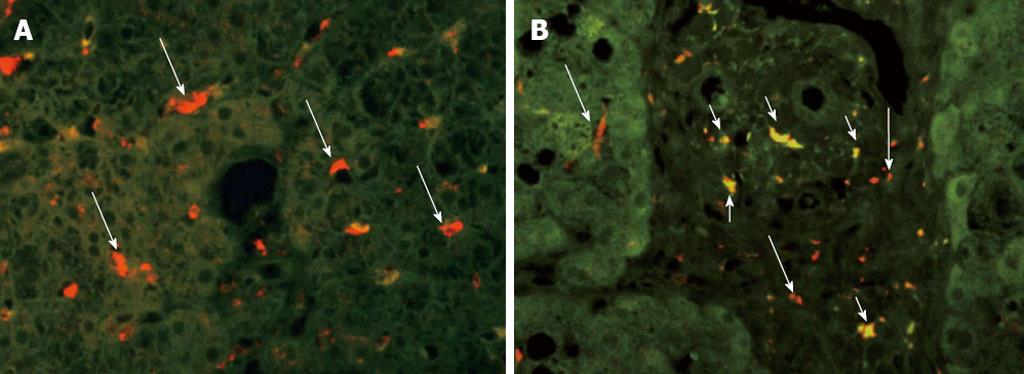
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining of liver biopsy specimens for CD68 and CD14 (×60).
Kupffer cells (CD68+) and lipopolysaccharide-sensitized Kupffer cells (CD14+) were compared between samples from conventional non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and NAFLD after pancreatoduodenectomy (PD). Long arrows represent CD68+ Kupffer cells; Short arrows represent CD68+ and CD14+ Kupffer cells. A: Conventional NAFLD; B: NAFLD after PD.
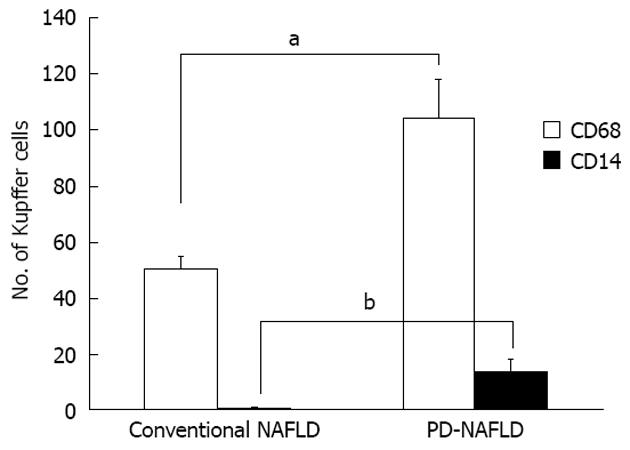
Figure 2 Number of cells positive for CD68 (a marker of Kupffer cells) and CD14 (a marker of lipopolysaccharide-sensitized Kupffer cells).
Conventional non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and NAFLD after pancreatoduodenectomy (PD). Conventional NAFLD and NAFLD after PD specimens showed mean cell counts of 50.6 ± 4.0 and 104.3 ± 13.3 CD68+ Kupffer cells per individual, respectively (aP < 0.05). Cell counts for CD14+ Kupffer cells were 0.6 ± 0.3 and 13.5 ± 4.2 cells per individual, respectively (bP < 0.001).
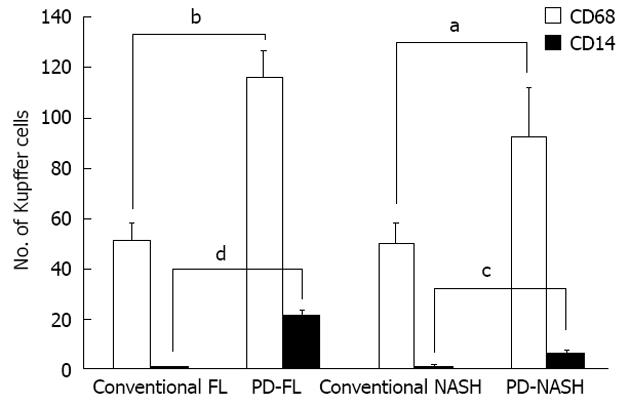
Figure 3 Number of cells positive for CD68 (a marker of Kupffer cells) and CD14 (a marker of lipopolysaccharide-sensitized Kupffer cells).
Conventional fatty liver and fatty liver after pancreatoduodenectomy (PD), in conventional non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and in NASH after PD. For simple steatosis, mean counts of CD68+ and CD14+ cells were 51.0 ± 6.8 and 0.4 ± 0.2 cells per individual in conventional fatty liver specimens, respectively, and 116.0 ± 10.7 and 20.5 ± 2.5 cells per individual, respectively, in fatty liver after PD specimens. This indicates more Kupffer cells and more lipopolysaccharide-sensitized Kupffer cells in simple fatty liver after PD specimens than in conventional simple fatty liver specimens (bP < 0.001; dP < 0.001). Regarding NASH, mean cell counts for CD68+ cells and CD14+ cells were 50.2 ± 7.4 and 0.8 ± 0.6 cells per individual, respectively, in conventional NASH specimens, and 92.5 ± 19.5 and 6.5 ± 0.5 cells per individual, respectively, in NASH after PD specimens. This showed that more Kupffer cells and more LPS-sensitized Kupffer cells were present in NASH after PD specimens than in conventional NASH specimens (aP < 0.05; cP < 0.05).
- Citation: Satoh D, Yagi T, Nagasaka T, Shinoura S, Umeda Y, Yoshida R, Utsumi M, Tanaka T, Sadamori H, Fujiwara T. CD14 upregulation as a distinct feature of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease after pancreatoduodenectomy. World J Hepatol 2013; 5(4): 189-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v5/i4/189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i4.189